Lecture
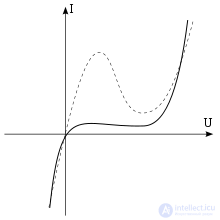
Volt-ampere characteristic of the inverted diode (continuous line), and tunnel diode (dotted)
An inverted diode is a semiconductor diode, the properties of which are significantly affected by the tunnel effect in the pn junction region. [1] In contrast to the tunnel diode, the current-voltage characteristic of the inverted diode has practically no “hump”, which is caused by a slightly lower concentration of impurities in the semiconductor than the tunnel diode. [2] Due to incomplete doping, it has a significant temperature dependence. [2] [3]
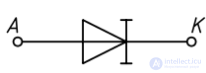
Designation on schemes. Anktoda to the anode - the direct (conductive) direction of the current. From the anode to the cathode - the opposite (locking) direction of the current. [3]
Inverted diode is used in high-frequency schemes for detecting weak signals, as well as in microwave signal mixers. [1] In this case, the maximum operating reverse voltage can lie in the range from 0.1 to 0.7 V.
Comments
To leave a comment
Electronics, Microelectronics, Element Base
Terms: Electronics, Microelectronics, Element Base