Lecture
The concept of "information technology".
Information technologies (IT, also - information and communication technologies [1]) - processes, methods of searching, collecting, storing, processing, providing, disseminating information and methods of implementing such processes and methods, methods and methods of using computer equipment when performing functions collection, storage, processing, transmission and use of data (GOST 34.003-90); resources required for collecting, processing, storing and distributing information (ISO / IEC 38500: 2008).
Information technology is formed as a scientific discipline about the methods of high-performance information technology.
The object of research of information technology as a scientific discipline is information technology, i.e. ways of organizing information processes.
The subject of research for information technology, as a science, should be the basics and methods of creating information technology, their design and effective implementation.
In a narrower sense, information technology is a set of software and hardware that operates with data and knowledge in order to obtain the final information product in the form of new knowledge.
Background of the emergence of new information technologies.
Until recently, information was not considered a major asset for the company. The process of managing the activities of an organization largely depended on the personal influence of the top officials of companies without an extensive process of coordinating managers' efforts and analyzing data. Business decisions were made by the first persons of companies most often on the basis of experience and intuition, and only in a small number of cases - on the basis of specially prepared information containing variants of decisions and an assessment of the probability of their feasibility. Only powerful companies could afford to have think tanks that prepared material for decision making. The development of computing technology has fundamentally changed the business environment. In fig. 1.1 shows the main prerequisites for the development of IT, based on computer and telecommunication technologies.
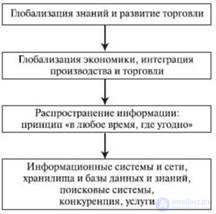
Figure 1.1 - IT Development Background
Globalization and integrated development of industrial economies significantly expands business opportunities. Information technology and information systems (IT / IS) provide mobile access and analytical power that meets the needs for conducting trade and managing enterprises across countries and continents. This creates threats to national and regional firms: global communications and management systems deliver information about offers, quality and prices to the consumer and allow making transactions and orders within 24 hours a day in any place where there is access to the network.
Table 1.1 summarizes the fundamental factors that irreversibly changed the business environment by the end of the twentieth century.
Table 1.1
|
Globalization |
Transforming industrial economies |
Enterprise transformation |
|
Global governance and control |
Knowledge and information based economy |
Informal goals and commitments |
|
Competition and interaction in global markets |
Strategic value information |
Decentralization and flexibility |
|
Global Information Delivery Systems |
Knowledge as the basis of performance and quality |
Local independence |
|
Distributed group work |
New products and services |
Empowerment |
|
International conventions and standards |
Competition based on optimal decision making speed |
Reducing the value of transactions through information marketing |
|
|
Expansion of staff knowledge |
Shift focus from technology to consumer |
Thus, the global market becomes open , none of the firms can feel safe. To become an effective participant in this market, companies need powerful information support and modern communication systems.
Types of information technology.
Information technology can be grouped as follows:
- Networks (Telephone, Broadband, Cellular, Telecommunications)
- Terminals (Personal computer, Cell phone, TV, Game console, Production control panel)
- Services (E-mail, Search system, business process management systems and other information processing systems, home appliances management systems - smart home, entertainment systems, etc.)
By purpose and nature of use it seems appropriate to distinguish two classes of information technologies:
- basic information technology;
- applied information technologies.
Basic information technologies are ways of organizing individual fragments of various information processes associated with the transformation, storage or transfer of certain types of information. Examples of such technologies can be information compression technology, its encoding and decoding, pattern recognition, etc.
The goal of basic information technologies is to achieve maximum efficiency in the implementation of a certain fragment of the information process based on the latest achievements of science.
The main task that is solved with the help of applied information technologies is the rational organization of one or another quite specific information process. The following areas can be considered as scientific directions in the field of applied information technology research:
1) development of methods for analyzing, synthesizing and optimizing applied information technologies;
2) the creation of the theory of designing information technology of various types and practical purposes;
3) creation of a comparative quantitative assessment methodology for various options for building applied information technologies;
4) development of requirements for hardware and software tools for automating the processes of implementing information technologies.
Comments
To leave a comment
Methods and means of computer information technology
Terms: Methods and means of computer information technology