You may not yet know what is included in the concept of a database, but the fact that you constantly use them is absolutely accurate. Every time you search for something in a search engine, you use a database. When you enter your username and password to enter any service, they are compared with the values that are stored in the database of this service.
Despite the fact that we constantly use databases, for many it remains unclear what it really is. And this is partly due to the fact that the same terms related to databases are used by people to define completely different things.
Let's understand the terms and concepts of databases:
A database is a collection of information stored in some orderly way. You can compare the database with the cabinet in which the documents are stored. In other words, a database is a data warehouse. The databases themselves would not be of interest if there were no database management systems (DBMS).
A database management system is a collection of language and software tools that provides access to data, allows them to be created, changed and deleted, ensures data security, etc. In general, a DBMS is a system that allows you to create databases and manipulate information from them. And it provides this access to the DBMS data through a special language - SQL.
SQL is a structured query language whose main task is to provide a simple way to read and write information to a database.
So, the simplest scheme of working with a database looks like this:

By the nature of the use of the DBMS is divided into single-user (designed to create and use databases on a personal computer) and multi-user (designed to work with a single database of several computers connected to local networks). In general, the division according to the nature of use can be represented by the following scheme:
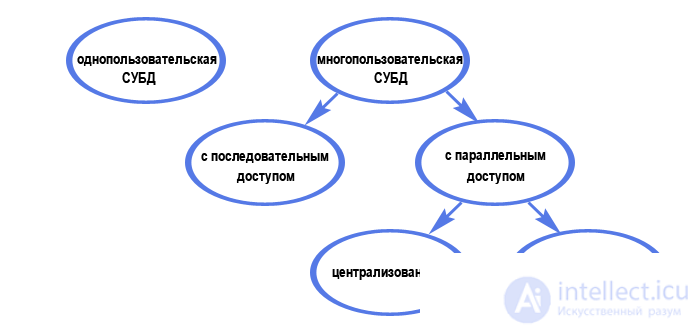
Without going further into details, we note that today the number of used DBMS is in the tens. The most well-known single-user DBMSs are Microsoft Visual FoxPro and Access, multi-user ones are MS SQL Server, Oracle and MySQL.
In these lessons we will use MySQL. First, it is free, and secondly, it is the de facto standard among Russian host providers. But more about that later, but for now let's get back to the basics. The database definition states that this information is ordered in some way. And how are they actually ordered? This will be discussed in the next lesson.

 Without going further into details, we note that today the number of used DBMS is in the tens. The most well-known single-user DBMSs are Microsoft Visual FoxPro and Access, multi-user ones are MS SQL Server, Oracle and MySQL.
Without going further into details, we note that today the number of used DBMS is in the tens. The most well-known single-user DBMSs are Microsoft Visual FoxPro and Access, multi-user ones are MS SQL Server, Oracle and MySQL.
Comments
To leave a comment
Databases, knowledge and data warehousing. Big data, DBMS and SQL and noSQL
Terms: Databases, knowledge and data warehousing. Big data, DBMS and SQL and noSQL