Lecture
IGBT - power transistors
Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor is a new class of power devices combining the advantages of bipolar and field-effect transistors.
Current control in such devices is carried out by the voltage supplied to the gate.
The IGBT was first developed at the General Elektrik research laboratory and launched on the market by Motorola.
IGBT is a bipolar pnp transistor controlled from a low-voltage MOSFET with an induced channel through a high-voltage n-channel.
IGBT designation
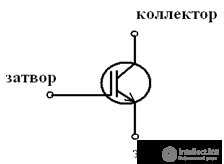
Principle of operation
The process of switching on the IGBT can be divided into two stages: after applying a positive voltage between the gate and the source, the field-effect transistor opens (an n-channel is formed between the source and the drain). The motion of charges from region n to region p leads to the discovery of a bipolar transistor and the occurrence of a current from the emitter to the collector. Thus, the field effect transistor controls the operation of the bipolar transistor.
• The power of the signal applied to the gate of such a device is significantly lower than in bipolar transistors, which allows the use of less powerful control circuits.
• Due to high speed, these devices allow to increase the operating frequency of power systems and thereby improve the efficiency and overall performance, i.e. solve problems of energy and resource saving
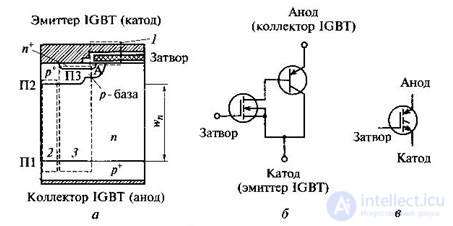
Fig. Structure (a), simplified equivalent circuit (b) and symbol (c) IGBT
Comments
To leave a comment
Electronics, Microelectronics, Element Base
Terms: Electronics, Microelectronics, Element Base