Lecture
Field effect transistors (PT)
A field-effect transistor is a semiconductor device whose amplifying properties are due to the flow of main charge carriers flowing through a conductive channel controlled by an electric field.
The current is determined by the movement of the main carriers of only one charge.
Field effect transistor electrodes
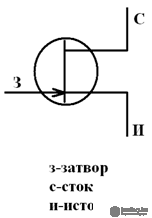
A source is an electrode through which charge carriers flow into a conducting channel;
Drain - an electrode through which charge carriers flow from a conductive channel;
A channel is a region in a semiconductor where the flow of the main charges is regulated
A gate is an electrode to which an electrical signal is applied to control the value of current through a conductive channel.
Types of field effect transistors
1. Field effect transistor with control pn-junction
n - channel
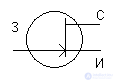
p - channel
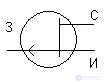
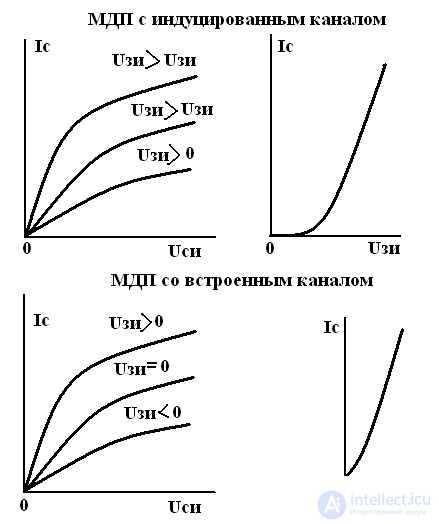
2. MDP (MOS) transistors
With integrated channel
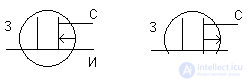
With induced channel
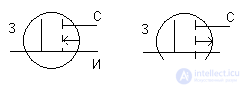
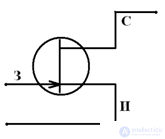
Field Transistor Circuits
With a common source
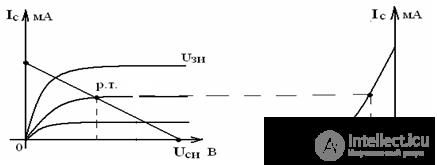
Voltage-current characteristics of a field-effect transistor
with control pn junction
The main parameters of the PT
• slope stopping speed (SZH)
with Usi = const
S = (∆ Ic / ∆ Uzi)
• Differential drain (channel) resistance at the saturation point
at Us = const
Rc = (∆Uci / ∆ Ic)
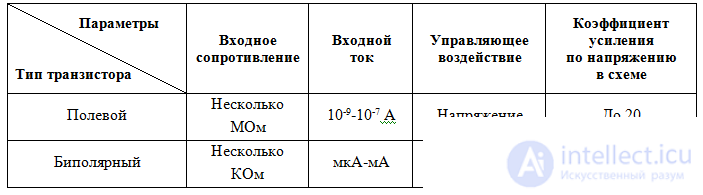
Parameters of field and bipolar transistors
Options
Comments
To leave a comment
Electronics, Microelectronics, Element Base
Terms: Electronics, Microelectronics, Element Base