Lecture
Metal based boards are used for products in which it is necessary to dissipate a large heat output. The most popular area are boards with high-power SMD LEDs.
Externally, a printed circuit board on a metal base is a conventional printed circuit board, on one side of which is a metal (aluminum or copper) plate. The metal plate is connected to the printed circuit board using an insulating gasket (prepreg) with good thermal conductivity.
Thus, the general limitations for such boards are:
Boards can be one-sided and multi-layered:
The world produces a number of materials consisting of a metal plate, a dielectric layer and copper foil. Otherwise, there is practically no difference from the usual single-layer board.
Heat dissipating printed circuit boards with a metal base for quite a long time from an exotic product turned into a massive, industrial solution. They have firmly occupied their niche, which has been rapidly expanding in recent years, particularly in connection with
with the development of LED lighting technology. Many companies develop and produce materials for such boards. One of these companies is the company LEDDesign.
With the increasing degree of integration of the element base and the density of components on printed circuit boards (PCB), accounting for thermal processes is becoming increasingly important. The heat sink problem is solved by various methods. One of the main use of boards with a heat-conducting base. To efficiently remove heat, the base of the board must have a low thermal resistance. It is defined as R = d / (σ · S), where σ is the thermal conductivity of the material, d is its thickness (the length of the heat-conducting portion), S is the sectional area of the heat-conducting portion. Substrates based on ceramic materials have the highest thermal conductivity (Table 1). But the latter, due to well-known reasons (cost, mechanical strength, the impossibility of obtaining large-size boards, processing complexity, etc.), are used only for special tasks. Therefore, for many years worldwide, the use of printed circuit boards with a metal base has been expanding.
Such boards are already quite widely used in LED devices, in various current transducers, electric motor drives, power units, in welding equipment, etc. In foreign literature for thermally conductive boards with a metal base, several terms are used: IMST (Insulated Metal Substrate Technology), MCS (Metal Core Substrate), Hitt Plate and IMS (Insulated Metal Substrate). Structurally, the material for PP with a metal base consists of a metal base, a dielectric and foil (Fig. 1). The thickness of the foil ranges from 35 to 350 microns, the dielectric - from 50 to 150 microns, the metal base ranges from 0.5 to 3.2 mm. The most common, in particular - for LED technology is a metal base with a thickness of 1–1.5 mm, a dielectric with a thickness of 100 μm, and a copper foil with a thickness of 35 μm.
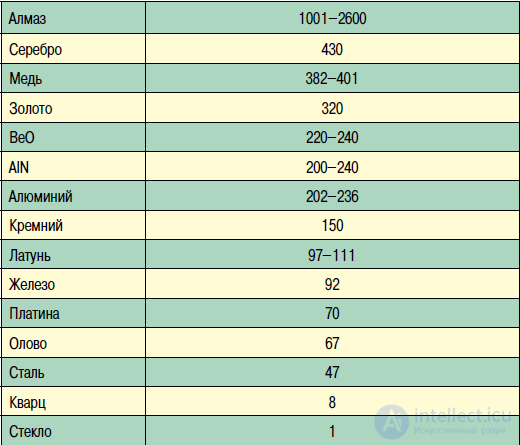
Table 1. Thermal conductivity of various materials, W / (m · K)
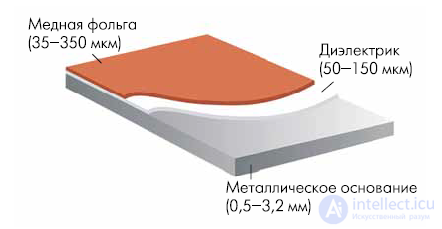
Fig.1 Material design PP with a metal base
Various alloys of aluminum are used as the metal base, as well as copper, iron and stainless steel. Consider each of these materials in more detail.
Among aluminum alloys (Table 2), the most commonly used materials are 1100 (according to GOST - AD), 5052 (AMg2.5) and 6061 (AD33).
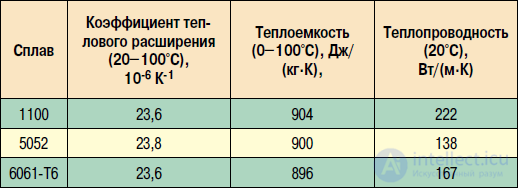
Table 2. Thermal properties of aluminum alloys
Aluminum alloy 1100 (BP) is very similar in composition to pure aluminum. Because of this, it has a very good thermal conductivity (220 W / (m · K)) and plasticity. At the same time, it has such very serious disadvantages as low mechanical strength and high viscosity. The last drawback is most significant, since it complicates the machining of the board by milling. But for stamping such material is ideal. Aluminum alloy 5052 (AMg2.5) is most commonly used because of its manufacturability and cheapness. It has not the highest thermal conductivity of 140 W / (m · K), but for most applications it is quite enough.
Aluminum alloy 6061 (AD33) is characterized by increased corrosion resistance and high thermal conductivity - about 170 W / (m · K). The material is well processed by milling. Its main drawback is the high price.
In addition to aluminum materials in a heat-conducting printed circuit board copper bases are quite common. Copper has a number of pronounced deficiencies. This material is viscous, and therefore poorly handled by milling. It has low corrosion resistance and a very high price. But these disadvantages are compensated for by the highest thermal conductivity of copper - 390 W / (m · K), which in a number of applications is a decisive advantage.
Stainless steel is also used as the base for heat-conducting printed circuit boards . Its obvious advantages are high corrosion resistance and mechanical strength, significantly exceeding aluminum and copper materials. But steel has a low thermal conductivity and relatively high price. In addition, the milling equipment used for the production of PP, poorly suited for steel processing.
The most important element of printed circuit boards , the most seriously influencing their properties and cost, is dielectrics. As a dielectric, FR4 prepregs (glass fabric with an epoxy binder), fiberglass and epoxy resin-based prepregs with various heat-conducting fillers, heat-conducting composite materials, as well as polyimide are used. Composite materials are most often used in heat-removing PP.
The trend setter in the field of thermally conductive materials for electronic equipment is Bergquist (USA). She was one of the first to start mass production of materials for PP with aluminum and copper bases (ThermalClad). Besides it, today the most active companies on the market are Laird (trademark - Thermagon) (USA), Totking (China), Ruikai (China), Denka (Japan), etc.
Bergquist company produces a whole product line of dielectrics (Fig. 2, Table 3), intended for various types of applications, including NT material for high-temperature applications. The difference in their properties is demonstrated by the thermal model of the device mounted on the PP of the same design, but with a different type of dielectric (Fig. 3) - FR4 in CML material, in materials МР, LTI and НТ - composite materials with heat-conducting fillers.
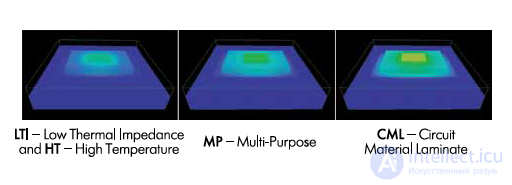
Fig.2 Line of materials from Bergquist
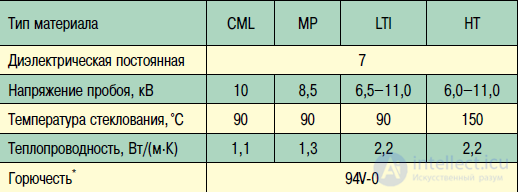
Table 3. Properties of different types of Bergquist materials

Fig.3 Thermal model for different types of Bergquist dielectric
The importance of using heat-removing PP is illustrated by an experiment on the degradation of the properties of white light-emitting diodes mounted on a PP with a metal base, but with a different type of dielectric (Fig. 4).
Fig.4. Degradation of white light LEDs depending on the type of dielectric
It can be seen that due to poor heat dissipation through an FR4-type dielectric, the LED is strongly degraded. Acceptable results demonstrate the PP with a dielectric type MP, and the best - with an LTI dielectric. Chinese manufacturers prefer to follow the industry leader. So, the company Totking, without inventing a bicycle, offers a product line similar to the Bergquist line (Fig. 5). However, this line has a number of features (Fig. 6, Tables 4 and 5).
Fig.5. Totking line of materials
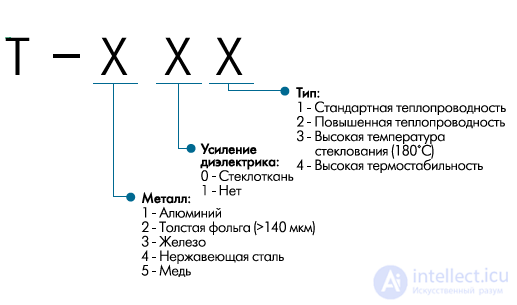
Fig.6. Marking Totking materials
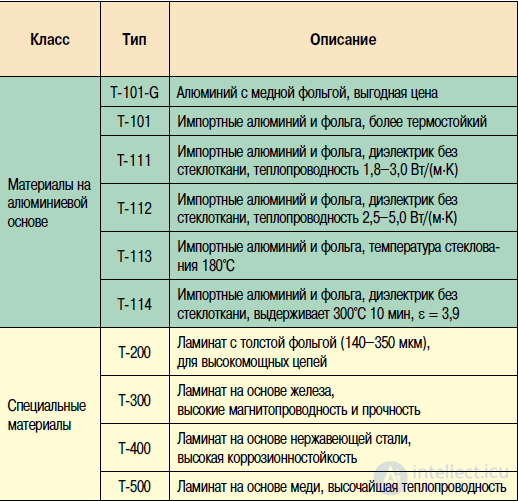
Table 4. Totking materials
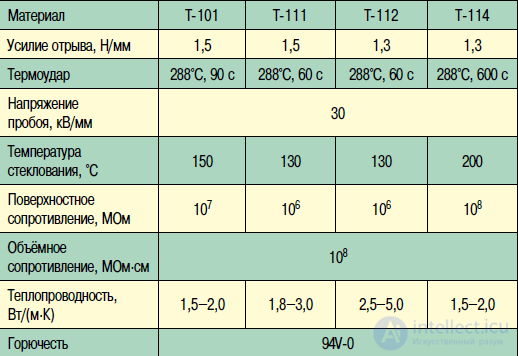
Table 5. Properties of materials company Totking
Let us dwell on it in more detail. Totking manufactures materials with aluminum, copper and steel bases for various applications. In addition, materials with a base of iron, designed for tasks requiring high magnetic conductivity, are also produced. Separately
highlighted materials with thick foil. The products of Ruikai, which closely cooperates with Bergquist (table 6), are also widely known.
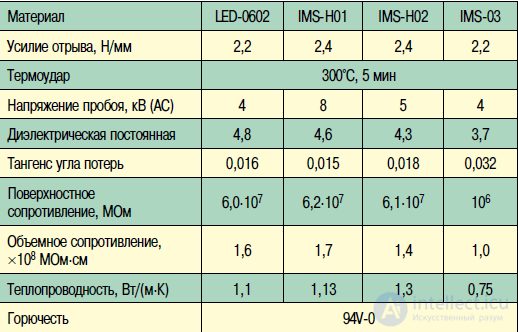
Table 6. Properties of the basic materials of the company Ruikai
In addition to single-sided boards , double-sided and multi-layer printed circuit boards are produced on a metal base. The design of such boards (Fig. 7) consists of a metal base on which PP is pressed, as the material of the dielectric layers in which not FR4 is used, but specialized materials with high thermal conductivity. But since the thermal conductivity of a polymer dielectric is significantly worse than that of copper or aluminum, special heat-conducting metallized holes can be formed in multilayer PP to improve the heat dissipation, allowing to increase the heat sink cross-sectional area (see Fig. 7). When designing, the layers with the largest metallization area tend to be located as close as possible to the metal base.
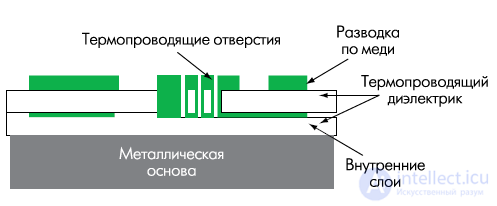
Fig.7. The design of multilayer PP on a metal base.
Note that in this case, you can also use a post installation. For this purpose, special cuts are provided in the metal base, and after pressing the base there is access for the installation of lead and / or hinged elements. At the same time, as a dielectric, when pressing the board to a metal base, it is necessary to use prepregs with low binder flowability.
For dielectric layers in multilayer printed circuit boards, special dielectrics are produced. In particular, such materials (prepregs and laminates) are produced by Bergquist under the trademark ThermalClad. We considered the properties of such materials with a thermal conductivity of 1.1–2.2 W / (m · K) above (see table 3).
In addition to Bergquist, prepregs and laminates for such multi-layer printed circuit boards are manufactured by Arlon (USA). The company presents the Arlon 91ML, 99ML and the newest 92ML series of materials. All these materials have a very high thermal conductivity (Table 7).
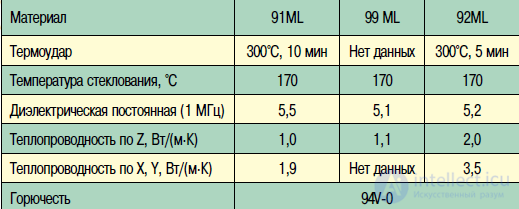
Table 7. Properties of materials company Arlon
The machining of printed circuit boards on a metal base is distinguished by a number of features. When drilling such boards, standard drills are used, as for FR4-based PCBs. Small and medium series of such printed circuit boards are processed by milling. It uses specialized milling cutters, for example - type MPK KEMMER ECA-30R.
Serious manufacturers of cutting tools produce special cutters for machining aluminum. Scribing is also actively used, for which specialized installations are used. They use special cutters and additional systems of liquid cooling of the working tool. Large series of printed circuit boards on a metal base, as a rule, are processed by stamping and scribing. Of course, the cost of a material with a metal base is high — on average, for substrates with an aluminum base, five times higher than usual. It is important to note that the cost of the PP as a whole, in addition to a host of other factors, is significantly affected by the layout of the materials for installation, i.e. material utilization rate.
In addition to the manufacture of printed circuit boards with the structure of the metal base dielectric-foil, other technologies are also being developed. For example, the known technology of manufacturing printed circuit boards based on heat-conducting plastics from the company Cool Polymers (USA). In particular, the company produces thermally conductive material CoolPoly D5108 based on polyphenylene sulfide (Polyphenylene Sulfide PPS). This material has a thermal conductivity of 10 W / (m · K), a dielectric constant of 3.7 (1 MHz) and a breakdown voltage of 29 kV / mm. In the manufacture of printed circuit boards, copper is chemically deposited on such a material, then a layer of galvanically deposited copper is formed and a conductive pattern is formed in the traditional way (Fig. 8). One of the serious problems of introducing such materials is their relatively high price. Suffice it to say that the initial granulate from which the plastic base is produced is worth about 80–90 dollars per kilogram in the United States.

Fig.8 PP based on CoolPolyr's CoolPoly materials
Manufacturing technology of printed circuit boards with a metal base is already quite common. In particular, in Ukraine the company "LEDDesign" has been producing LED lamps for over 5 years, and, following the trends in the world of technology, we use aluminum boards in the production of these lamps.

Fig.9 Board developed by LEDDesign
Comments
To leave a comment
Design and engineering of electronic equipment
Terms: Design and engineering of electronic equipment