Lecture
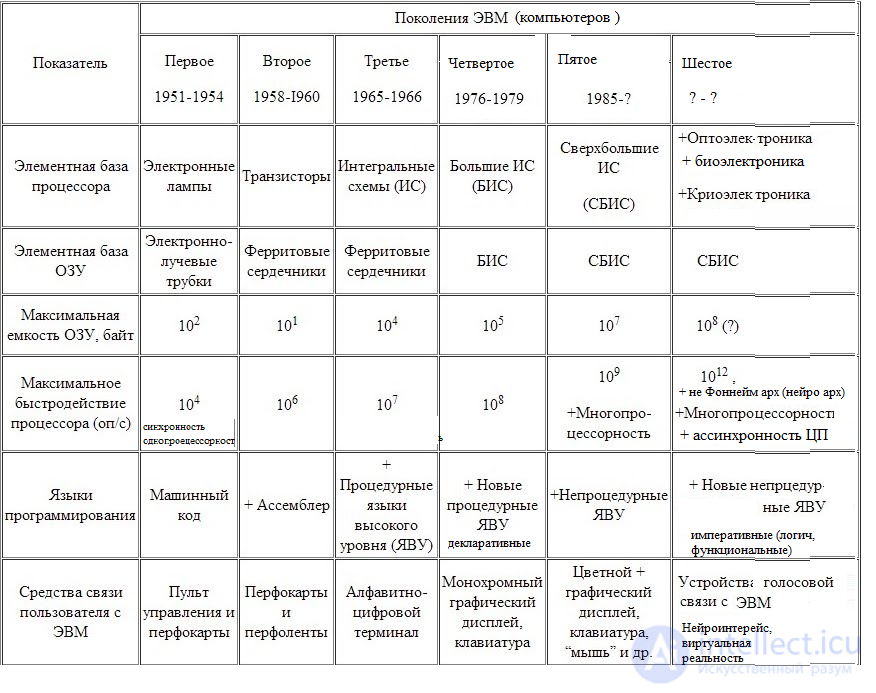
Sixth-generation computers In the foreseeable future, analysts say, we are entitled to expect that the 6th generation of computers will appear. It will be characterized by the use of neural elements in the architecture of microcircuits, the use of processors in a distributed network. The performance of computers in the next generation will probably be measured not in gigahertz, but in a fundamentally different type of calculus.
The sixth generation can be defined as the era of intelligent computers based on artificial neural networks or “artificial brains”. Artificial intelligence (AI) or artificial brain is a programming concept that allows devices to think and act independently. , This concept has influenced the world of games, robotics and voice recognition. These will be computers that use superconductors as raw materials for their processors, which will allow you not to spend electricity on heat due to lack of resistance, increase productivity and save energy. The performance gain will be approximately 30 times higher than that of a processor of the same frequency using base metals. AI is a major change in the sixth generation of computers.
Using the latest technological advances, computers can now take verbal instructions (voice recognition) and copy human reasoning. The ability to translate a foreign language is also moderately possible with fifth-generation computers. At first, this feat seemed like a simple goal, but much more difficult when programmers realized that human understanding depends on both context and meaning, and on a simple translation of words. Not only is technology improving, but the price is dropping as technology improves. The sixth generation of computers has provided consumers with the opportunity to get more power at a smaller size.
Scientists are working hard to create computers of the sixth generation in all developed countries of the world, including the USA, Japan, Western Europe. Moreover, since the 1950s, the field of science called “artificial intelligence” and the field of engineering called “robotics” began to develop rapidly. Computer-controlled robots can, to some extent, recognize visual images, recognize speech, control their movements and perform complex tasks. A huge number of different programs, including games, have been created. Programs are sometimes so perfect that the average person cannot compete with them in solving assigned tasks. For example, there are programs that seek and prove new theorems of mathematical logic, and even a good grandmaster may not defeat modern chess programs. Artificial intelligence and robotics are computer-based and are developing almost as fast as computers, because they depend on the speed and memory of the latter. Production of industrial robots is also developing rapidly. If the development of electronics will continue at the same pace (and no reason to reduce them is expected), then in the next 50 ... 100 years, by the end of the next 21st century, electronic computers will be equal in power to the human brain. The path that biological mankind has chosen over tens of millions of years will pass them through a half to two centuries.
The computer industry of the future will strive to create microscopic machines using new technologies, mainly quantum and optical, and in a quarter of a century the number of computers will decrease by about 100 thousand times compared to existing ones. All this will lead to the emergence of "devices the size of a blood cell that can be introduced into our body to maintain its health and into our brain to expand our intellectual capabilities." Probably such devices will be able to "create virtual reality, providing the full effect of presence, from inside the nervous system."
Comments
To leave a comment
History of computer technology and IT technology
Terms: History of computer technology and IT technology