Lecture
TBasic concepts
A trigger is an electronic device that can save one of two possible states.
Trigger inputs are divided into:
installation - to set the initial state of the trigger;
informational - to enter information;
Executive - to set the moment the trigger.
Triggers run on the front or on the slice
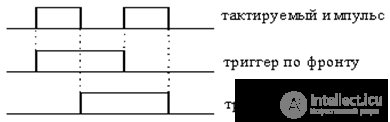
Designations of the impact of the executive impulse

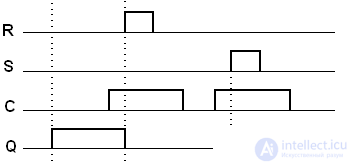
Asynchronous RS trigger
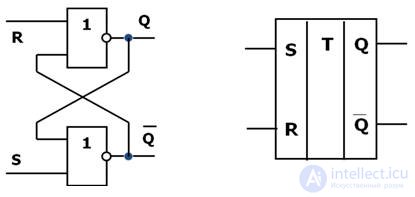
S - set - set to “1” Designation
R - reset - reset to "0"
RS - asynchronous trigger, i.e. the transition from one state to another is not related to clock signals.
RS-Trigger Truth Table

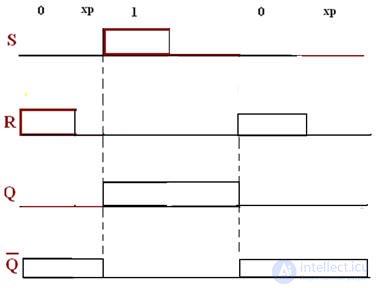
Timing diagrams for an asynchronous RS trigger
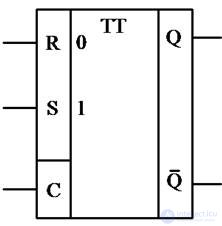
Synchronous RS trigger
Designation
Preliminary on Q = "1", change on "0" is possible, when on R and C "1", if necessary on Q = 1, then S = 1 and C = 1, etc.
Timing charts
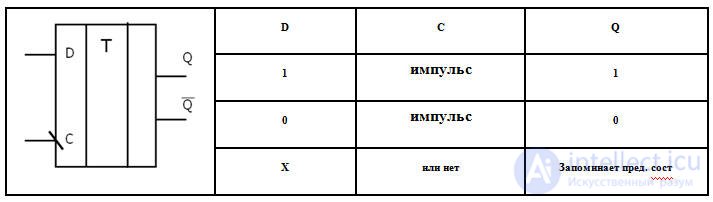
D-trigger
D-trigger - (delay delay data delay) - synchronous trigger, the output state of which coincides with the signal at its information input (D-input), which he had on the previous clock cycle synchronization
Symbol and the truth table of trigger triggering on the front
Timing charts
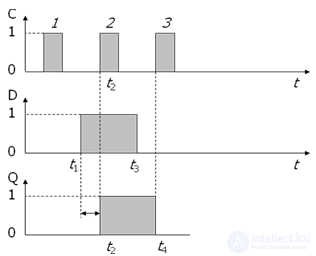
D-trigger delays for 1 clock cycle the information that exists at the input D.
On D - triggers, registers can be built to fill an 8-bit word with 8 D-triggers.
The information in the D-flip-flops is stored until the permission to change the information is received and then another number is written.
T- Triggers
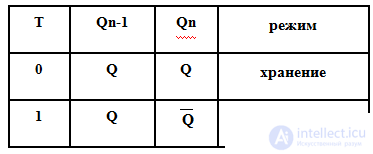
The counting trigger (T-trigger) changes its state whenever there is an active signal level at its only information input T.
Designation
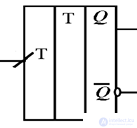
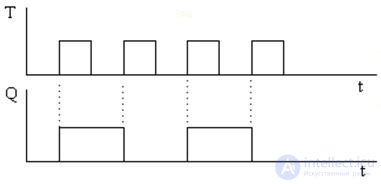
T-trigger - frequency divider by 2.
Timing charts
Truth table
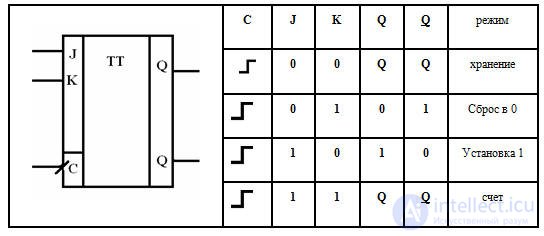
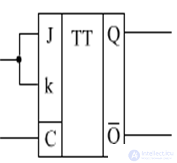
JK trigger (universal)
Notation Truth Table
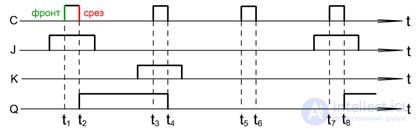
Timing charts

If we connect J and k, we get a T-trigger. T-trigger, when C = 1
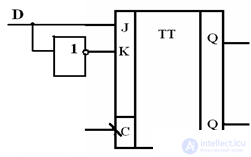
D-trigger on JK-trigger
Comments
To leave a comment
Electronics, Microelectronics, Element Base
Terms: Electronics, Microelectronics, Element Base