Lecture
The pyramidal sorting method, invented by D. Williams, is an improvement in traditional tree sorting.
A pyramid ( heap ) is a binary tree such that
a [i] ≤ a [2i + 1];
a [i] ≤ a [2i + 2].
More details
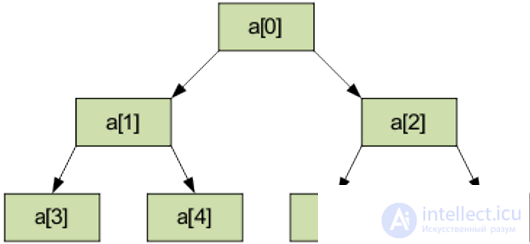
a [0] is the minimum element of the pyramid.
The general idea of pyramidal sorting is to first build a pyramid from the elements of the original array, and then sort the elements.
The execution of the algorithm is divided into two stages.
Stage 1 Construction of the pyramid. We determine the right side of the tree, starting from n / 2-1 (lower level of the tree). We take an element to the left of this part of the array and sift it through the pyramid along the path where its smaller elements are located, which simultaneously rise up; of the two possible paths, select the path through the smaller element.
For example, an array to sort
24, 31, 15, 20, 52, 6
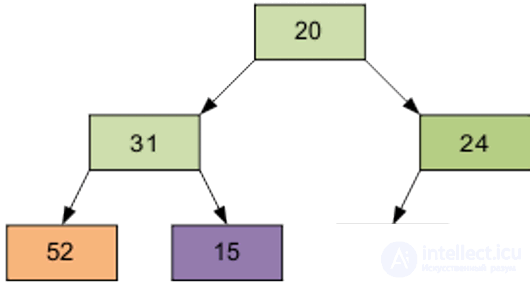
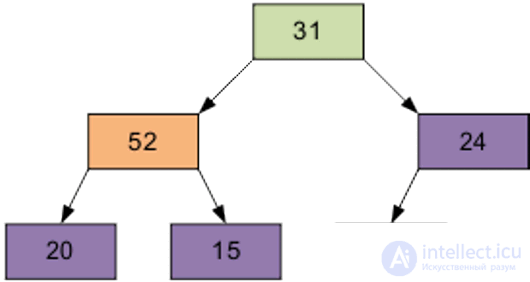
Arrange the elements in the form of the original pyramid; element number of the right part (6 / 2-1) = 2 - this is element 15.
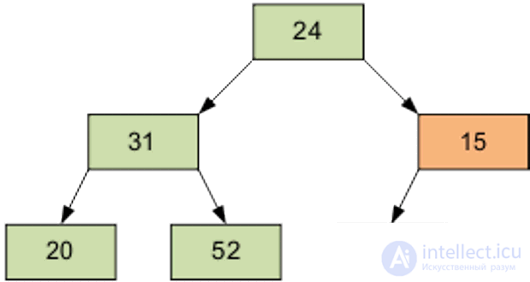
The result of sifting element 15 through the pyramid.
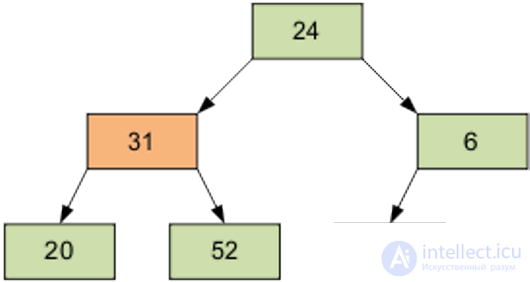
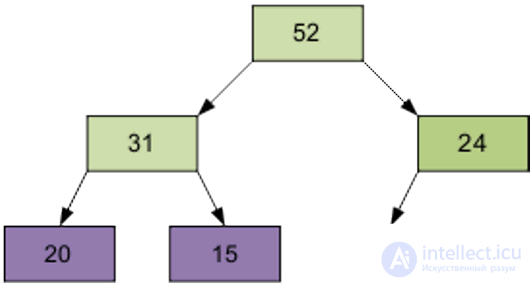
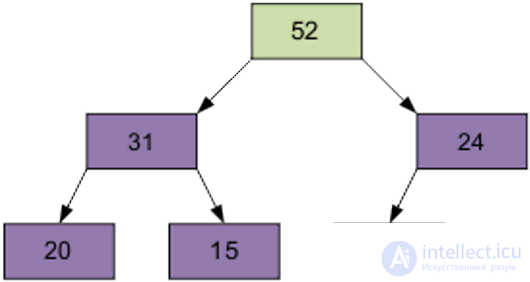
The next screened item is 1, equal to 31.
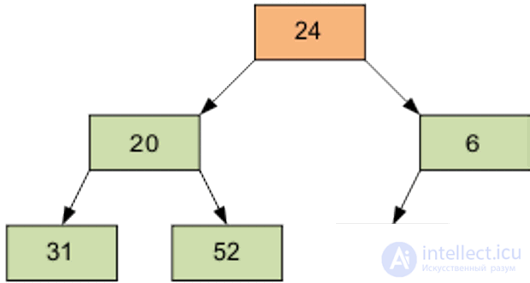
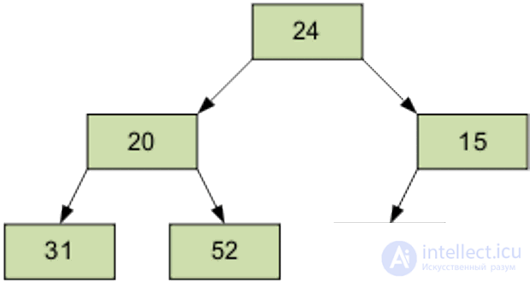
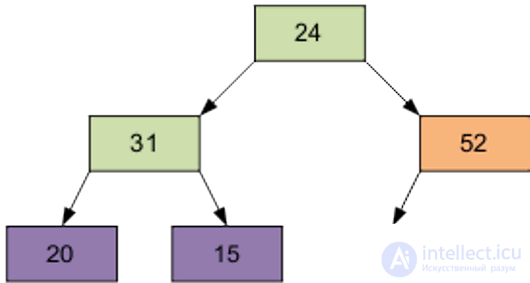
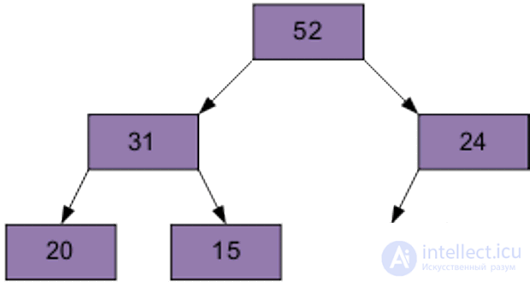
Then, element 0, equal to 24.
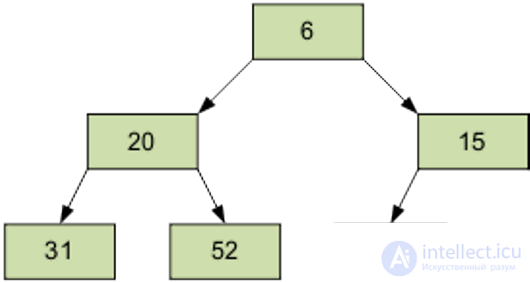
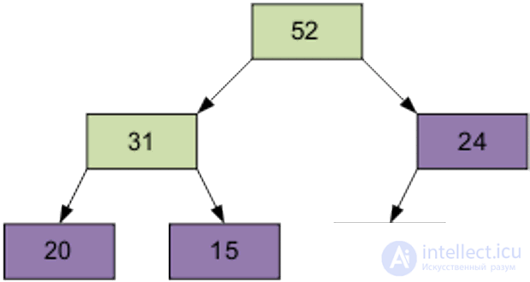
Of course, the resulting array is not yet ordered. However, the screening procedure is the basis for pyramidal sorting. As a result of sifting, the smallest element is at the top of the pyramid.
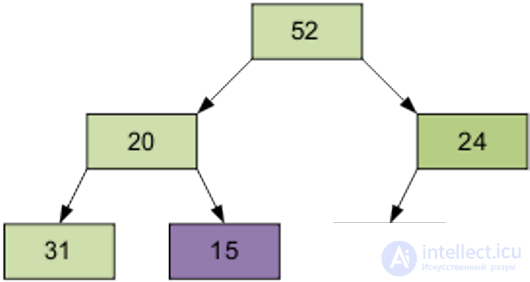
Stage 2 Sorting on the built pyramid. We take the last element of the array as the current one. We change the upper (smallest) element of the array and the current one in places. Sift the current element (it is now the top one) through the n-1 element pyramid. Then we take the penultimate element, etc.
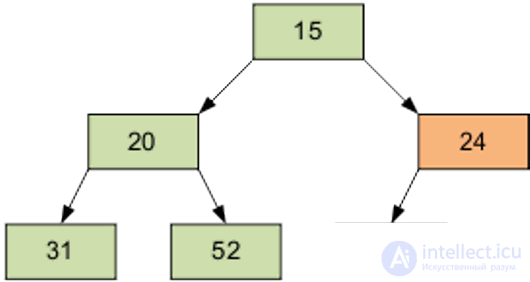
We continue the process. As a result, the array will be sorted in descending order.
Implementing pyramidal sorting in C
#include
#include
// Функция "просеивания" через кучу - формирование кучи
void siftDown(int *numbers, int root, int bottom)
{
int maxChild; // индекс максимального потомка
int done = 0; // флаг того, что куча сформирована
// Пока не дошли до последнего ряда
while ((root * 2 <= bottom) && (!done))
{
if (root * 2 == bottom) // если мы в последнем ряду,
maxChild = root * 2; // запоминаем левый потомок
// иначе запоминаем больший потомок из двух
else if (numbers[root * 2] > numbers[root * 2 + 1])
maxChild = root * 2;
else
maxChild = root * 2 + 1;
// если элемент вершины меньше максимального потомка
if (numbers[root] < numbers[maxChild])
{
int temp = numbers[root]; // меняем их местами
numbers[root] = numbers[maxChild];
numbers[maxChild] = temp;
root = maxChild;
}
else // иначе
done = 1; // пирамида сформирована
}
}
// Функция сортировки на куче
void heapSort(int *numbers, int array_size)
{
// Формируем нижний ряд пирамиды
for (int i = (array_size / 2) - 1; i >= 0; i--)
siftDown(numbers, i, array_size - 1);
// Просеиваем через пирамиду остальные элементы
for (int i = array_size - 1; i >= 1; i--)
{
int temp = numbers[0];
numbers[0] = numbers[i];
numbers[i] = temp;
siftDown(numbers, 0, i - 1);
}
}
int main()
{
int a[10];
// Заполнение массива случайными числами
for (int i = 0; i<10; i++)
a[i] = rand() % 20 - 10;
// Вывод элементов массива до сортировки
for (int i = 0; i<10; i++)
printf("%d ", a[i]);
printf("\n");
heapSort(a, 10); // вызов функции сортировки
// Вывод элементов массива после сортировки
for (int i = 0; i<10; i++)
printf("%d ", a[i]);
printf("\n");
getchar();
return 0;
}
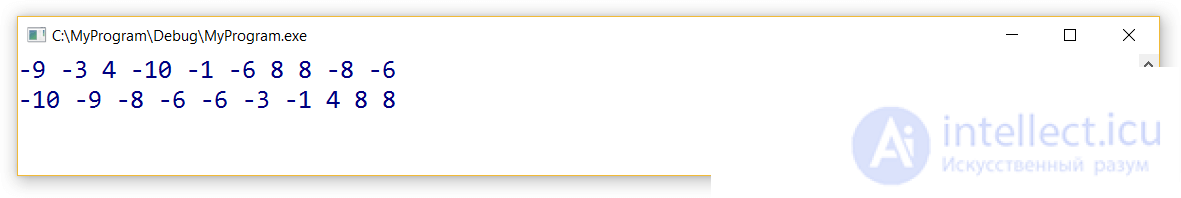
Результат выполнения
Despite some external complexity, pyramidal sorting is one of the most effective. The sorting algorithm is effective for large n . In the worst case, n · log 2 n steps are required that move the elements. The average number of movements is approximately equal
(n / 2) log 2 n ,
and deviations from this value are relatively small.
Advantages
disadvantages
Application
The heap sorting algorithm is actively used in the Linux kernel.
Comments
To leave a comment
Algorithms
Terms: Algorithms