Lecture
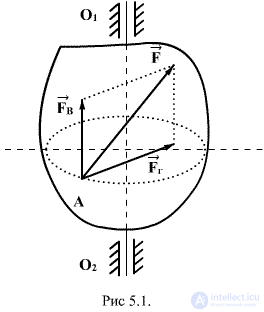
Consider the motion of a rigid body, having an axis of rotation 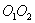 by arbitrary force
by arbitrary force 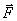 applied to the body at a certain point A, which can be decomposed into two components: vertical and horizontal (Figure 5.1). The vertical component can cause the body to move in the direction of the axis of rotation, so when considering the rotational motion, it can be excluded. The horizontal component
applied to the body at a certain point A, which can be decomposed into two components: vertical and horizontal (Figure 5.1). The vertical component can cause the body to move in the direction of the axis of rotation, so when considering the rotational motion, it can be excluded. The horizontal component 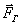 if it does not intersect with the axis
if it does not intersect with the axis 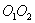 causes rotation of the body. The effect of this force depends on its numerical value and the distance of the line of action from the axis of rotation.
causes rotation of the body. The effect of this force depends on its numerical value and the distance of the line of action from the axis of rotation.
Comments
To leave a comment
Physical foundations of mechanics
Terms: Physical foundations of mechanics