Lecture
1960 year |
|
|
In 1960, Robert Noyce (Robert Noyce, 1927-1990) from Fairchild Semiconductor proposed and patented the idea of a monolithic integrated circuit (US Patent 2981877) and using the planar technology produced the first silicon monolithic integrated circuits. This technology has received the name - the technology of monolithic integrated circuits.
|
|
|
At the same time, Jack Kilby (Jack Saint-Clair Kilby, 08/11/1923–20.06.2005) from Texas Instruments manufactured a trigger on a single germanium crystal, completing the connections with gold wires. This technology is called the technology of hybrid integrated circuits.
The US Court of Appeals rejected Kilby’s application and declared Noyce the inventor of monolithic technology, although it is obvious that Kilby’s trigger is analogous to a monolithic integrated circuit.
Newspaper "INFORMATICS" CHIPS
|
|
|
In a short time, the CODASYL group (Conference on Data System Languages) under the leadership of Joeseph Wegstein (04/07/1922) and with the support of IBM, developed a standardized business programming language COBOL (Comnon business oriented language). This language is focused on the solution of economic problems, and more precisely - on the processing of information. |
|
In 1960, ALGOL (Algoritmic Language - algorithmic language) appeared, focused on scientific application, and many new concepts were introduced into it, for example, a block structure. This language has become the conceptual basis of many programming languages. Thirteen European and American programming specialists in Paris approved the ALGOL-60 programming language standard .
|
|
|
J. Schwartz and others from the company System Development are developing a programming language Jovial (Jovial). The name comes from the Jule's Own Version of International Algorithmic Language. Procedural HLL, version of Algola-58. Used mainly for military applications by the US Air Force. |
|
IBM has developed a powerful Stretch computing system (IBM 7030). |
|
1961 |
|
Developed by American professor John McCartney (John McCarthy, September 4, 1927) the LISP (List procssing language) language. The newspaper "INFORMATIKA" GENERATOR OF FANTASTIC IDEAS
J. Gordon, head of modeling systems development at IBM, created the GPSS language (general-purpose modeling system).
The first minicomputer (PDP-1, P rogrammed D ata P rocessor-1) appeared with a monitor and keyboard input.
|
Employees of the University of Manchester under the leadership of Tom Kilburn (Tom Kilburn, August 11, 1921 - January 17, 2001) created the Atlas computer, which for the first time implemented the concept of virtual memory.
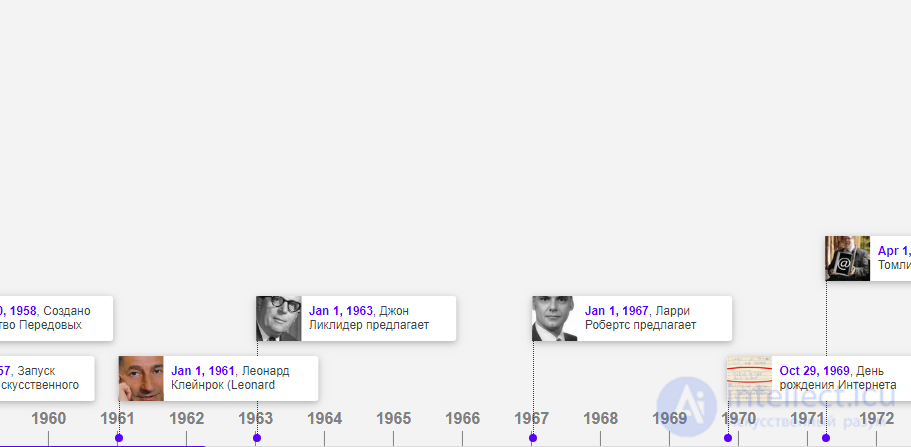
Leonard Kleinrock (Leo-nard Kleinrock) from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) developed a theory of packet switching for data transmission , the main points of which were published only in 1964. Kleinrock formulated the key principles of the organization of global information networks and substantiated the advantage of his new theory used in That time the method of data transmission - circuit switching. |
1962 |
|
Ralph E. Griswold, Ivan P. Polonsky and David J. Farber have developed a string processing language SNOBOL (StriNg Oriented and symBOlic Language). A graduate student at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) Steve Russell developed the first computer game . What was this game, unfortunately, is not known. |
|
|
E.V. Evreinov and Yu.Kosarev proposed a model of a team of calculators and justified the possibility of building supercomputers based on the principles of parallel execution of operations , variable logical structure and constructive homogeneity. |
|
D.Slotnik from Wesinghouse Electric published an article on the SOLOMON system project . |
|
|
IBM has released the first external memory devices with removable disks . |
|
Kenneth Iverson, IBM, published a book entitled "A Programming Language" ( APL ). Initially, this language served as a notation for writing algorithms. The first implementation of APL / 360 was in 1966 by Adin Falkoff (Harvard, IBM). There are versions of interpreters for the PC. Because of the difficulty of reading programs on the submarine, it is sometimes called the “Chinese Basic”. Actually, this is a procedural, very compact, language of super-high level. Requires a special keyboard. Further development - APL2. |
|
1963 |
|
|
The American Standard Code for Information Interchange - ASCII (American Standard Code Informatio Interchange) has been approved. At the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), Ivan Sutherland developed the Sketchpad system, which marked the beginning of the computer graphics era. General Electric Company created the first commercial DBMS (database management system). |
1964 |
|
U. Dahl and K.Nyugort created SIMULA-1 modeling language. |
|
An employee of the Stanford Research Center Douglas Engelbart (Douglas (Doug) Engelbart, 1/30/1925) demonstrated the work of the first mouse . WATCH THE VIDEO
|
|
Control Data Corp. announced the CDC 6000 computer developed by Seymour Krayem using 60-bit words and parallel processing. The CDC 6600 has been the most productive computer in the world for several years. |
|
|
On March 19, 1964, IBM management decided to develop and launch the IBM 360 family of computers (System 360), which became the first third-generation computers. This step for many years determined the further development of computers. Until now, each machine was produced with its own unique software, but now programs written for one of the machines could be run on others.
|
|
|
The BASIC language (Beginners all-parpouse sumbolic instraction code - a multi-purpose language of symbolic instructions for beginners) was developed by professors of Dartmouth College Tom Kurtz (Thomas Eugene Kurtz, 02.28.1928) and John Kemeny (John George Kemeny, 05.31.1926 - 26.12.1992) for students unfamiliar with computer technology. Over time, the language has a variety of dialects: Basica (IBM), GW-Basic, MSX-Basic, Turbo-Basic (Borland), Quick-Basic (Microsoft), XYBasic, QBasic, CBasic, Basic-80, 86 and 87Basic / 387Basic (MicroWay), etc. BASIC was first used in the IBM 704 computer, but it became widespread in the early 1980s, after Bill Gates and Paul Allen wrote the Basic interpreter for the first Altair 8800 PC in 1975. Over time, the language spawned many dialects. |
|
1965 |
|
Maurice Vincent Wilks (Maurice Vincent Wilkes, 06/26/1913) based on the idea of Gordon Scherott proposed a cache memory technology. Cache memory (cache, cache memory) - this memory, as a rule, is an order of magnitude faster than the main memory, is located as a buffer, between the processor and the main memory - RAM, and is used for temporary storage (within its volume) of all data consumed or generated by the processor.
Digital Equipment Corp. (DEC) has released one of the first PDP-8 minicomputers based on transistor circuits. Lawrence Roberts (Lowrens Roberts) first organized the interaction between computers on the basis of packet switching.
|
|
1966 |
|
The first publication on the REFAL programming language developed by V.F. Turchin appeared. |
|
K. Iverson and A. Falkoff on a computer of the IBM 360 family was implemented a modified version of the submarine language. Description of his language Iverson was released in 1962. Charles Kar and George Hockman suggested a prototype of the optical network. |
|
1967 |
|
|
Under the leadership of S.A.Lebedev and V.M. Melnikov, a high-speed computer BESM-6 was created in ITM and VT .
|
|
A joint project of IBM and the user group SHARE - the development of a new programming language that combines the possibilities of processing scientific data and solving business problems. They called it PL / 1 (Programming language - universal program-oriented).
Edward Feytenbaum of Stanford University developed the first DENDRAL expert system with a production representation of knowledge. |
|
|
Jack Kilby, Jerry Merimen, and James van Tassel invented a four-function pocket calculator .
|
|
|
Jack Deninis of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology advanced the concept of a streaming machine (computer-controlled data flow architecture). |
|
|
|
A. Bobeck (Andrew H. Bobeck, 10/01/1926) at Bell Laboratories developed memory on cylindrical magnetic domains (bubble memory).
|
1968 |
|
In the United States, Burroughs released the first high-speed computer on BIS ( large integrated circuits ) - B2500 and B3500.
|
|
|
|
In 1968-1970, Professor Niklaus Wirth (him. Niklaus Wirth, born February 15, 1934) created the PASCAL language at Zurich Polytechnic University, named after BLASA PASCAL, the first designer of the device, which now belongs to the class of digital computers. It was created as a language that, on the one hand, would be well suited for teaching programming, and on the other, it would provide an opportunity to effectively solve a wide variety of tasks on modern computers. Newspaper "INFORMATIKA" |
|
|
Dutch scientist Edsger Dijkstra developed the concept of structured programming. |
|
|
|
On September 9, 1968, at the San Francisco Computer Engineering Conference, Douglas Engelbart revealed the cornerstones of the new information age: interactive programming, database sharing, video conferencing, navigation in virtual spaces, a prototype window interface.
Engelbart literally shook the audience, showing in action the device, much easier human-computer interaction. The control panel consisted of a conventional keyboard with which text was entered, a set of keys for transmitting commands to a computer, and a pointing device “mouse” for selecting characters on the screen.
|
|
MR Cuillian of Carnegie Mellon University proposed a method for representing knowledge in the form of semantic networks. A small company BBN (Bolt, Beranek and Newman, Inc.) signs a contract with ARPA (Advanced Research Projects Agency - Advanced Planning Department for Research and Development - Special Department of the Pentagon) for building a network (prototype ARPANET) and writing software for it. The network was decided to build on the basis of specialized mini-computers, called IMP (Interface Message Processor, interface message processor), connected by communication lines that transmit information at 50 kbit / s. To increase reliability, each IMP had to be connected to two other IMPs. |
|
|
|
July 18th. Intel , a California- based manufacturer of semiconductor storage devices, is set up in the California town of Mountain View to become a cheaper alternative to magnetic memory components. Intel was founded by Robert Noyce (Robert Noyce), Gordon Moore (Gordon Moore) and Andrew Grove (Andrew Grove). Then the company was registered as MN Electronics (Moore-Noyce Electronics). A little later, the founders acquired the rights to the Intel name (represented as INTegrated ELectronics ) for $ 15,000 from a company that owned a chain of hotels. Thus began the era of Intel - the world's largest manufacturer of microprocessors, equipment for computers and telecommunications. |
1969 |
|
IBM has separated the concepts of hardware ( hardware ) and software ( software ). The company began selling software separately from hardware, initiating the software industry. |
|
|
Employees of Bell Laboratories Ken Thompson (Ken Thompson) and Dennis Ritchie (Dennis Ritchie) began to develop an operating system UNIX. In 1972, Bell Laboratories began releasing official versions of UNIX .
Firm Control Data Corp. has released a high-performance computer CDC-7600 .
|
|
Professor of Mathematics at MIT (Massachusetts Institute of Technology) Seymour Papert and his colleagues created a new language based on Lisp, calling it Logo (which the word means in Greek). At the initiative of Papert, the so-called bug was used in the language, providing the connection “object - thought” (first a mechanical bug was used crawling on the floor, and then its conventional image on the screen). As Papert noted, “the computer usually leads the child step by step,” and the Logo, on the contrary, “convinces the child that he is able to control the machine, allows the child to say:“ I am the master here. ” At first, the logo was intended for large computers and mini-computers that are available at MIT, but then penetrated into thousands of classes of elementary schools. |
|
|
|
Under the auspices of the Advanced Studies Agency of the United States of America (ARPA), the development and implementation of a global military computer network linking research laboratories in the United States began. October 29, 1969 is considered to be the birthday of the Network.
Testing became possible due to the fact that by September 1, 1969, BBN (Bolt, Baranek and Newman) had manufactured the first copies of the IMP (Interface Message Processor) device that provides communication between computers via telephone channels. |
|
Историю сети Интернет ( Интернет - это сокращение от «Interconnected Networks» (взаимосвязанные сети)) можно разделить на несколько этапов:
The weekly "Computerworld" №38-2001 СОЗДАТЬ INTERNET ЗАНОВО (Роберт Кан — один из создателей TCP/IP и руководитель разработки сети Arpanet) Газета "ИНФОРМАТИКА" №2001 (Лето) ПЕРВЫЙ ТРАНС-АТЛАНТИЧЕСКИЙ (Инициатором прокладки телеграфной линии между Старым и Новым Светом стал предприниматель Сайрус Филд) По материалам книги В.Г. Олифер, Н.А. Олифер «Компьютерные сети. Принципы, технологии, протоколы» ИСТОРИЯ РАЗВИТИЯ КОМПЬЮТЕРНЫХ СЕТЕЙ. |
Interesting Facts 1971 : Написана первая программа для эл.почты |
Comments
To leave a comment
History of computer technology and IT technology
Terms: History of computer technology and IT technology