Lecture
The range of noise encountered in image processing is quite wide [1, 2]. For example, in the statistical simulation of sensor intrinsic noise, which occurs due to insufficient lighting and / or high temperature, in most cases an additive Gaussian model with a noise probability density is used.
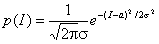 , (one)
, (one)
where I is the intensity of the image, 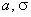 - distribution parameters.
- distribution parameters.
Impulse noise occurs when fast transients occur in the process of acquiring an image, for example, incorrect switching. In the simulation of impulse noise, the intensity value of each image point with probability Р а is replaced with value a , with probability Р b - by value b and with probability 1– ( Р а + Р b ), where Р а + Р b ≤1, remains unchanged . Probability density of impulse noise
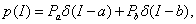 (2)
(2)
Where 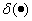 -
- 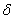 -function.
-function.
In systems using natural light, spatial illumination changes often occur that cause multiplicative noise in an image. It is modeled by the operation.
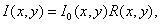 (3)
(3)
Where 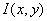 - halftone image,
- halftone image, 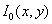 - the reflectivity of the object,
- the reflectivity of the object, 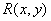 - the illumination of the object
- the illumination of the object 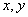 - spatial coordinates. In order for the structure and parameter estimates of the automated noise identification system to be reasonable, it is necessary to select the interference situation model. Taking into account noise factors in [1], the statistical model of the image
- spatial coordinates. In order for the structure and parameter estimates of the automated noise identification system to be reasonable, it is necessary to select the interference situation model. Taking into account noise factors in [1], the statistical model of the image 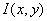 it seems like
it seems like 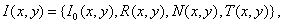 where
where 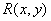 determined by formula (3),
determined by formula (3), 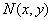 - additive Gaussian noise with a probability density (1),
- additive Gaussian noise with a probability density (1), 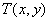 - impulse interference with distribution density (2). Since the object is primarily affected by light, and then it is exposed to sensors, the sensor's own noise and image transients cause a Gaussian and impulse noise on an unevenly lit image, which is described by the product of the reflectivity of the object and its light.
- impulse interference with distribution density (2). Since the object is primarily affected by light, and then it is exposed to sensors, the sensor's own noise and image transients cause a Gaussian and impulse noise on an unevenly lit image, which is described by the product of the reflectivity of the object and its light. 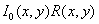 . Then the statistical model of the interference situation, which is used in this work, is presented in the form:
. Then the statistical model of the interference situation, which is used in this work, is presented in the form:
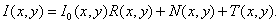
The method of forming the feature space for identifying interference in an image was proposed using an example of an image affected by one of three types of interference: additive Gaussian, pulsed or multiplicative. The statistical model of the interference situation (1) takes the form:
- in the case of additive Gaussian interference 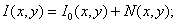
- in case of impulse noise 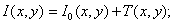
- in case of multiplicative interference 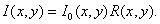

Window filtering of images in the spatial domain
A typical window filtering procedure assumes that the filtering window sequentially moves along the input image (for example, the algorithm can crawl the image in read order: from top to bottom along the lines, from left to right in each row), while at each window position all pixels are analyzed currently belonging to the window, and on the basis of such an analysis, one or another final value is assigned to the central pixel of the window on the output image. The output image thus formed is also called the result of filtering.
Window filtering procedures may vary:
the size and shape of the window (aperture);
the type of local statistics collected in the window;
a decision-making method based on collected statistics.
Thus, when constructing and investigating window procedures for filtering images, we should always evaluate the observed filtering quality by the following two main positions:
the ability of the filter to remove (filter) noise from the image;
the ability of the filter to keep small-sized parts and the shape of contours on the image.
Comments
To leave a comment
Methods and means of computer information technology
Terms: Methods and means of computer information technology