Lecture
Visible light consists of the spectral distribution of electromagnetic energy with wavelengths in the range of 400-700 nm. Waves outside this range are called ultraviolet (UV) and infrared (IR). It is with perception that human processing of graphics, video and audio information begins. According to the theory of color vision, the color is perceived by receptors, the photosensitive retina of the eye with rods and flasks capable of perceiving light of different wavelengths.
Three-component theory of Helmholtz. Color sensation provided by three types of flasks that are sensitive to one part of the spectrum (red, green, or blue).
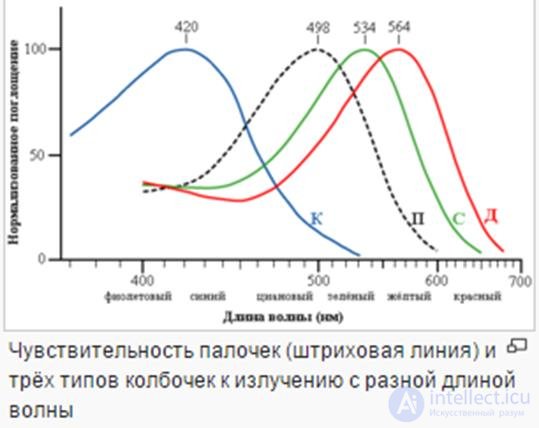
The Young – Helmholtz theory explains color perception only at the level of retinal cones and cannot explain all color perception phenomena, such as color contrast, color memory, color sequential images, color constancy, etc., as well as some color vision disorders, such as color agnosia.
The theory of Goering as a theory of the reverse process or Theory of Goering
. In flasks there are substances sensitive to white-black, red-green and yellow-blue radiation.
Thus, a person in the process of processing visual information is able to distinguish the color, brightness, shape and size of objects visible to them.
At the same time, physical, physiological and mental processes take place and the eyes, the nervous system are involved, incl. brain.
He relied not only on the existence of five psychological sensations, namely the sensation of red, yellow, green, blue and white, but also on the fact that they apparently act in opposite pairs, simultaneously complementing and excluding each other. Its essence lies in the fact that some "different" colors form intermediate when mixing, for example green and blue, yellow and red. Other pairs of intermediate colors cannot form, but they give new colors, for example, red and green. There is no red-green color, there is yellow.
Instead of postulating three types of cone reactions, as in Jung-Helmholtz theory, Goering postulates the presence of three types of opposite pairs of reaction processes for black and white, yellow and blue, red and green. These reactions occur at the post-receptor stage of action of the visual mechanism. Goering's theory highlights the psychological aspects of color vision. When three pairs of reactions go in the direction of dissimilation, warm sensations of white, yellow and red colors appear; when they proceed assimilatively, they are accompanied by cold sensations of black, blue and blue colors. The use of four colors in the synthesis of color gives more possibilities than the use of three.
The Goering model well explained the “negative” sequential images. The model of Goering gained not only supporters, but also opponents. The arguments of the latter boiled down to the following.
First: five different types of light in the eye - a bit too much. In addition, why the yellow receptor, if the yellow color is obtained by mixing the signals of "red" and "green"?
Secondly, why do the opposite yellow and blue give white, while the opposite red and green give yellow?
There is no anatomical or physiological evidence of this hypothesis.
Zone theory
At one time, there was heated debate among supporters of each of the theories described. However, now these theories can be considered mutually complementary interpretations of color vision. In Criss's band theory, proposed 80 years ago, an attempt was made to synthesize these two competing theories. It shows that the three-component theory is suitable for describing the functioning of the receptor level, and the opponent theory is for describing the neural systems of a higher level of the visual system.
The modern matrix is a microcircuit whose surface consists of a multitude of light-sensitive elements. Each element is an independent light receiver that converts the light incident on it into an electrical signal, which, after preprocessing, is recorded on a memory card. The image that we see consists of a set of digitally recorded signals from each element, which means it has a discrete structure.


There are two technologies of converting light into a signal on which the camera matrix can operate. The first is based on the property of semiconductor diodes to accumulate an electric charge under the influence of light, and is called a CCD (charge-coupled device) or CCD (the same in English). The second technology also uses charge accumulation, but not a diode, but a transistor is used as a receiver, which allows you to organize the amplification of the signal directly in the photosensitive element itself. This technology is called CMOS (decoding will say little to a non-specialist, I will not give it) or CMOS in English. Accordingly, there are two types of matrices - CCD and CMOS .
The first matrix worked on CCD technology, since this technology is simpler and was introduced first. Nowadays, the CMOS principle is considered more promising , since preamplification of a signal directly in a matrix element allows to increase sensitivity, reduce noise, reduce energy consumption and reduce matrix cost. Despite this, CCDs are still used today.
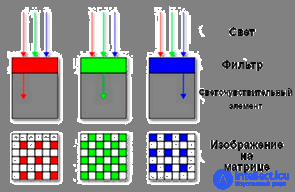
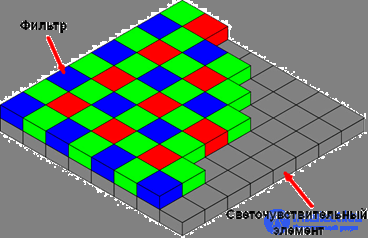
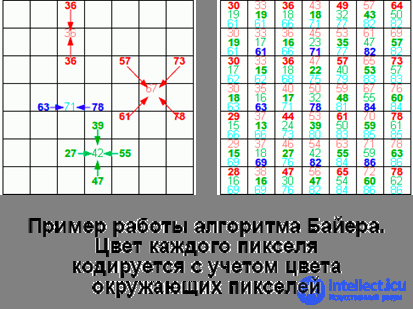
The elements that make up the matrix of the camera are able to capture only the intensity of the light incident on them. In order to record color , it is necessary at least three such elements (this number is associated with the perception of color by the human eye, which has three types of cones), each of which is responsible for its own spectral region. To realize color sensitivity, a light filter is placed in front of each element, which only lets through a well-defined color — red, green, or blue (the RGB model — Red-Green-Blue — which is used in the vast majority of arrays).
Thus, it turns out that the matrix consists of a set of three types of sensors, while they can be placed in different ways - a quadrilateral, a hexagon for some matrices, and the number of elements of different colors can be different. For example, in the widespread Bayer filter for each red and blue element there are two green ones, and they are also randomly distributed. This is done to simulate the increased color sensitivity of the human eye to green.

And what then is the well-known pixel ? This is easy to understand if you imagine that the camera works just like an eye. The image is built by the pupil (lens), perceived by the retina with rods and cones (matrix) and processed by the brain (processor). Actually we see the picture itself as a brain, because the structure of the retina is as discrete as the camera matrix.
So a pixel is a logical structure that is formed as a result of signal processing by a camera processor using special algorithms. A pixel can consist of one light-sensitive element, or three or more. For example, in the Bayer filter, which is already familiar to us, the color of each element is calculated from the information obtained from the elements surrounding it, and consequently, a pixel consists of a single photosensitive element. Different matrices and algorithms may have this differently.
продолжение следует...
Часть 1 24 Fundamentals of the theory of color perception by man and a computer system.
Comments
To leave a comment
Methods and means of computer information technology
Terms: Methods and means of computer information technology