Lecture
Controlled rectifiers
Rectifiers that combine AC voltage rectification with rectified voltage control are called control.
The main element of the controlled rectifier is a thyristor.
Voltage control is reduced to time control of the thyristor unlocking.
Classification of controlled rectifiers
• single-phase half-wave
• single-phase bridge: with a full number of thyristors and with an incomplete number, i.e. 2 thyristors, 2 diodes
• three-phase with output from the midpoint of the transformer and bridge.
Full-wave controlled rectifier
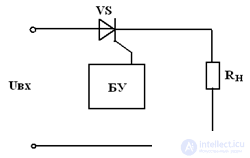
CU - control unit The control current in the positive half-period e (t) opens the 1st pn junction and turns on the thyristor. In the negative half-period, the opening of the 1st pn junction does not lead to the opening of the 3rd pn junction, because diffusing carriers do not reach it, since they have time to almost completely recombine.
The average and effective value of the rectified current (voltage) can be regulated over a wide range by changing the phase of the supply of the control current.
The presented circuit incorporates a control circuit, which greatly complicates it, since a sufficiently accurate synchronization of the control current frequency with the frequency of the rectified voltage is required.
Timing charts
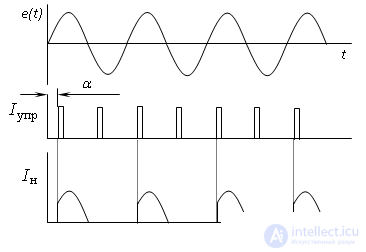
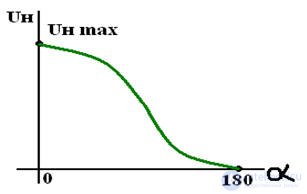
Medium voltage regulation at the rectifier output for a half-wave rectifier
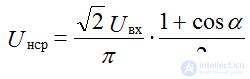
voltage can be adjusted within
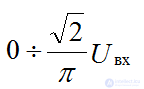
when changing the angle of regulation
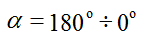
for full-wave rectifier
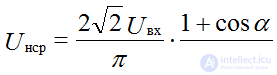
control characteristic of a controlled rectifier
Comments
To leave a comment
Electronics, Microelectronics, Element Base
Terms: Electronics, Microelectronics, Element Base