Lecture
Annotation: The lecture reviewed the history of computer development, presented computer generations, computer parameters of different generations, computer valuations. Presented 3 stages of information technology, as well as the basic principles of the computer.
The idea of using software control to build a device that automatically performs arithmetic calculations was first put forward by the English mathematician Charles Babbage in 1833. However, his attempts to build a mechanical computer-controlled computing device were unsuccessful.
The first operating universal automatically controlled VM is considered the Mark-1 settlement-mechanical machine (USA, 1944). Machine downtime accounted for most of the time. The performance of the Mark-2 car, built on a relay of improved design, turned out to be just as poor.
The project of the first ENIAC computer was developed by J.Mouchli (USA, 1942); in 1946, the machine entered service. This car has 18.000 electric lamps, 1500 electromechanical relays. The use of lamps has increased the speed of operations 1000 times compared with the device "Mark - 1".
For the reference point of the computer era, they take sessions of the experimental operation of the ENIAC machine, which began at the University of Pennsylvania in 1946.
Here are some of the technical characteristics of this computer: the total weight - 30 tons, performance - 5000 operations per second. 40 years after the launch of the first computer, the annual production of the components of the computer was estimated by 1985. 10 14 active elements (logical elements), which is equivalent to 1 ENIAC for each inhabitant of the earth. For comparison: for 500 years of the development of printing by 1962. the total circulation of all publications has reached a level of 2 books per inhabitant of the Earth.
Electron tubes became the elemental base of the first-generation VM. The main scheme - a symmetric trigger was created in 1918. Soviet scientists Bonch-Bruevich MA In 1919 a similar scheme was also developed by the American scientists Ikkles and Jordan.
The first projects of domestic computers were proposed by S.А. Lebedev, B.I. Rameev in 1948. In 1949-51gg. by project SA Lebedev was built MESM (small electronic counting machine). The BESM-1 computer (a large electronic counting machine), the development of which is led by S.A. Lebedeva was completed in 1952, it contained 5 thousand lamps, worked without failures for 10 hours. The speed reached 10 thousand operations per second. Almost simultaneously, the Strela computer was designed under the direction of Yu. Ya. Bazilevsky, in 1953. She was put into production. Later, the Ural - 1 computer appeared, marking the beginning of a large series of Ural machines developed and introduced into production under the guidance of B.I. Rameeva. In 1958 launched into mass production of the first-generation computer M - 20 (speed up to 20 thousand operations / s).
With the advent of transistors in the mid-50s, the first generation of computers was replaced by second-generation computers built on semiconductor devices.
In our country, semiconductor computers of various purposes were created: small computers of the Nairi and Mir series, medium-sized computers with a speed of 5-30 thousand operations / s - Minsk-22 and Minsk-32, Razdan-2 "," Hrazdan - 3 ", BESM - 4, M - 220 and the best of the second generation machines - BESM - 6 with a speed of up to 1 million operas / s.
In the early 60s, a new direction in electronics appeared - integrated electronics. The use of integrated circuits for building a computer was a revolution in computer technology and promoted the emergence of 3rd generation machines.
Since 1972 Began production of models of the first phase of the EU computer (together with the socialist countries). A row - 1: the EU - 1010, 1020, 1022, 1030, 1033, 1040, 1050, 1052. The second stage (Row - 2): the EU - 1015, 1025, 1035, 1045, 1055, 1060, 1065 had a more modern circuit design, design and technological base, due to which they have increased productivity, and expanded functionality.
One of the characteristic features of the 4th generation computer is the transition from integrated functional circuits to integral computer subsystems. It is estimated that the introduction of LSI increases the reliability of not less than 10 times. From domestic computers to machines of the 4th generation, first of all, include the Elbrus family of vehicles.
Table 1.1 shows the relationship between the basic parameters of circuit design and computer generations. High-speed performance is characterized by a signal propagation delay introduced by one elementary element (conjunctor, disjunctor, etc.). An important indicator is the packing density, the number of units per 1 cm 3 .
| Generations | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sign, parameter of the computer | 1st 1946-1955 | 2nd 1955-1965 | 3rd | 4th after 80g. | ||
| 1965-1970 | after 70g | |||||
| Main elements | Relays, electronic lamps | Semiconductor devices | IS | BIS | VLSI | |
| Speed (delay / element or circuit) | 1ms | 1mks | 10ns | 1ns | <1ns | |
| Packing density, el-t / cm 3 | 0.1 | 2-3 | 10-20 | 1000 | > 10,000 | |
After 30 years, the computer industry is passing, as can be seen from fig. 1.1 hundred billion in overall financial weight, the milestone and still retains the highest growth rate of sales among all US manufacturing industries.
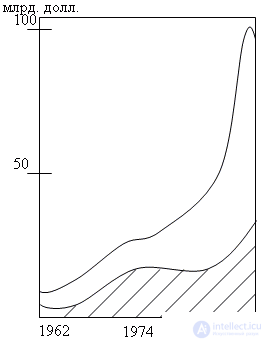
Fig. 1.1. The dynamics of the total sales of models of military equipment in the US (shaded area - peripheral equipment)
The growth of the world computer park and the dynamics of its structure are shown in the figures. Each new class of computer first goes through a stage of exponential growth, after which the total number of this type of computer park is stabilized within the boundaries determined by the typical area of its applications. For large computers, these boundaries were outlined by the total number of existing fairly large organizations capable of acquiring them. The range of applications of mini-computers has already included medium, as well as some small enterprises, individual units, etc. For personal computers, these boundaries are determined only by the total number of people employed in the national economy of industrialized countries. The imposition over time of the processes of rapid growth and the subsequent stabilization of the fleet of computers of various types leads to the exponential growth of the world computer park that has been observed for more than 30 years.
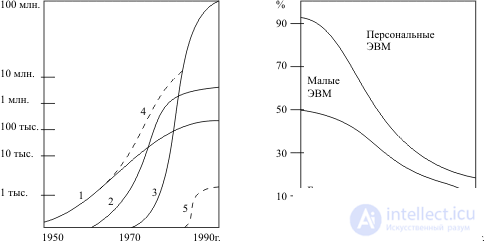
Fig. 1.2. Structural changes in the American computer industry: the relative distribution of annual sales of large, small and personal computers (estimated by Gromov G.R.)
1 - Large computers
2 - Minicomputers
3 - Personal computers
4 - Total Park Universal Computers
5 - New type of computer
The exception is the relatively small (by the number of machines installed) super-computer class ("Cray - 1", "Star - 100", "Cyber - 205", etc.). A hit in this class is determined precisely by a noticeable margin from other types of computers in terms of performance.
In 1953 American mathematician Claude Shannon, the creator of information theory, wrote: “Our VMs look like scholastic scientists. When calculating the long chain of arithmetic operations, digital computers considerably overtake people. When they try to adjust digital computers to perform non-arithmetic operations, they are clumsy and unsuitable for such work.”
Stage 1: machine resources . The functional limitations noted by Shannon, as well as the awesome cost of the first computers, fully determined the main task of the information technology of the 50s - early 60s. - increasing the efficiency of data processing using already formalized or easily formalized algorithms.
The main goal then was to reduce the total number of machine cycles that a program required for its solution, as well as the amount of RAM it occupied. The main costs of data processing were then almost in direct proportion to the machine time spent on them.
Stage 2: programming . In the mid-60s, the 2nd stage of development of information technology began, which lasted until the beginning of the 80s. From the technology of the effective execution of programs to the technology of effective programming, it was possible to determine the general direction of the change in the efficiency criteria during this stage. The most famous result of this first radical revision of the criteria for programming technology was the UNIX operating system created in the early 70s. The UNIX operating system, aimed primarily at improving the efficiency of the work of programmers, was developed by Bell Lebs employees K. Thompson and D. Ritchie, who were completely dissatisfied with the batch mode-oriented primitive software design tools. At the turn of the 80s, UNIX was regarded as a classic OS model — it began a triumphal march on a mini-computer series PDP-11 in the mid-70s.
Stage 3: the formalization of knowledge . A personal computer, as a rule, has developed tools for self-learning of a novice user to work at the console, flexible means of protection against his mistakes and, most importantly, all hardware and software tools of such a computer are subordinated to one “super-task” - to provide a “friendly response” of the machine to any including inadequate, user actions. The main task of personal computing is the formalization of professional knowledge - performed, as a rule, by an independent non-programmer user or with minimal technical support from a programmer.
Any form of human activity, any process of functioning of a technical object is associated with the transmission and transformation of information. Information refers to information about certain natural phenomena, events in public life and processes in technical devices. Information embodied and recorded in a material form is called a message. Messages can be continuous and discrete (digital). A continuous (analog) message is represented by a physical quantity (electric voltage, current, etc.), the changes of which in time reflect the course of the process in question.
For a discrete message is characterized by the presence of a fixed set of elements, from which at certain points in time various sequences are formed. Computers or computers are information converters. In them, the initial data of the task are converted into the result of its solution. In accordance with the used form of presenting information, the machines are divided into 2 classes: continuous - analog and discrete - digital. We study computers (digital).
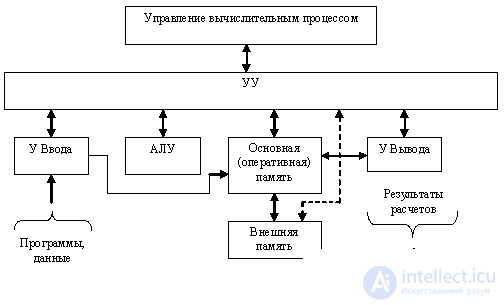
Fig. 1.3. Classical block diagram of a computer
Arithmetic logic unit (ALU) - converts machine words
Memory - main or operational (internal) memory (OP); external memory (VP)
The memory cells are numbered, the cell number is called the address.
In the storage devices (memories) that realize the function of memory in a computer, the operations are performed to read the stored information for transfer to other devices and to record information from other devices.
The algorithm for solving a problem by a numerical method is a sequence of arithmetic and logical operations that must be performed on the source data and intermediate results to obtain a solution to the problem. The algorithm can be specified by specifying which operations should be performed, in what order and on which words. The description of the algorithm in the form perceived by a computer is called a program.
The program consists of individual teams. Each command prescribes a specific action and indicates which words (operands) this action is performed on. The program is a set of commands recorded in a certain sequence, providing a solution to the problem on a computer.
Suppose, for example, to calculate
F = (a - x) / (ax + c),
for given numerical values of a, c, x. The calculation program F can be represented by the following sequence of commands:
In order for the control device to accept commands, they must be digitally encoded.
Automatic control of the process of solving a problem is achieved on the basis of the principle of programmed control, which is the main feature of a computer.
Another important principle is the principle of the program stored in memory, according to which a program encoded in digital form is stored in memory along with numbers. The team does not indicate the numbers involved in the operations themselves, but the addresses of the OP cells in which they are located and the address of the cell where the result of the operation is placed.
The use of binary schemes, principles of program management and the program stored in the memory made it possible to achieve high performance and reduce many times the number of instructions in programs for solving problems containing calculated cycles compared to the number of operations that the machine performs when executing these programs.
Commands are executed in the order corresponding to their location in consecutive memory cells, except for unconditional and conditional jump commands that change this order, respectively, unconditionally or only when a certain condition is met, usually specified as equality to zero, positive or negative result of the previous command or relation of type <, =,> for the numbers specified by the command. Due to the presence of conditional transition commands, a computer can automatically change the course of the process being performed, solve complex logical problems.
Using the input device, the program and the source data are read and transferred to the OP.
Comments
To leave a comment
History of computer technology and IT technology
Terms: History of computer technology and IT technology