Emitter Repeater (Current Amplifier)
An amplifier in which the transistor is connected in a circuit with a common collector is called a current amplifier.
The main resistor, which is removed from the output voltage, is included in the emitter circuit. The collector is connected to a common point with the ground of the amplifier, since Rвн of the Ek power supply is small.
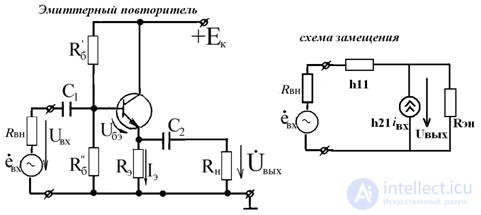
Main settings:
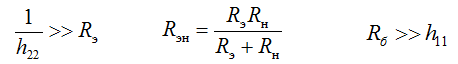
Gain
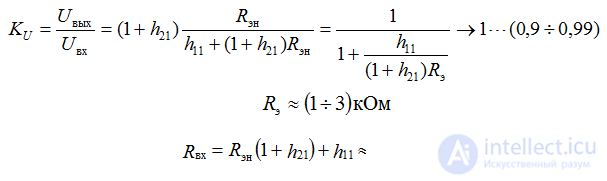
Output impedance
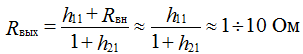
Current gain
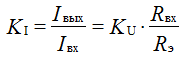
Comparing the current amplifier with the voltage amplifier we can draw the following conclusions:
input and output voltages are in the same phase;
input impedance (1 + h21) times greater than in the UNIVERSITY;
output impedance (1 + h21) times less than in the UN

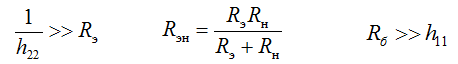
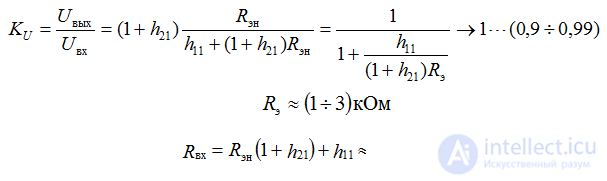
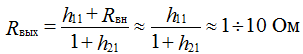
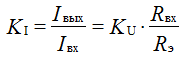
Comments
To leave a comment
Electronics, Microelectronics, Element Base
Terms: Electronics, Microelectronics, Element Base