Lecture
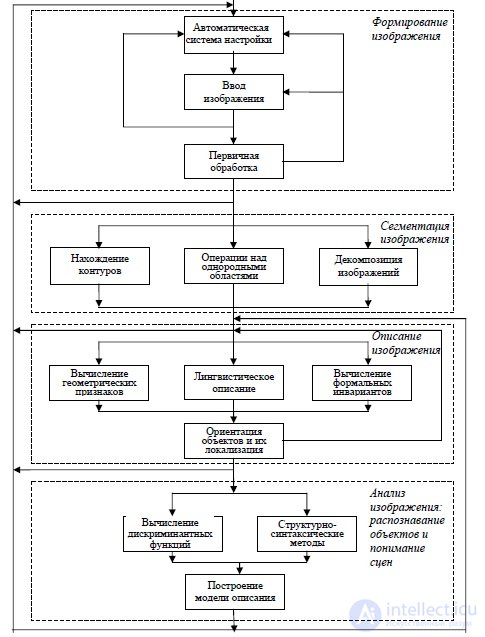
Primary processing and segmentation of images
Most images are characterized by the presence of an interfering background, as well as
uncertainty in the position and orientation of individual elements leading to
large redundancy, which dictates the need to use methods of preliminary
image processing: filtering, smoothing, skeletonization. Usually,
effective methods can be obtained taking into account the specificity of the images of that or
other subject area: handwritten numbers and letters, signatures, topological
integrated circuit layer or photomask, car license plate, etc. The
However, we have developed basic algorithms that can be quite effectively
use to process various images.
The processing is based on fast descriptor calculation algorithms in
various orthogonal bases [4], filtering algorithms based on transformations
Walsh, Haar and Hadamard [5-8], which can be mapped to parallel
computational structures of systolic type [9].
Along with general processing methods, methods are proposed that
on a specific area of the application
The general scheme of image frame processing includes the following steps:
1. Binarization.
2. Preliminary median filtering in a window of a given type and size with
the maximum number of iterations to ten is performed for
eliminate noise components along the edges of objects and to blur the image.
3. Correction of the histogram in brightness in order to eliminate shadows along the borders
objects.
4. Gaussian filtering with given parameters (operator size,
sigma, number of iterations) for a stronger image blur.
5. Filtering, taking into account the type of the layer and the size of objects.
6. Threshold image separation and contour selection. Threshold values
automatically selected according to histogram of value distribution
the intensity of the original image. Improving the quality of the binary image -
elimination of inclusions, alignment of boundary lines. Selection and description of the contours of the segments
Fast contour extraction algorithms based on 2D Walsh and Haar functions [19], compared with gradient algorithms, provide a narrower contour line, since image processing is performed by a window with a smaller size and high speed. In addition, when using the functions of the flash, there is no need for threshold processing and accordingly
threshold values, which is one of the key issues in defining contours with gradient operators, and the Haar functions allow you to select contour low-contrast images.
Two-dimensional orthogonal functions are also used to identify the handwritten characters as spectral shape descriptors. From the set of orthogonal transformations, discrete Walsh and Haar functions are considered. This is primarily due to the fact that the basis functions of these transformations take the values +1, –1 and +1, –1, 0, respectively
They are naturally displayed on the elements of digital computing equipment and provide additional opportunities for speeding up calculations. For the description of the areas highlighted by contour lines, the proposed method of approximation by straight-line segments [20-21], which includes the following steps:
- calculation conversion Hafa,
- selection of maxima in the Hough transform space,
- search for “candidate points” at fracture, which are the points of intersection of straight lines and
located in the field of the image
- image coverage with “elementary” areas,
- determining the color of each “elemental area”,
- the merger of "elementary areas",
- removal of "extra" points that are not breakpoints, and getting
final vector description of segmented areas
Image analysis
Image identification algorithms based on the use of spectral descriptors in various orthogonal bases, as well as the apparatus of moment functions, are especially effective in recognizing handwritten characters. Proof invariance of geometric, momentary and spectral primitives for various groups of affine transformations provided a high (more than 95%) recognition accuracy.
The reduction of the dimensionality of the vector of informative features is necessary to reduce the computational cost, while the probability of correct recognition of the image but the possibility should not be reduced. For example, the number of spectral coefficients obtained as a result of performing spectral conversion, which are used as informative features of the recognizable image, is quite large.
Comments
To leave a comment
Methods and means of computer information technology
Terms: Methods and means of computer information technology