Operational amplifiers
1. Determine the voltage at the output of the adder fig: if
U1 = U2 = U3 = 1B, R1 = 1 kΩ, R2 = 2 kΩ, R3 = 4 kΩ, R4 = 12 kΩ
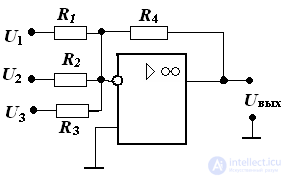
Pic
Decision:
Uout = - (Kos1U1 + Kos2U2 + Kos3U3) Kos = - R4 / Ri
Uout = - (12U1 + 6U2 + 3U3) = - 1 • 21 = - 21 V
2. What is the output voltage of the inverting amplifier in Fig. 3, if
R1 = 500 Ohm, R2 = 5000 Ohm, Uin = 0.2 V
Decision:
Kos = - R2 / R1 = 10
Uout = Uin • Kos = 2 V
3. Non-inverting amplifier based on OU, works from a source with voltage Uin = 150 mV.
Resistance of resistors R1 = 20 kΩ, R2 = 200 kΩ.
Determine the output voltage of the amplifier Uout and the gain KU.
Decision:
KU = 1 + R2 / R1 = 11
Uout = Uin • Kos = 1,650 V
4. Calculation of the inverting amplifier.
It is given: Uin = 80 mV, Uout = 4 V, Rn = 10 kΩ, OU type 14DUD7
MW = √2 is the frequency distortion coefficient in the high-frequency region. Calculate the values of R1, ROS, R2 in the inverting amplifier.
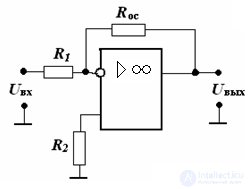
Decision:
Determination of resistance resistors.
Draw the amplifier circuit
Determine the gain of the amplifier
KOS = (Uвых / Uвх) = 4 • 103/80 = 50
Find ROS from the relation
Rin> = 10 • Rn = 10 • 10 = 100 kΩ
Defined by R1:
R1 = ROS / KOS = 100/50 = 2 kΩ
Calculate the value of R2. This resistor is installed in the amplifier to align the input currents.
R2 = R1Ros / (R1 + Ros) = (2 • 100/102) ~ 2 kΩ
5. The calculation of the adder on the OS.
Given:
Er1 = - 2 V, Er2 = 3 V, Er3 = 1 V, Rg1 = 0.5 kOhm, Rg2 = 0, Rr3 = 1 kOhm.
Input gains:
Kos1 = 5, Kos2 = 2, Kos3 = 10, Rn = 2 kΩ. OU type 153UD1.
Calculate the resistance values in the adder and determine Uout
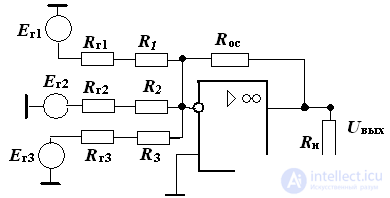
Decision:
Choose ROS> = 10 • Rn, ROS = 10 • 2 = 20 kOhm
From the expressions for the gain factors in the adder:
Kos1 = ROS / (R1 + Rg1) = 5
Kos2 = ROS / (R2 + R2) = 2
Kos3 = Roc / (R3 + Rg3) = 10
Find
R1 = 3.5 kΩ, R2 = 10 kΩ, R3 = 1 kΩ
Determine Rн, required to align the input currents
Rn = Roc / (R1 + Rg1) / R2 / (R3 + Rg3) = 1.3 kΩ
Find the output voltage of the adder:
Uout = Er1 • Kos1 + Er2 • Kos2 + Er3 • Kos3 = 10 - 6 - 10 = - 6 V
Determine the current output circuit:
Iout = Ioc + In = Uout / Ros + Uout / Rn = 3.3 mA
This value of Iout does not exceed the value of the output current of the OU type 153UD1, equal to 20 mA.
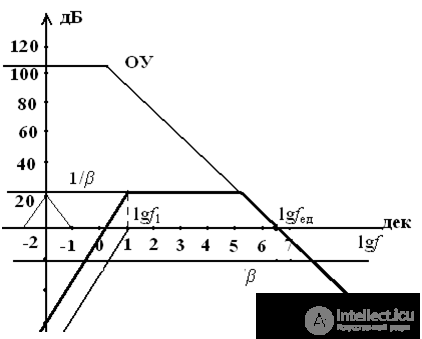
6. Build LAFC amplifier, determine the gain, fn and fv, if
R1 = 20 kΩ, R2 = 10 kΩ, R3 = 100 kΩ K = 200000, fed = 3 MHz C1 = 0.7 μF
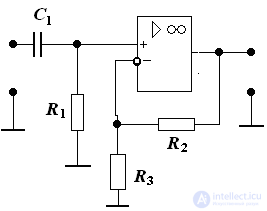
Solution: operational amplifier
Kdb = 20 lgK = 20 • 5.3 = 106 dB
lgfed = 6.5 dec
Input circuit:
τ1 = R1 • C1 = 20000 • 0.7 • 10-6 = 0.014 s
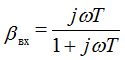
The frequency of the breakpoint LAFC of the input circuit:
f1 = 1 / 2πТ1 = 11.4 Hz lgf1 = lg11.4 = 1.06 dec
Feedback link:
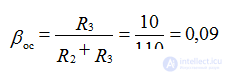
20lg βos = 20 lg0.09 = - 20.8 dB
Since the amplifier uses “deep” negative feedback, Kos = 1 / β = 11
construction LAFC:




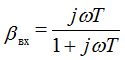
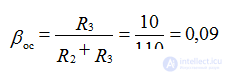

Comments
To leave a comment
Electronics, Microelectronics, Element Base
Terms: Electronics, Microelectronics, Element Base