Lecture
Solving electronics problems involving diodes and rectifiers requires an understanding of the basic principles of diode operation and the features of rectifier circuits. Here is a general step-by-step approach to solving such problems:
Understand diode properties: Study the basic properties of diodes such as the direction of current flow, switching voltage, and forward and reverse saturation current. This will help you determine how the diode behaves under various conditions.
Analyze the circuit: Consider a given circuit with diodes and determine their mode of operation. When working with rectifiers, also consider the type of rectifier (half-wave, full-wave, etc.).
Use diode equations: Use diode equations such as the Shockley-Reed equation to determine the current through and voltage across the diodes.
Calculate characteristics: Calculate the characteristics of the circuit such as the current and voltage across each element, power, efficiency, etc.
Check and interpret the results: Check the obtained values for compliance with physical limitations and applicability. Interpret the results in light of the problem objectives and the circuit component specifications.
Account for Imperfections: Consider possible component imperfections such as diode voltage drops, wire resistance, etc.
Practice: Solve different types of diode and rectifier problems to improve your skills and understanding.
It is important to understand that electronics with diodes and rectifiers can be complex and solving problems requires an understanding of the basic principles and circuit analysis skills. Regular practice and study will help improve your skills in this area. If you have any difficulties, seek help from experienced professionals or teachers.
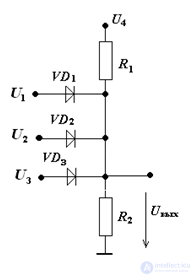
1. Given: circuit (Fig. 1), U1 = 10 B, U2 = 13 B, U3 = 15 В, U4 = 22 B, R1 = R2 =1 кОм.
Determine Uout
Solution:
When U1 = U2 = U3 = 0, the diodes are closed and the voltage
Uout = U4•R2 / (R1 + R2) = 11 V.
If we connect U1, Uout will not change - the diodes are closed.
When U2 is connected, the voltage Uout will be equal to 13 V (the diode in the branch with U2 will be open).
When U3 is connected, the diode in this branch will open, the voltage Uout will be equal to 15 V. The remaining diodes will be closed.
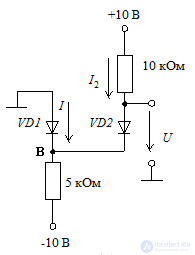
2. Considering the diodes to be ideal, find the current and voltage for the circuits shown in the diagram.
Solution:
For the circuit in the diagram, it is not obvious whether both diodes are in the conducting state. In this case, we will make an assumption about the diodes being in the conducting state, perform calculations and check the correctness of our assumption.
For the circuit in the diagram, from the assumption about the conductivity of both diodes, it follows that
UB = 0; U = 0
The current through the diode VD2 can be determined from the expression
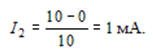
Writing the equation for the currents in node B, we have
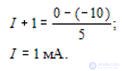
Thus, the diode VD1 is in the conducting state, as we initially assumed, and the final results
I = 1 mA and U = 0 V.
3. etermine the current in the circuit and the voltage on the diodes, the current-voltage characteristics of which are presented if Uin = 2.5 V, Rn = 25 Ohm
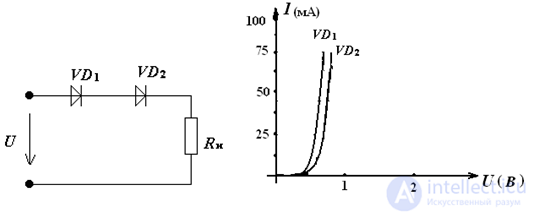
Solution:
we will construct the total I-V characteristic of the diodes and the "inverted" VA characteristic of a load resistor.
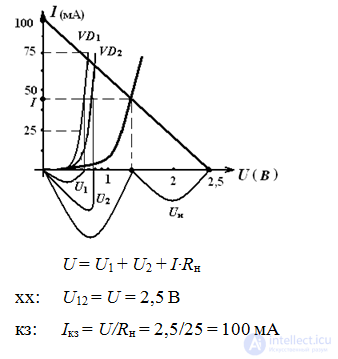
Answer: U1 = 0,6 В, U2 = 0,7 В, Uн = 1,2 В, I = 45 мА
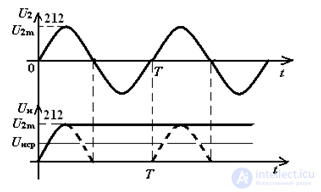
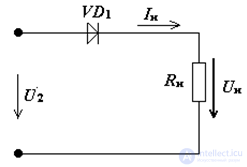
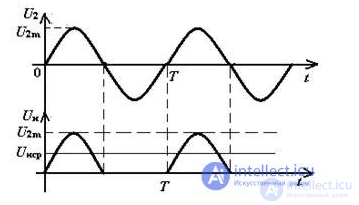
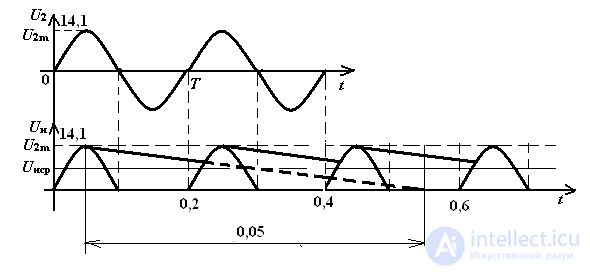
In Electronics, a diode is often used as a rectifier
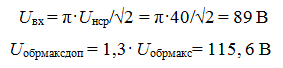
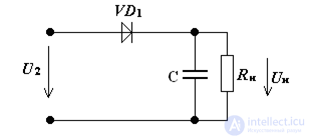
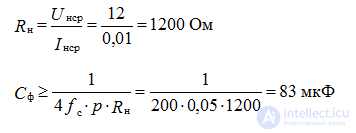
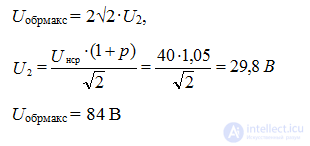
Comments
To leave a comment
Electronics, Microelectronics, Element Base
Terms: Electronics, Microelectronics, Element Base