Lecture
Every science has its own subject of study. The subject of pedagogical science is education as a special function of human society.
Education is a social, purposeful creation of conditions (material, spiritual, organizational) for the new generation of social and historical experience to assimilate it for public life and productive work. The category of “education” is one of the main ones in pedagogy. Describing the scope of the concept, education in a broad social sense is singled out, including in it an impact on the personality of society as a whole, and education in a narrow sense - as purposeful activity, designed to form a system of personality traits, attitudes and beliefs. Education is often interpreted in an even more local sense - as the solution of a particular educational task (for example, the cultivation of certain character traits, cognitive activity, etc.).Being a complex social phenomenon, education is the object of study of a number of sciences. Philosophy explores the ontological and epistemological foundations of education, formulates the most general ideas about the higher goals and values of education, in accordance with which its specific means are determined.
Sociology studies the problem of the socialization of the individual, reveals the social problems of its development.
Ethnography examines the patterns of education among the peoples of the world at different stages of historical development, the “canon” of education that exists among different peoples, and its specific features.
Economic science determines the role of education in the growth of the effectiveness of social production, financial and material and technical resources necessary to create an optimal infrastructure of the education system.
Psychology identifies individual, age-related features and patterns of development and behavior of people, which is an essential prerequisite for determining the ways and means of education.
Pedagogy studies the essence of education, its laws, trends and development prospects, develops theories and technologies of education, determines its principles, content, forms and methods.
In the early stages of human development, education was carried out in the process of children's participation in the life of adults (industrial, social, ritual, and play). It was limited to the assimilation of vital practical experience and everyday rules passed down from generation to generation.
With the increasing complexity of work and life increased the amount of knowledge and skills that a person had to master. This led to the allocation of education in a special sphere of public life. Systematic learning begins to play an increasingly important role, the main function of which was to select a system of knowledge and to target it.
With the development of production relations, education becomes one of the most important functions of the state. By confronting education with the task of effectively forming the type of citizen necessary for him, the state increasingly consistently engaged in improving the education system. The formation and development of the system of public education led to the beginning of the XVII century. the intensive development of the science of education - pedagogy and interest in its problems in a number of other sciences. Various concepts of education appeared (authoritarian, free, natural, new, etc.), developed on fundamentally different theoretical grounds.
The most important function of education - the transfer to the new generation of the experience accumulated by mankind - is carried out through education. Education is the side of education, which embodies the system of scientific and cultural values accumulated by previous generations. Through specially organized educational institutions that are combined into a single educational system, the transfer and assimilation of the experience of generations is carried out in accordance with the goals, programs and structures with the help of specially trained teachers.
In the literal sense of the word “education” means the creation of an image, a certain completeness of education in accordance with a certain age level. In this sense, education is interpreted as the result of a person’s mastering the experience of generations in the form of a system of knowledge, skills and abilities, relationships.
In education, there are processes that designate directly the act of transferring and learning experience. This is the core of education - learning.
Training is the process of directly transferring and assimilating the experience of generations in the interaction of the teacher and the student. As a process, learning includes two parts: teaching, in the chord of which the transfer (transformation) of a system of knowledge, skills, activity experience, and teaching is carried out, like learning experience through its perception, understanding, transformation and use. In Figure 1, the learning process is presented as follows:
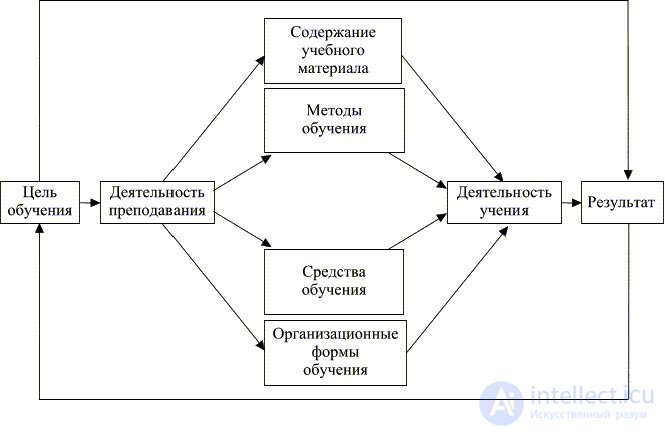
FIG. Model structure of the educational process
The level of development of any science is judged by the degree of differentiation of its research and by the variety of links of this science with others, thanks to which boundary scientific disciplines arise.
The system of pedagogical sciences includes (Fig. 2) :
Let us dwell on professional pedagogy. Determining the status of professional pedagogy as a full-fledged science implies a clear formulation of its object and subject.
As is known, the object of science is that area of reality, that set of real phenomena and processes, on the study and substantiation of which this area of scientific knowledge is directed.
Professional pedagogy can and should be viewed as a system of interdisciplinary scientific knowledge of a fairly wide range, not limited to just a very specific, narrow-profile training of a worker and a specialist in a particular profession or specialty. Ideas, methods and approaches developed in professional pedagogy can and should “permeate”, in essence, all levels, all parts of a single educational system, or, as they say now, a single system of continuous education.
This feature of professional pedagogy is due to the very nature of each person’s ascent of the “ladder” of his personality. Such a “ladder” can be represented as a sequential movement of a person to higher and higher achievements in his educational level along the following steps:
So, the scheme of a person’s ascent to more and more individual –personal cultural – educational acquisitions can be represented as follows: literacy (general and functional) - education - professional competence - culture - mentality.
It is easy to conclude in this connection that the subject of professional pedagogy is the process of forming professionally significant personal qualities, taking into account the specific features of vocational education of a particular level and profile.
But is it just such a purely procedural vision and definition of the subject of pedagogy in general, and professional pedagogy in particular?
The teacher, a practice, even the most gifted and creative, needs a curriculum, a curriculum, previously developed and properly substantiated teaching materials, which indicate the goals of education at one level or another, its content, possible methods, means, and organizational forms.
In other words, the process of education (as the implementing stage of movement from the goal to the result) must be preceded by a thorough theoretical and methodological development of the system of the upcoming educational activity. It is systems, since in its interconnection all components of the “score” of the teacher’s future activity should be presented - practice: relevant educational standards, goals, methods, means and organizational forms of training, education and development of students.
Thus, in pedagogy, along with the genre of practical pedagogical activity, there is also a genre of multifaceted (research, methodological) activity in the design and construction of pedagogical systems, in order to substantiate, first of all, the goals and content of education, which, in turn, create prerequisites for an informed choice of methods, means and organizational forms of educational activities.
In view of the above, the subject of professional pedagogy acquires a two-aspect, dual nature: the pedagogical process of forming the required professional qualities of the individual and the pedagogical system setting the target, informative and procedural (technological) components of such formation.
Engineering pedagogy is an integral part of professional pedagogy. It is aimed at training specialists implementing engineering activities and are characterized by specific goals, principles, content, forms of organization, methods and means of training. These are determined by its essence, boundaries, object and subject.
The object of engineering pedagogy is the pedagogical system of training engineering personnel, and the subject is the design and implementation of the content of vocational education, forms of organization, methods and means of education.
Engineering pedagogy reveals the theory and methods of design, constructive, gnostic, communicative, managerial and other functions; theory and methods of teaching technical, technological knowledge, skills and abilities, the formation of specific methods of engineering.
The theory of engineering pedagogy develops under the influence of social needs in the field of engineering education, the development of technical sciences that nourish engineering pedagogy.
The development of engineering pedagogy also occurs as a logical development of general pedagogical concepts and categories: goals, principles, content, forms, organization, methods, means of control and self-control. While preserving the pedagogical essence, they are focused on engineering education, on the practical-cognitive interaction of man with technology.
At the same time, engineering pedagogy is not limited to general pedagogical categories. Theory and practice show that scientific and technical knowledge, engineering activity, personality of a specialist and communication in the process of professional activity act as specific categories for engineering pedagogy.
Scientific and technical knowledge is the process of mastering a person by objectively new natural science, technical and technological knowledge in the field of science, technology, production, ways of doing business, and anticipating the prospects for their development.
Engineering activity is a dynamic system of interaction between an engineer and tools, mechanisms, structures that must be built artificially, based on scientific knowledge and methods of activity.
The personality of a specialist is an educated, professional-competent person with a high level of general and professional culture, intellectual development, competitive to active professional and social activities.
Communication is the establishment and development of business relations between people in the process of professional activity, generated by the need for joint work, management, in the development of a common strategy of interaction, in the exchange of information, in mutual understanding.
Comments
To leave a comment
Higher education pedagogy (engineering pedagogy)
Terms: Higher education pedagogy (engineering pedagogy)