Lecture
Alderfer's ERG theory is one of the most common meaningful theories of motivation. These theories describe the structure of needs, their content, connection with a person's motivation for activity. Clayton Alderfer [en] (1940-2015) - a psychologist at Yale University .
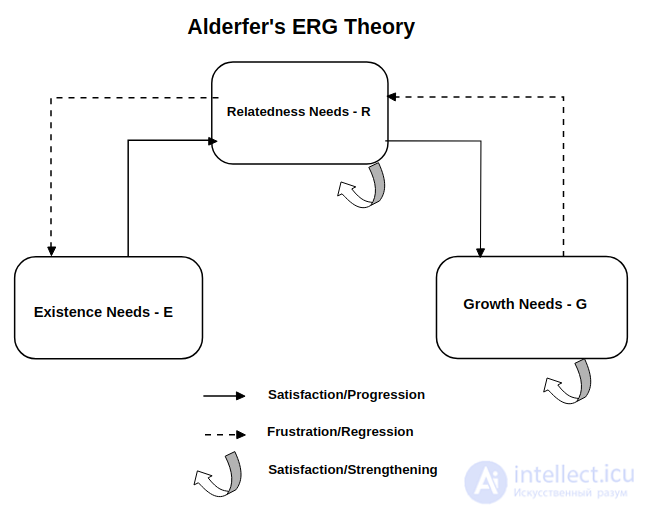
The relationship between the needs of communication (R), existence (E) and personal growth (G) according to Alderfer
Alderfer agrees with Maslow's theory , but identifies only three needs that people care about:
Alderfer argued that these three needs are similar to those identified by Maslow. The need to exist is analogous to the physiological need. The need to communicate with others is a social type need. The need for growth is the need for self-realization, for respect.
Clayton Alderfer argued that today's needs may remain unmet in five years, and then the guidelines can be changed. As a young person, a person may aspire to become the president of a company. In adulthood, he may no longer want to become president, as this takes too much of his life. This is a different way of looking at human needs.
Alderfer tried to establish a connection between satisfying needs and their activation and as a result identified the following seven principles:
1) The less satisfied the needs of existence (E) , the more they manifest themselves.
2) The less satisfied social needs (R) , the stronger the effect of the needs of existence (E) .
3) The more fully the needs of existence (E) are satisfied , the more actively social needs (R) declare themselves .
4) The less satisfied social needs (R) , the more their effect is enhanced.
5) The less satisfied the needs of personal growth and self-realization (G) , the stronger social needs (R) become .
6) The more fully satisfied social needs (R) , the more actualized the needs of personal growth (G) .
7) The less satisfied the needs for personal growth (G) , the more actively they manifest themselves. The more the need for personal growth is satisfied, the stronger it becomes.
Thus, Alderfer showed that the order of actualization of needs can be different than Maslow indicated, and depend not only on its place in the hierarchy, but on the degree of satisfaction of both this need and some other needs.
Differences from Maslow's theory
Alderfer's theory has a fundamental difference from Maslow's theory - the movement along the hierarchy can be carried out both from bottom to top and from top to bottom if the need of the upper level is not satisfied. You can move from the need to exist to the need to communicate. But your career growth may slow down, and instead of striving for advancement through the career ladder, you will be interested in relationships with people.
see also
Comments
To leave a comment
General psychology
Terms: General psychology