Lecture
Diodes
Semiconductor diodes are called semiconductor devices with one pn junction and two terminals.
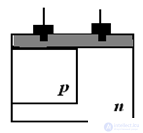
Classification of semiconductor diodes and their symbols
Notation system
1 - source material:
germanium - the letter D or the number 1;
silicon - the letter K or the number 2;
Gallium - the letter A or the number 3;
indium - letter I or number 4
2 - device type:
A - microwave diodes
B - Varicaps
D - rectifier and pulse
And - tunnel diodes
L - emitting diodes (LEDs)
H - diode thyristors (dinistors)
C - Zener diodes
C - rectifier columns and blocks
3 - numbers indicate some basic parameters of the diode (power) (for zener diodes, the fourth element characterizes the stabilization voltage),
4 - letters and / or numbers indicating the serial number of the design
5 - the letter defining the classification by parameters.
Planar Rectifier
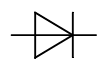
Zener diode
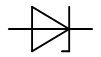
Tunnel
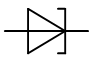
Varicaps
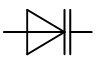
LEDs
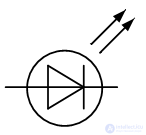
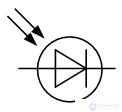
Photodiodes
Dotted
Low Power
Rectifier
microwave - diodes
Volt-ampere characteristic (VAC) of a real diode
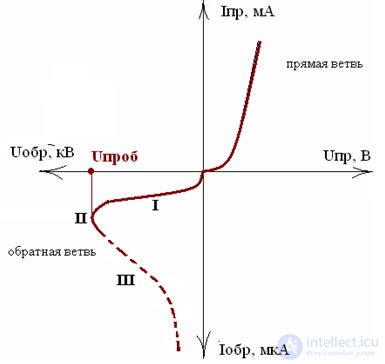
For technical purposes, the current – voltage characteristics are used in linear coordinates.
At high voltages of reverse bias in the diode, breakdown can develop - a sharp increase in the reverse current with a slight change in voltage. During avalanche breakdown, electrons in an electric field of the pn junction acquire enough energy to ionize their own semiconductor atoms. This leads to avalanche multiplication of charge carriers, a sharp increase in their local concentration and, accordingly, current. After the development of avalanche breakdown, the diode does not lose its efficiency. This type of breakdown is used in semiconductor zener diodes, the properties of which will be discussed below.
Thermal breakdown develops as a result of local heating of the pn junction region, and as a result, an increase in the carrier concentration. Thermal breakdown is irreversible, after which the diode loses its properties and performance.
Volt-ampere characteristic of an ideal diode
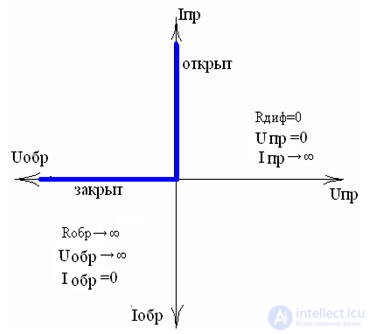
The main parameters of the diode
system parameters are given in reference books. This system allows you to choose the right diode for use in specific conditions.
Ipr - direct current passing in the forward direction,
Upr - direct voltage,
Ipr max - the maximum available direct current,
Ubr max - the maximum available reverse voltage,
Ivr - reverse current diode,
Vr - reverse diode voltage - (DC voltage applied to the diode in the opposite direction).
Example: KD204A Ipr = 2 A, Uobrmax = 400 V,
Upr = 1.4 V, Ibr = 150 μA
Diodes, as nonlinear elements, are characterized
static rc = u / i
differential (dynamic) Rdif = ∆U / ∆I
Comments
To leave a comment
Electronics, Microelectronics, Element Base
Terms: Electronics, Microelectronics, Element Base