Lecture
Start
Some historians believe that the beginning of robotics can be considered the time of ancient Greece. Around 270 BC. er Greek engineer Ktesibus created musical organs and clepsydra (water clock), in which there were moving figures.
Other historians believe that robotics began with the advent of mechanical dolls. Around 1770, Pierre Jacquet-Drew, a Swiss watchmaker and inventor of a wristwatch, made three wonderful dolls. One of the dolls he created “knew how” to write, the other - to play the organ, and the third - to draw pictures. These amazing mechanical dolls, designed to entertain the royal family, showed their “art” with levers, gears and springs.
Later, in 1898, Nikola Tesla built a remotely operated "diving" boat. For 1898, this was no small achievement, and the boat was displayed at Madison Square Garden. Tesla planned to create a boat capable of autonomous navigation, but due to lack of funding, the research had to be stopped.
The word “robot” first appeared in 1921 in the play “R.U.R.” (Rossum Universal Robots), written by the famous Czech playwright Karel Čapek. Robot in Czech means "worker". The play described the mechanical servants - "robots". When these robots were endowed with human emotions, they rebelled against their masters and destroyed them.
Historically, you can find many examples of robots - objects of inanimate nature, copying the human appearance and some human "functions". Such "human-like" robots are called androids.
Thanks to Karel Chapek, robots became the protagonists of many science fiction books and films. The development of the theme of "robots" led to the emergence of their many varieties. Along with the old-fashioned "iron" people, cyborg appeared - creatures partly of "human", and partly - of "machine" origin, and androids - robots having a human appearance.
Many saw the “real” robot for the first time at the 1939 world fair. Westinghouse Electric has created the Electro robot - a moving person. Electro had motors and a drive system that allowed him to “move” with his legs, arms and mouth. The robot did not “know how” to do any useful work - it was simply shown on the stage in the company of the “mechanical” dog Sparko.
Why create robots?
The use of robots turned out to be absolutely necessary for many industries, primarily because the cost of the “labor” of the robot turned out to be significantly lower than the cost of the same operation performed by a human worker. Moreover, it is enough to program the robot once, and it will perform the required action with an accuracy that exceeds the work of any skilled worker. On the other hand, a person is able to perform various tasks and, from this point of view, is much more flexible. Robots, as a rule, are designed to perform a single operation. For example, a robot designed for welding is unlikely to be able to “teach” to count the parts in the bunker.
The existing most advanced industrial robots will very soon turn into "dinosaurs." Today's “infant” stage of the evolution of robots is ending, new, much more universal robots are emerging, incorporating all the new qualities of human intelligence.
The personal computer has already revolutionized society, but the “personal” robot has not yet appeared. The reason is obvious - the creation of such a robot is much more complicated. In addition to a developed intellect, he must be well “able” to orient and move in space and carry out the necessary manipulations to achieve his goal.
Application of robots
It is clear that it is much easier to create a "home" robot that performs some one job. For example, today there are small mobile robots that can “independently” mow the grass on the lawn. These robots are solar powered and do not require programming. A wire is buried along the perimeter of the lawn; the robot feels this wire and remains inside the perimeter, without going beyond it.
Creating a useful personal robot is very difficult. Generally speaking, this problem is beyond the scope of this book, and, perhaps, of any modern book on robotics. It is reasonable to ask - what is the purpose of this book in general then? I hope that by reading this book and building several models of robots, you will gain the necessary experience and be able to contribute to the development of robotics.
The ability to create a new one is not the necessary belonging exclusively to a university degree. Robots are created not only by scientists in the walls of universities and industrial companies. Experimenting and "playing" with robots, you can learn many useful things: the work of artificial intelligence, the principles of neural networks, competent goal setting, the tasks of "navigation", the work of sensors and actuators, etc. Initial acquaintance with the fundamentals of robotics can grow into serious study. And from this point of view, “amateur” robotics contributes, sometimes offering elegant and original solutions that are superior to “professional” ones.
As the saying goes: "Measure seven times - cut once." Before you start building a robot, ask yourself the question: “For what purpose is it intended? What will he do and how? ”My dream is to create a small robot that would automatically serve the cat toilet.
This book contains the necessary information about the electrical circuits, "sensitive" elements, systems that provide the movement, neural networks and microcontrollers that may be required when creating a robot. But before we get started, let's look at some known and possible future applications of robots. Currently, the most advanced robots are created by NASA engineers and military experts. It is not difficult to guess that NASA uses robots to explore space and organize remote transmission of information. On the other hand, the military are trying to use robots for military purposes.
Research
NASA regularly sends unmanned automatic stations in cases where sending astronaut explorers is not possible. The main reason for this decision is simple - the economy. It is much cheaper to send a “non-returnable” robot into space than a human. The astronaut needs special conditions: breathing air, food, warmth and sufficient living space. And, frankly speaking, the astronaut's clear desire is to survive on a space expedition and return to Earth, so to speak, “while alive”.
The space station flies through the solar system and with the help of its “electronic” eyes transmits to the Earth impressive pictures of the planets and their satellites. The automatic station Viking searched for signs of life on Mars and transmitted photographs of the Martian landscape to the earth. NASA is developing all-terrain vehicles for the study of planets, space probes, special all-terrain vehicles on spider legs and underwater all-terrain vehicles. At present, NASA has the world's best remote control robots programs created by the Space Administration and Technology Agency (OSAT).
NASA claims that in 2004, more than 50 percent of the actions outside the spacecraft will be through remote control systems. More detailed explanations of the principles of remote control and surveillance can be found in Chapter 9.
The robotized space stations launched from the Earth made it possible to observe stunning imaginations of the neighboring planets of the solar system. In this age of shrinking budgets, research robots will be able to make the best use of taxpayer funds. It is clear that automatic robotic stations are much cheaper than habitable ones. Here is one example. Martian Pathfinder (Pathfinder) is just a new generation of low-cost space research devices.
Martian Pathfinder (Sojourner)Martian "tracker" consists of a descent module and the rover. It was launched from Earth in December 1996 using the McDonnel Douglas Delta II launch vehicle and began its journey to Mars. The device reached the surface of Mars on July 4, 1997.
The Pathfinder did not enter the circular orbit of Mars; instead, it flew into the Martian atmosphere at a speed of 27 thousand km / h, or 7.6 km / s. To prevent the apparatus from burning in the atmosphere, there were provided: a heat-resistant outer shell, parachutes, brake missiles and air bags. Although the landing was softened by pillows, the acceleration on impact reached 40 g.
The Pathfinder landed in the Ares Vallis area. The landing site is located at the mouth of the ancient channel of the Martian "channel" - a place where many different rocks can be in the access zone of the rover. Presumably these rocks were washed away from the Martian mountains at the time when there were water currents on Mars. After landing, the descent vehicle opened (see Fig. 1.1) and the automatic rover “released”.
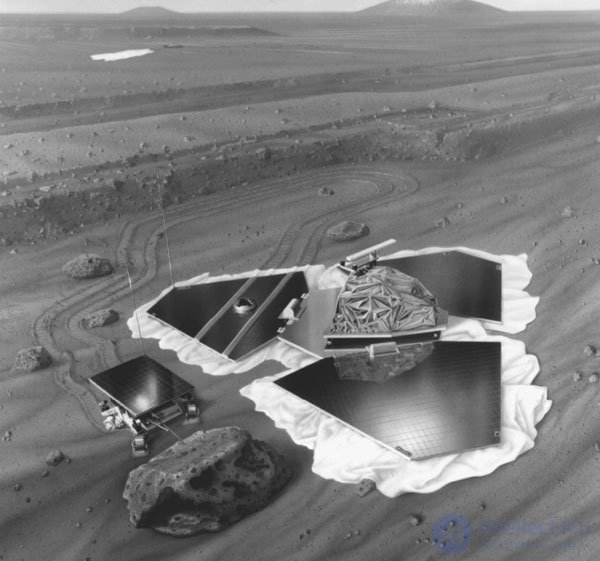

Fig. 1.1. Martian tracker. NASA Photos
The all-terrain vehicle itself, or the rover, delivered by the Ranger was named "Sojourner". The fellow traveler is a new class of small robotic research complexes, sometimes called micro-all-terrain vehicles. With a weight of only 10.5 kg, it has dimensions: 280 mm in height, 630 mm in length and 480 mm in width. The rover is equipped with a unique six-wheel mobility system (Rocher-Bogie - mountain wagon), developed by Jet Propulsion Laboratories (JPL) in the late 80s. The main source of energy for the rover is a solar panel that contains more than 200 cells with an output of approximately 16 watts of battery power. The fellow traveler began a study of the surface of Mars in July 1997. Before that, this robot was known as Rocky IV. Improvement of this micro-all-terrain robot has gone through several stages, reflected in prototypes from Rocky I to Rocky IV.
Both the descent vehicle and the rover itself are equipped with a stereo video surveillance system. To determine the composition of rocks, the rover has an X-ray spectrometer for analyzing alpha particles. The descent vehicle had equipment for conducting atmospheric and meteorological observations, and also played the role of a repeater for transmitting data and pictures from the rover to Earth.
The purpose of the expedition. The rover "fellow traveler" in itself was the goal of the experiment. The data obtained from the rover, confirmed that the use of such "micro", is economically justified and useful. In addition to the tasks described above, the expedition pursued the following objectives:
• Photographing near and far vicinity of the surface of Mars
• Analysis of soil movement
• Determination of the navigation numbering position on Mars
• Measurement of Martian Ground
• Record device movement data
• Determination of thermal conditions of the rover
• Monitoring the operation of the optical system of the device
• Determining the quality of VHF communication
• soil wash analysis
• soil adhesion analysis
• Evaluation of alpha-particle X-ray spectrometer performance
• Evaluation of the operation of the device deployment of the spectrometer
• Photographing a descent vehicle
• Damage assessment
The control of the actions of the “fellow traveler” was carried out remotely by commands from the Earth. The operator asked the movement of the rover on the basis of visual data obtained from the rover and from the descent vehicle. Due to the fact that the delay time of the reactions of the rover with respect to the commands from the Earth ranged from 6 to 41 minutes depending on the mutual positions of Mars and Earth, to prevent fatal actions, such as falling from a cliff, the device had onboard intelligence.
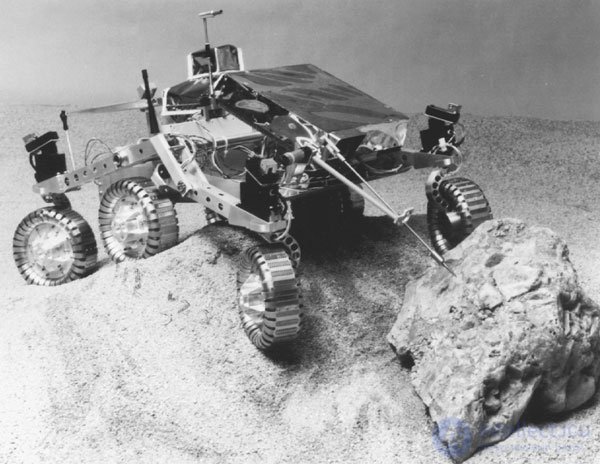

Fig. 1.2. Mars rover "fellow traveler". NASA Photos
NASA continues to research in the field of creating robotic "microbrothers". For further studies of Mars, it is planned to create “intellectual” all-terrain vehicles capable of orientation, overcoming obstacles and making other decisions. Such robotic systems make the most of taxpayer money.
The last “micro-all-terrain vehicle”, intended for the next Martian expedition, will again look for signs of life there. On August 7, 1996, NASA issued a statement that it hopes to find fossil microscopic traces of life on Mars. This information has sparked interest in the search for life on Mars.
Use of robots in the industry
Robots are indispensable in many industries. For example, welding robots are widely used in the manufacture of automobiles. Other robots equipped with paint sprayers are engaged in painting parts. In the electronic industry, robots are used to solder microscopic conductors to semiconductor chips (spot welding). Other robots, which are called "take and place", are engaged in the placement of integrated circuits on printed circuit boards. This process is called PCB “stuffing”.
These specialized robots do the same high-precision work day after day. For a person, such work is boring and tedious - from monotony comes fatigue, which causes mistakes. Production errors reduce labor productivity, which in turn leads to an increase in production costs. For the end consumer, the rising cost of production is reflected in higher retail prices. At the same time, it is clear that in a competitive environment the company with the best price-performance ratio will be the most successful.
Robots are ideal for monotonous, monotonous work. The speed of their work is higher, they are cheaper than workers - people and are not subject to fatigue. This is one of the reasons for the low price of products. Robots can improve product quality and expand the boundaries of profitability (competitiveness) of the enterprise.
Design and modeling
Robots were capable of performing not only cyclic operations. Manufacturing companies make extensive use of computer-aided design CAD (computer aided manufacturing CAM) and computer numerical control CNC (CNC) systems to create various projects, manufacture components and control the assembly process. These technologies allow an engineer to design a device or part using CAD and quickly get a prototype using computer-controlled equipment. The computer provides support at all stages - from design to production.
Hazardous production
In some hazardous industries involving risks to health or life, people can be successfully replaced by robots (see Figure 1.3). For example, take the task of bomb disposal. Many sapper teams make extensive use of robots. As a rule, such robots have the form of small armored tanks and are controlled remotely by operators using video cameras located in the front of the robot (remote video monitoring system). Robotic arms are capable of seizing a suspicious object and placing it in an explosion-proof container for subsequent explosion or neutralization.
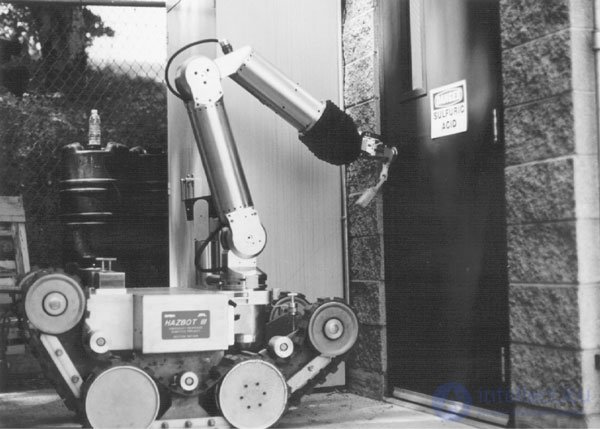
Fig. 1.3. Robot rescuer. NASA Photos
Such robots allow you to clear the area from toxic waste. They are able to function in conditions of strong chemical or radiation contamination of the environment. Robots are able to “work” in conditions where a quick death awaits an unprotected person. The nuclear industry was the first to start developing and using robotic automatic manipulators for working with radioactive materials. These manipulators allowed specialists to perform operations in the radioactive zone, while being in clean and safe premises.
Maintenance and repair
Operational robots were specially created for movements inside pipelines, collectors and air ducts in order to monitor their condition and possible repair. The operator monitors the process with the help of a video camera attached to the robot. When damage is detected, the operator can effectively and quickly use the robot for minor repairs.
Fire robots
Many homes have fire extinguishers, but what about a fire robot? Such a robot can detect a fire in any part of the room, move there and extinguish the fire.
The idea of a fire robot was so popular that for several years now there have been competitions between the designers of such devices. These competitions are sponsored by Trinity College, the Connecticut Robotics Society and some corporations. As a rule, the fire robot is activated by an alarm signal received by the fire detection system. During the competition, the robot needs to pave the way in a special “virtual” room, get to the place of fire and extinguish the fire.
Robots in medicine
Роботов, используемых в медицине, можно отнести к трем категориям. Роботы первой категории используются в диагностике. Весной 1992 года компания Neuromedical Systems Inc. of Suffern, NY, выпустила на рынок изделие под названием Papnet. Система Papnet представляет собой устройство, использующее принцип нейронных сетей, которое помогает специалистам цитологам диагностировать рак шейки матки более точно и, что важнее, с меньшими затратами.
До появления Papnet анализы шеечных мазков производились вручную. Лаборант рассматривал каждую пробу под микроскопом, стараясь обнаружить отдельные раковые клетки в большой массе здоровых клеток. Понятно, что наличие дефектных клеток служит индикатором рака или предракового состояния, однако во многих случаях лаборант не замечал эти клетки из-за утомления или недостаточного внимания.
В течение двадцати лет ученые пытались автоматизировать процесс обнаружения раковых клеток, используя стандартные алгоритмы выбора решающего правила. Данный подход не оправдал себя, поскольку классические алгоритмы не работали в силу большого количества и сложности параметров, которые позволяют отличить пораженные клетки от здоровых.
Papnet использует усовершенствованную систему распознавания образов, построенную на принципе нейронных сетей, и отбирает 128 наиболее «подозрительных» клеток исследуемого мазка для дальнейшей оценки специалистом-цитологом.
Использование Papnet показало очень хорошие результаты, позволяя определить дефектные клетки в 97 % случаев. Поскольку для каждой пробы лаборанту теперь приходится проверять всего 128 клеток, а не 200 или даже 500 тысяч, то влияние фактора утомления неизмеримо снизилось. Более того, время, необходимое для тестирования пробы, сократилось от пяти до десяти раз. Соответственно, процент ошибок для нового метода не превышает 3 % по сравнению с 30–50 % при ручной проверке.
Роботы второй категории представляют собой дистанционно управляемые устройства, используемые в хирургии. Такие устройства позволяют хирургу проводить операции, находясь вне непосредственного контакта с пациентом. Подобные роботы имеют уникальную систему тактильной обратной связи, позволяя хирургу непосредственно «чувствовать» органы и ткани, которые оперируются инструментами робота. Такие роботы обеспечивают хирургу возможность проводить операции практически в любой точке земного шара, не выходя, так сказать, из собственного кабинета.
К третьей категории относятся роботы, использующие принципы виртуальной реальности и изменения кратности манипулирования. При использовании такого робота движения хирурга преобразуются в движения хирургического инструмента определенным образом. Допустим, хирург переместил руку на 10 см. Компьютерная система, управляющая роботом, может преобразовать это перемещение в движение скальпеля на 1 см или даже на 1 мм. Таким образом, хирург может производить микроскопические операции, которые ранее были невозможны.
Нанотехнологии
Nanotechnologies are the research and creation of objects of molecular or even atomic size. At present, it has become possible to create electronic or mechanical components based on individual atoms. Such tiny components can be used to create bacteria-sized devices. IBM has already managed to create transistors, conductors, lever mechanisms and transmissions at the atomic level.
Каким же образом можно манипулировать отдельными атомами? Для этой цели Гердом Биннигом и Хайнрихом Ререром был сконструирован специальный сканирующий туннельный микроскоп (STM), который позволил осуществить исключительно точное позиционирование области, имеющей атомарные размеры. В 1990 году инженерам IBM с помощью подобного микроскопа удалось написать название компании «IBM» на никелевой подложке с помощью всего 35 атомов ксенона. Фотография этой пластинки со словом «IBM», написанным атомами, стала мировой сенсацией и обошла страницы многих журналов и газет. Этим было положено начало эры нанотехнологий, и ее постоянное совершенствование находит все новые применения в производстве, исследованиях и медицине.
Медицинские нанороботыНанотехнологии могут оказать неоценимую помощь в создании нанороботов, т. е. роботов, имеющих микроскопические размеры. Представим себе робота, имеющего столь малые размеры, что он может быть непосредственно помещен в кровоток пациента. Перемещаясь по кровотоку, робот может достигнуть области сердца и начать удалять там холестериновые бляшки, восстанавливая полноценную циркуляцию крови. Другие роботы смогут отыскивать раковые опухоли и удалять в них все пораженные клетки. Некоторые пациенты, которые сейчас считаются неоперабельными, смогут быть излечены с применением нанотехнологий.
Другая надежда, возлагаемая на нанороботов, – борьба с процессами старения в организме. Интересные возможности откроются с появлением нанороботов, имеющих размеры вирусов, способных внедряться непосредственно в клетки и переводящих внутриклеточные «часы» на начало «отсчета».
Развитие нанотехнологий оказало существенное влияние на всю технологию производства роботов: как микроскопических, так и обычных, макроскопических, спектр возможностей которых неизмеримо расширился, начиная от задач уборки помещений и кончая автоматизированным производством продукции. С нанотехнологиями связаны большие надежды на производство новых высококачественных материалов и изделий с относительно низкими затратами.
Военные роботы
Если государство оказывается вовлеченным в военный конфликт, то для достижения скорейшей победы при минимальных потерях использование роботов имеет исключительно важное значение, особенно в современных условиях. Например, использование беспилотной авиации позволяет вести наблюдение за расположением и перемещением сил противника.
Израильские военные нашли для беспилотной авиации остроумное применение. Беспилотный самолет был сконструирован так, чтобы представлять собой удобную цель для радаров. После запуска на вражескую территорию он, естественно, обнаруживался радарами, а израильтяне в свою очередь засекали местоположения этих радаров. После их уничтожения реактивные истребители могли беспрепятственно пролететь через эту территорию.
«Умные» бомбы и крылатые ракеты представляют собой другой пример «интеллектуализованных» вооружений. Мне очень нравятся три закона робототехники, придуманные Айзеком Азимовым, которые гласят, что робот никогда не может намеренно причинить вред человеку, но реальность с ее военными роботами именно такова.
Война роботов
В нашей мирной жизни устраиваются специальные соревнования – «войны роботов». Участники подобных соревнований создают специальных радиоуправляемых роботов разных весовых категорий и устраивают поединки один на один для определения лучшего «бойца».
Арена для подобных соревнований представляет собой ровную асфальтовую площадку размерами примерно 9 на 17 м, для безопасности болельщиков огороженную стенами высотой примерно 2,5 м. Более подробную информацию можно найти на сайтеhttp://www.robotwars.com.
The battles of robots turned out to be so popular that they generated a lot of varieties of such competitions. Some links can be found here:
Battlebots http://www.battlebots.com
Robotica http://tic.discovery.com/fansites/robotica/robotica.html
MicroBot Wars http://microbw.hypermart.net
Civilian applications of unmanned aerial vehicles
Unmanned automated aircraft, both aircraft and airships, designed for military use, can be used in civilian life to monitor traffic or the situation in especially criminal areas of the city. Such devices may have very small dimensions, since they do not have a pilot's seat. Apparently, the use of unmanned airships is more justified, since they are safer in operation. It is clear that an unmanned aircraft can be in the air only in motion, and errors in its piloting can have disastrous consequences, especially in conditions of dense urban development. The airship, in turn, can move very slowly or even “hover” in the air, providing better conditions for observing traffic, residential neighborhoods, industrial facilities and the situation in areas of high criminality.
Home robots
In the household, robots can find many different uses. With the help of robots, you can wash windows and floors, do minor home repairs, clean furniture upholstery, wash, cook and make cat feces. Here an interesting debatable question arises: can we consider dishwashers, microwave ovens, washing machines and dryers already present in the household as robots or are they still automatic machines? I think that when these machines "learn" to automatically "provide" themselves with work, independently getting food from the refrigerator to prepare them or collecting dirty laundry for the house, they will pass through the machine stage and turn into real robots.
How to get into the "top ten"?
As they say, especially in the field of computer software, in order for the software product to “go” and gain popularity, you need to find its “killer application”. At one time, such a computer product was the creation of text editors and the mode of page separation. The creation of which robot will turn out to be “golden”, i.e., I do not know by hitting the “bull's eye” that will induce everyone to purchase such a robot. But I know that the scope of use of robots is constantly expanding, and many “exotic” applications of robots in the near future will become quite familiar with the development of their mass production, reflecting the development of the capabilities, hopes and demands of society.
Other uses
It is impossible to keep track of all the scientific and technological developments in the field of robotics - everything happens extremely quickly. To find the necessary information is best to use the Internet.
Comments
To leave a comment
Robotics
Terms: Robotics