Lecture
The main parameter of the resistor is its nominal resistance. An equally important resistor parameter is the limiting power that it can withstand. This parameter mainly depends on the dimensions of the resistor and the materials from which it is made. The large size of the resistor increases its area, and as a result improves heat exchange with the environment (usually air). More heat-resistant materials allow resistor to operate at a higher temperature, which increases the heat transfer of the resistor to the surrounding space.
The power released by the resistor during the flow of current can be determined by the following formula:
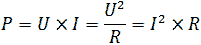
With the spread of semiconductor technology, the calculation of the power of resistors has practically ceased to be performed, since the power dissipated on them has become less than the minimum power dissipation of produced resistors. The situation has now changed again. Surface-mounted resistors (smd resistors) are widely used. The maximum allowable power of these resistors has decreased. Therefore, when calculating the electric principal circuit, it is again necessary to take into account the power allocated to the resistor, and to select the appropriate type nominal size of the surface-mounted resistor. Typical power values of surface-mounted resistors (smd resistors) are shown in Table 1 The main dimensions of surface-mounted resistors.
Sometimes due to the construction of the smd resistor, it is possible to dissipate the heat released during the flow of current through its outputs. In this case, the printed circuit board under the surface-mounted resistor should have increased thermal conductivity, then the section of the printed circuit board under the surface-mounted resistor will serve as a radiator that dissipates additional heat. In a multilayer printed circuit board, increased thermal conductivity can be obtained by using metal landfills under a surface-mounted resistor in its inner layers. Figure 1 shows a drawing of metallized sites designed to remove heat from a surface-mounted resistor (smd resistor).
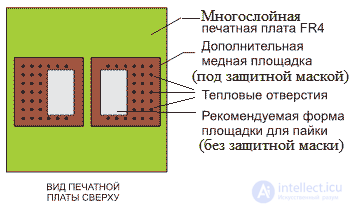
Figure 1. Additional sites for dissipating power from a surface-mounted resistor (top layer)
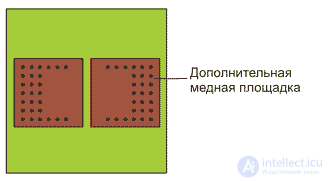
Figure 2. Additional sites for dissipating power from a surface-mounted resistor (inner layers and back layer)
Such a PCB design can work as a metallic copper radiator, which removes heat from a surface-mounted resistor (smd resistor) of 1 cm 2 and allows to dissipate about 1 W. More accurate calculations of heat removal are carried out through the concept of thermal resistance. Heat resistance can be determined by the following formula:
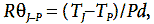
where ( T j −T p ) is the difference between the temperature of the resistor and the temperature of the soldering point;
P r - power dissipated on the resistor.
The thermal resistance of the resistor is a reference parameter and can be determined from the product specification (datasheet).
Similarly, the resistance between the soldering point and the printed circuit board is determined. Graph of the thermal resistance of the printed circuit board is shown in Figure 3.
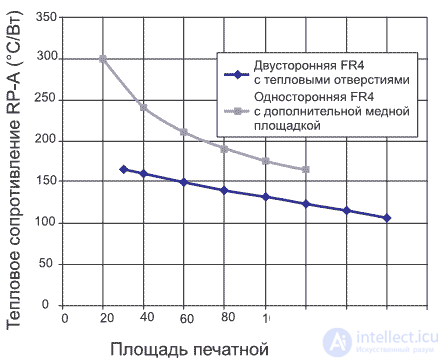
Figure 3. The dependence of thermal resistance on the area of metallized areas on the printed circuit board
In some cases, a radiator is attached under the smd resistor to improve heat removal from the printed circuit board section. A similar solution is shown in Figure 4.
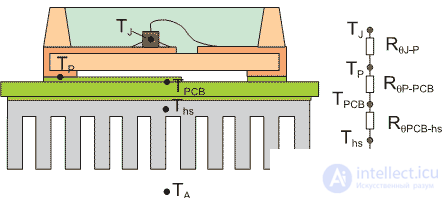
Figure 4. Additional heat dissipation from a resistor using a radiator
For high-power devices, special surface-mount resistors in the TO220 and TO221 packages were developed. These resistors can dissipate power up to 1.5 watts. Resistors in the TO220 package can be mounted on radiators to increase power dissipation. In this case, the power dissipated by the resistor in the TO220 package can reach 50 watts. The appearance of high-power surface-mounted resistors is shown in Figure 5.

Figure 5. The appearance of high-power surface-mounted resistors.
Such resistors can be used as part of attenuators that attenuate *** the power of a radio transmitter signal.
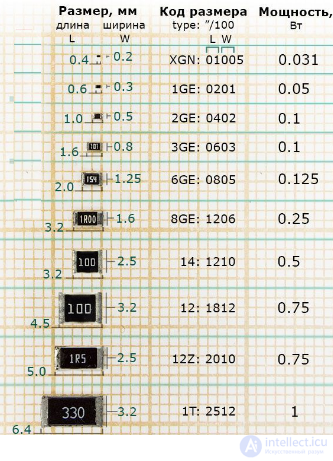
SMD Resistors Power Dissipation vs It's Size
Comments
To leave a comment
Design and engineering of electronic equipment
Terms: Design and engineering of electronic equipment