Lecture
Consider first a mechanical system, for example, a stone thrown upwards. Thermal processes are absent, i.e. 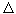 S = 0. (The role of free energy is played by mechanical energy.) The equilibrium of such a system can come with a minimum of potential energy, i.e., U = U max . The direction of the spontaneous process is associated with a decrease in potential energy.
S = 0. (The role of free energy is played by mechanical energy.) The equilibrium of such a system can come with a minimum of potential energy, i.e., U = U max . The direction of the spontaneous process is associated with a decrease in potential energy. 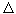 U <0, while increasing the kinetic energy.
U <0, while increasing the kinetic energy.
If the system * is isolated, then spontaneous processes lead, as already mentioned, to equilibrium, at which
In addition to an isolated system (IP), which does not exchange energy or matter with the environment, there are other systems.
A closed or closed system (CS) does not exchange matter with the environment, but exchanges energy.
An open system (OS) is exchanged with the environment and matter and energy.
Consider the equilibrium conditions of the CS at T = const and P = const. This may be, for example, a flask in a thermostat, a chemical reaction takes place in the flask. The equilibrium conditions of such a system is the Gibbs free energy minimum.
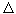 G <0.
G <0. As follows from (1)
Decrease of free energy
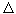 G =
G = 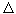 H - T
H - T 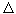 S (2)
S (2) 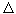 H and entropy increases
H and entropy increases 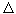 S.
S. Different options are possible here:
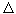 H and increase
H and increase 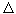 S;
S; 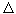 H but increasing and
H but increasing and 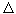 S, while
S, while 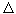 S>
S> 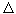 H / T;
H / T; 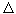 H, entropy simultaneously decreases
H, entropy simultaneously decreases 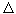 S, if at the same time the entropy decreases faster and condition (2) is not satisfied at all, that is, condition
S, if at the same time the entropy decreases faster and condition (2) is not satisfied at all, that is, condition 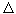 G <0 is also not executed.
G <0 is also not executed. The process is implemented only in the case when the free energy falls. Changes in enthalpy and entropy should not be considered separately, since this will not give an answer to the question about the direction of the process. Let's look at this process with concrete examples.
We repeat that in a giant factory of natural processes of nature, entropy plays the role of a director who prescribes the type and flow of all transactions, and the law of conservation of energy takes the place of an accountant who balances debit and credit. The change in entropy during a phase transition determines the very possibility of phase transitions. There would be no change in entropy - there would be no our world.
Comments
To leave a comment
Synergetics
Terms: Synergetics