Lecture
The use of SQL JOINS syntax when working with Databases is quite popular, without them any serious SQL query can do. I thought the article about SQL joins Ligaya Turmelle 'is a great example for new programmers. The use of Venn diagrams to explain their work is quite natural and clear. However, commenting on her article, I found that her Venn diagrams did not quite match the SQL join syntax.
I decided to clarify this with examples below. Suppose we have the following two tables. Table A on the left, and Table B on the right. We place in each of them 4 records (lines).
id name id name - ---- - ---- 1 Pirate 1 Rutabaga 2 Monkey 2 Pirate 3 Ninja 3 Darth Vader 4 Spaghetti 4 Ninja
Let's join these tables using SQL join over the "name" column in several ways and see how it will look on Venn diagrams.
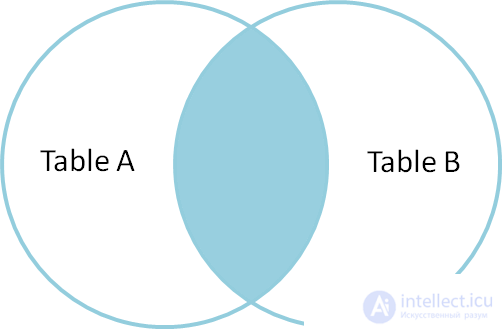
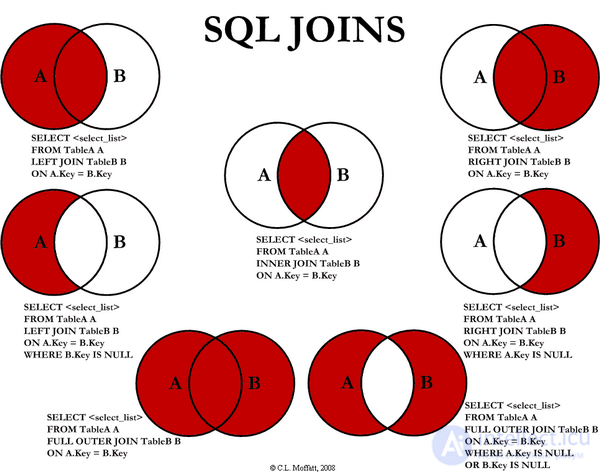
SELECT * FROM TableA INNER JOIN TableB ON TableA.name = TableB.name id name id name - ---- - ---- 1 Pirate 2 Pirate 3 Ninja 4 Ninja Inner join (inner join) produces a selection of only rows that are in both table A and table B.
|
 |
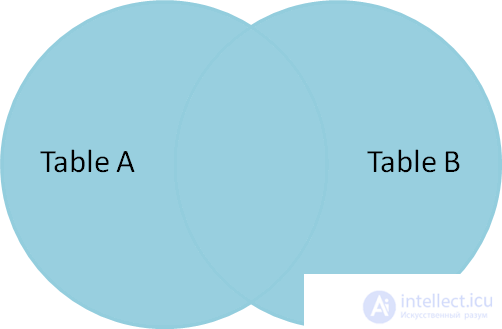
SELECT * FROM TableA FULL OUTER JOIN TableB ON TableA.name = TableB.name id name id name - ---- - ---- 1 Pirate 2 Pirate 2 Monkey null null 3 Ninja 4 Ninja 4 Spaghetti null null null null 1 Rutabaga null null 3 Darth Vader Full outer join (full outer join - union) selects all rows from table A and B, and with all possible variations. If there is no record from either side, the missing record will contain an empty string (null values). |
 |
|
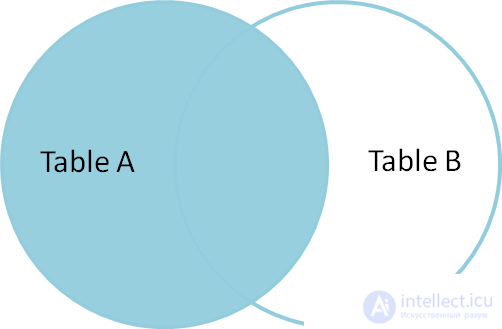
SELECT * FROM TableA LEFT OUTER JOIN TableB ON TableA.name = TableB.name id name id name - ---- - ---- 1 Pirate 2 Pirate 2 Monkey null null 3 Ninja 4 Ninja 4 Spaghetti null null Left outer join (left outer join) makes a selection of all rows of table A with the available rows of table B. If rows of table B are not found, then an empty result (null) is substituted.
|
 |
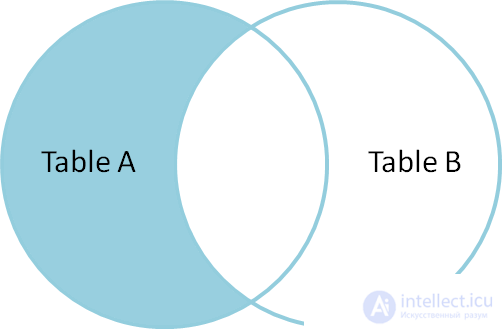
SELECT * FROM TableA LEFT OUTER JOIN TableB ON TableA.name = TableB.name WHERE TableB.id IS null id name id name - ---- - ---- 2 Monkey null null 4 Spaghetti null null To select rows from Table A that are not in Table B, we perform the same LEFT OUTER JOIN, then exclude lines that are filled in Table B. That is, select all records of Table A that are not in Table C, we also execute jeft outer join, but we exclude empty records of table B. |
 |
SELECT * FROM TableA FULL OUTER JOIN TableB ON TableA.name = TableB.name WHERE TableA.id IS null OR TableB.id IS null id name id name - ---- - ---- 2 Monkey null null 4 Spaghetti null null null null 1 Rutabaga null null 3 Darth Vader To select unique records of tables A and B, we perform a FULL OUTER JOIN, and then exclude records that belong to both table A and table B using the WHERE clause. |
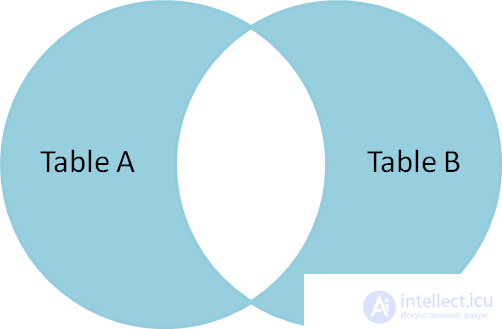 |
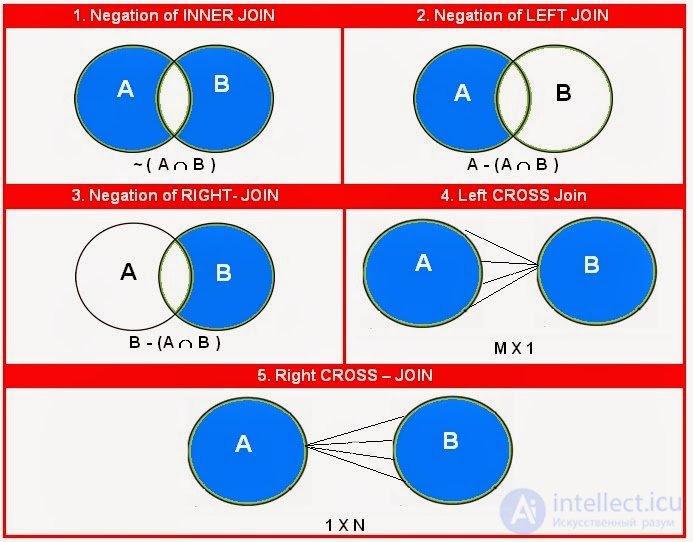
There is also a Cartesian connection or CROSS JOIN , which, as far as I can tell, cannot be expressed in the Venn diagram:
SELECT * FROM TableA CROSS JOIN TableB
It connects "all with all", as a result we get 4 * 4 = 16 lines, which is much more than in the original tables. This is very dangerous for tables containing a large amount of data. That is, ALL possible combinations are obtained, including all Null-null lines.
fetching data from the top of the matrix (mysql select unique pairs)
SELECT fg.uid AS u1, fg2.uid as u2
FROM
data fg
, data fg2
where
fg.uid! = fg2.uid and fg.uid <= fg2.uid
Category: / Mine Blog / PHP (LAMP)
Let's look at an example. We have two tables: users and departments.
U) users D) departments
id name d_id id name
-- ---- ---- -- ----
1 Владимир 1 1 Сейлз
2 Антон 2 2 Поддержка
3 Александр 6 3 Финансы
4 Борис 2 4 Логистика
5 Юрий 4
SELECT u.id, u.name, d.name AS d_name
FROM users u
INNER JOIN departments d ON u.d_id = d.id
The query returns merged data that intersects by the condition specified in INNER JOIN ON <..>.
In our case, the condition . < must match .
As a result, there are no :
- user Alexander (department 6 - does not exist)
- Finance department (no users)
id name d_name
-- -------- ---------
1 Владимир Сейлз
2 Антон Поддержка
4 Борис Поддержка
3 Юрий Логистика
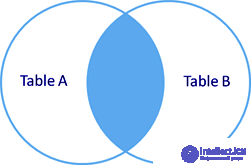
rice Inner join
Internal join INNER JOIN (synonym JOIN, the keyword INNER can be omitted).
Only matching data from the joined tables is selected. To obtain data that is not suitable for the condition, you must use
external union - OUTER JOIN.
Such a join will return data from both tables matching one of the conditions.
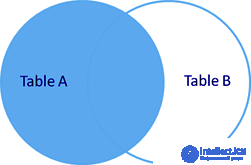
rice Left join
There are two types of external join OUTER JOIN - LEFT OUTER JOIN and RIGHT OUTER JOIN.
They work the same way, the difference is that LEFT - indicates that the "external" table will be located on the left (in our example it is the users table).
The keyword OUTER can be omitted. The LEFT JOIN record is identical to the LEFT OUTER JOIN.
SELECT u.id, u.name, d.name AS d_name
FROM users u
LEFT OUTER JOIN departments d ON u.d_id = d.id
We get a complete list of users and related departments.
id name d_name
-- -------- ---------
1 Владимир Сейлз
2 Антон Поддержка
3 Александр NULL
4 Борис Поддержка
5 Юрий Логистика
Adding a condition
WHERE d.id IS NULL
Only 3 # Alexander will remain in the sample, since he has not assigned a department.
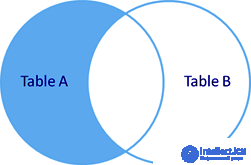
rice Left outer join with field filtering
RIGHT OUTER JOIN will return a full list of departments (right table) and associated users.
SELECT u.id, u.name, d.name AS d_name
FROM users u
RIGHT OUTER JOIN departments d ON u.d_id = d.id
id name d_name
-- -------- ---------
1 Владимир Сейлз
2 Антон Поддержка
4 Борис Поддержка
NULL NULL Финансы
5 Юрий Логистика
Additionally, you can filter the data by checking for NULL.
SELECT d.id, d.name
FROM users u
RIGHT OUTER JOIN departments d ON u.d_id = d.id
WHERE u.id IS NULL
In our example, specifying WHERE u.id IS null, we will select the departments in which users are not listed. (3 # Finance)
All examples you can test here:
SQLFiddle
Self joins
So-called loopback sampling (and not at all closure). We need if we need to choose more than one.
values from a table for several conditions.
We have: a set of filters for information whose values are stored in the filts_data table.
Necessary: filter products by date, article number and available filters
CREATE TABLE filts_data
(
id serial NOT NULL,
fid integer NOT NULL, -- product_item.id
value integer NOT NULL, -- значение фильтра filts_items.id
pid integer NOT NULL -- фильтр filts.id
)
There is a table of conditional goods product_item
CREATE TABLE product_item
(
id serial NOT NULL,
section_id integer,
date timestamp,
art text,
title text
)
Example: select records added after 01/17/2009 and with filters set 3 = 14 and 4 = 15 and 6 = 19.
Logic will tell us such a request (non-working):
SELECT p1.title FROM products_item p1
INNER JOIN filts_data p2 ON p1.id = p2.fid
WHERE p1.date > '17.01.2009'
AND (p2.pid = 3 AND p2.value = 14)
AND (p2.pid = 4 AND p2.value = 15)
AND (p2.pid = 6 AND p2.value = 19)
This query will not find the elements in the table.
Rewrite the query using join to:
SELECT p1.* FROM product_item p1
INNER JOIN filts_data p2 ON p1.id = p2.fid
INNER JOIN filts_data p3 ON p1.id = p3.fid
INNER JOIN filts_data p4 ON p1.id = p4.fid
WHERE p1.date > '17.01.2009'
AND (p2.pid = 3 AND p2.value = 14)
AND (p3.pid = 4 AND p3.value = 15)
AND (p4.pid = 6 AND p4.value = 19)
In this case, we get records for which all three filters are set and the date of addition later than the specified one.
fashin
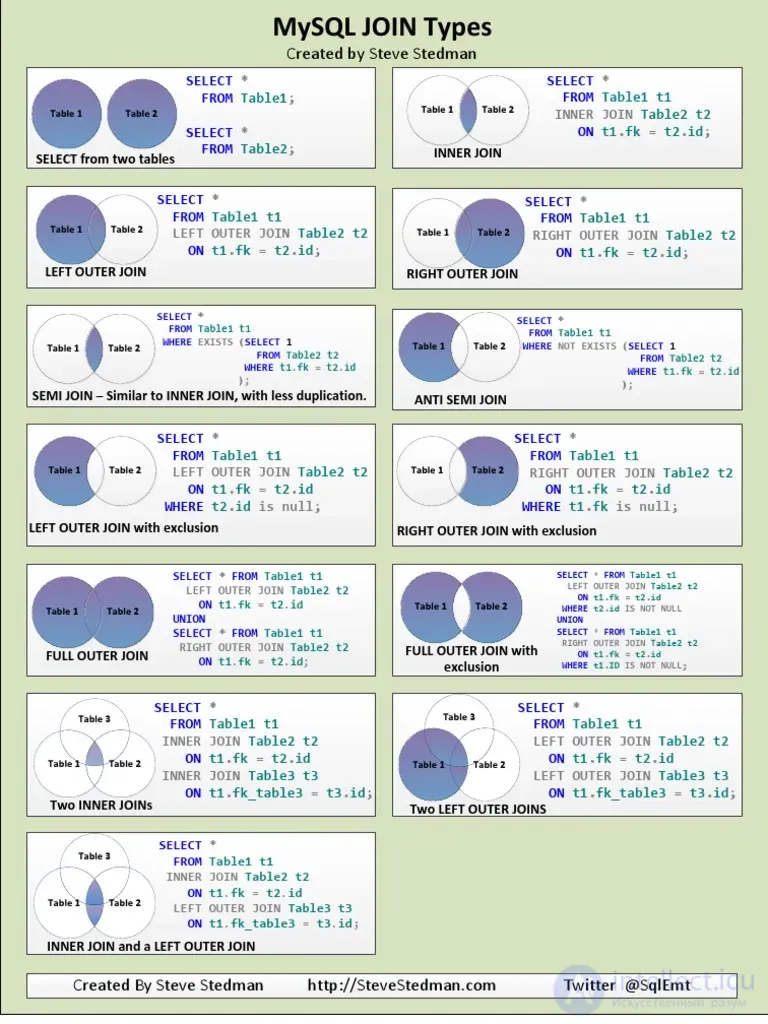
JOIN : return rows when there is at least one match in both tables.
LEFT JOIN : all rows from the left table are returned, even if there are no matches in the table on the right
RIGHT JOIN : all rows from the right table are returned, even if there are no matches in the table on the left
FULL JOIN : return rows when there is a match in one of the tables.
There is also a CROSS JOIN - the Cartesian product of two tables, but it is used very rarely.
Comments
To leave a comment
Databases, knowledge and data warehousing. Big data, DBMS and SQL and noSQL
Terms: Databases, knowledge and data warehousing. Big data, DBMS and SQL and noSQL