Lecture
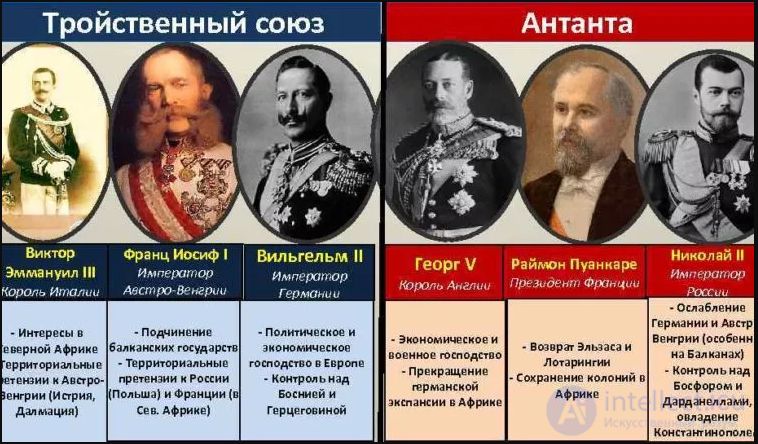
The situation on the eve of the war. At the beginning of the XX century. there was a design of blocks of countries - participants of the First World War. On the one hand, these were Germany, Austria-Hungary, Italy, which formed into the Triple Alliance (1882), and on the other, England, France, and Russia, who created the Entente (1904-1907). The leading role in the Austro-Germanic and Roman-British blocs was played respectively by Germany and England. The conflict between these two states was at the heart of the future world war. At the same time, Germany sought to win a worthy place under the sun, England defended the established world hierarchy.
At the beginning of the century Germany reached the second place in the world in terms of industrial production (after the USA) and first place in Europe (in 1913 Germany produced 16.8 million tons of pig iron, 15.7 million tons of steel; England, respectively - 10 , 4 million tons and 9 million tons (for comparison, France - 5.2 million and 4.7 million tons, respectively, and Russia - 4.6 million tons and 4.9 million tons). At a fairly rapid pace Other spheres of national economy of Germany, science, education, etc. developed.
At the same time, the geopolitical position of Germany did not correspond to the growing power of its monopolies, the ambitions of a strengthening state. In particular, the colonial possessions of Germany were very modest in comparison with other industrialized countries. Of the 65 million square meters. km of total colonial possessions of England, France, Russia, Germany, USA and Japan, in which 526 million natives lived, Germany accounted for 2.9 million square meters by the beginning of the First World War. km (or 3.5%) with a population of 12.3 million (or 2.3%). It should be borne in mind that the population of Germany itself was the largest of all the countries of Western Europe.
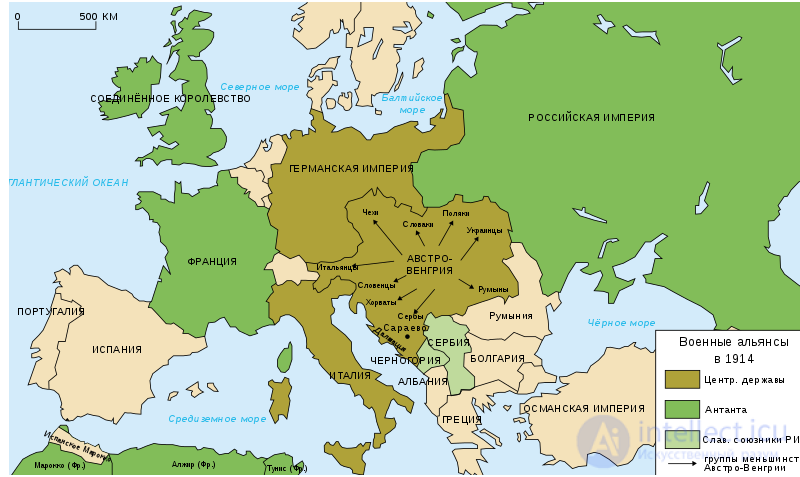
Европа в 1914 году.
Already at the beginning of the XX century. Germany’s expansion in the Middle East is intensifying in connection with the construction of the Baghdad railway; in China, in connection with the annexation of Jiaozhou Port (1897) and the establishment of its protectorate over the Shandong Peninsula. Germany also establishes a protectorate over Samoa, the Caroline and Mariana Islands in the Pacific Ocean, acquires the colonies of Togo and Cameroon in East Africa. This gradually aggravated the Anglo-German, German-French and German-Russian contradictions. In addition, German-French relations were complicated by the problem of Alsace, Lorraine and the Ruhr; German-Russian intervention of Germany in the Balkan question, its support there the policy of Austria-Hungary and Turkey. German-American trade relations in the field of exports of engineering products in Latin America, Southeast Asia and the Middle East also sharpened (at the beginning of the century, Germany exported 29.1% of world exports of machinery, while the share of the United States was 26.8%. Forerunners The First World War were the Moroccan crises (1905, 1911), the Russo-Japanese War (1904-1905), the seizure of Tripolitania and Cyrenaica by Italy, the Italian-Turkish war (1911-1912), the Balkan Wars (1912-1913 and 1913).
On the eve of the First World War, the propaganda of militarism and chauvinism sharply increased in almost all countries. She lay down on the raised ground. Developed industrial states, which achieved tangible superiority in economic development in comparison with other nations, began to feel their racial, national superiority, ideas of which from the mid-19th century onwards. cultivated by individual politicians, and by the beginning of the XX century. become an essential component of the official state ideology. Thus, the Pan-German Union established in 1891 openly proclaimed the main enemy of the peoples of England that entered into it, calling for the seizure of its territories, as well as Russia, France, Belgium, and Holland. The ideological basis for this was the concept of the superiority of the German nation. In Italy, propaganda was carried out to expand domination in the Mediterranean; in Turkey, the ideas of Pan-Turkism were cultivated with an indication of the main enemy - Russia and Panslavism. At the other extreme - in England the preaching of colonialism flourished, in France - the army cult, in Russia - the doctrine of protection of all Slavs and Panslavism under the auspices of the empire.
Preparing for war. At the same time, the military-economic preparation of the world slaughter was conducted. So, from the 90s. in 1913, the military budgets of the leading countries grew by more than 80%. The military-defense industry was booming: in Germany, 115 thousand workers were employed, 40 thousand in Astro-Hungary, 100 thousand in France, 100 thousand in Britain, 80 thousand in Russia. By the beginning of the war, military production in Germany and Austria-Hungary was only slightly lower than that in the Entente countries. However, the Entente received a clear advantage in the event of a protracted war or the expansion of its coalition.
Considering the latter circumstance, German strategists have long developed a blitzkrieg plan (A. Schliefen (1839–1913), H. Moltke (1848–1916), 3. Schlichting, F. Bernardi , etc.). The German plan provided for a lightning victorious strike in the West with simultaneous deterrent, defensive battles on the eastern front, followed by the defeat of Russia; The Austro-Hungarian headquarters planned a war on two fronts (against Russia and the Balkans). The plans of the opposing side included the offensive of the Russian army on two directions at once (north-west against Germany and south-west against Austria-Hungary) with forces of 800 thousand bayonets with passively waiting tactics of the French troops. German politicians and military strategists pinned hope on the neutrality of England at the beginning of the war, for which in the summer of 1914 they pushed Austria-Hungary into a conflict with Serbia.
The beginning of the war. In response to the murder on June 28, 1914 of the heir to the Austro-Hungarian throne, Archduke Franz Ferdinand, in the city of Sarajevo, Austria-Hungary immediately opened military actions against Serbia, in support of which on July 31 Nikolay II announced general mobilization in Russia. On the demand of Germany to stop the mobilization of Russia refused. On August 1, 1914, Germany declared war on Russia, and on August 3, on France. The hopes of Germany for the neutrality of England, which came out with an ultimatum in defense of Belgium, after which it began military operations against Germany at sea, officially declaring war on 4 August, did not materialize.
At the beginning of the war, many states declared neutrality, including the Netherlands, Denmark, Spain, Italy, Norway, Portugal, Romania, the United States, and Sweden.
Military operations in 1914 on the Western European front were offensive from Germany, whose troops, having passed Belgium from the north, entered the territory of France. In early September, between the cities of Verdun and Paris, a grand battle took place (about 2 million people participated), lost by the German troops. The Russian army was advancing in the East European direction; the troops of the North-Western and Western fronts (commanded by General Raninkampf and General Samsonov) were stopped by the Germans; the troops of the South-Western Front achieved success, occupying the city of Lviv. At the same time, hostilities unfolded on the Caucasian and Balkan fronts. In general, the Entente managed to thwart the blitzkrieg plans, as a result of which the war acquired a protracted, positional character, and the scale began to lean in its direction.
Military actions (in 1915-1918) . In 1915, there were no major changes on the Western European front. Russia as a whole lost the campaign of 1915, surrendering Lviv to the Austrians, and Liepāja, Warsaw, Novogeorgievsk to the Germans.
Contrary to the pre-war obligations, in 1915 Italy declared war on Austria-Hungary, as a result of which a new Italian front was opened, where hostilities did not reveal a clear advantage of the parties. This advantage in favor of the Entente in the south of Europe was neutralized by the design in September 1915 of the Fourth Austro-German-Bulgarian-Turkish Union. One of the results of its formation was the defeat of Serbia with the subsequent evacuation of its army (120 thousand people) to Corfu Island.
In the same year, actions on the Caucasian front were transferred to the territory of Iran with the participation of not only Russia and Turkey, but also England; after the landing of the Anglo-French troops in Thessaloniki, the Thessaloniki Front was formed, the British occupied the territory of South-West Africa. The most significant naval battle of 1915 was the battle for the capture of the Bosphorus and the Dardanelles.
1916 on the Western European front was marked by two major battles: near the town of Verdun and on the r. Somme, where on both sides were killed, wounded and captured 1 million 300 thousand people. This year the Russian army conducted offensive operations on the North-Western and Western fronts in support of the Allies, during the battle of Verdun. In addition, a breakthrough was made on the South-Western Front that went down in history by the name of General A, Brusilov (1853-1926), as a result of which 409 thousand Austrian soldiers and officers were captured and a territory of 25 thousand square meters was occupied. km
In the Caucasus, parts of the Russian army occupied the cities of Erzerum, Trebizond, Ruvanduz, Mush, Bitlis. England won the North Sea in the largest naval battle of the First World War (the battle of Jutland).
In general, the success of the Entente provided a turning point in the course of military operations. The German command (generals Ludendorff (1865-1937) and the Hindenburg) moved from the end of 1916 to defense on all fronts.
However, next year the Russian troops left Riga. The weakened position of the Entente was reinforced by the entry into the war on its side the United States, China, Greece, Brazil, Cuba, Panama, Liberia and Siam. On the Western front, the Entente did not manage to acquire a decisive advantage, while on the new Iranian front the British occupied Baghdad, while in Africa they consolidated the victory in Togo and Cameroon.
In 1918, a single allied command of the Entente countries was created. Despite the absence of a Russian front, the Germans and Austrians still held up to 75 divisions in Russia, leading a difficult game under the prevailing conditions after the October Revolution. The German command launched a major attack on the r. Somme ended in failure. The Allied counterattack forced the German General Staff to request a truce. It was signed on November 11, 1918 in Compiegne, and on January 18, 1919, the Conference of 27 Allied countries opened in the Palace of Versailles, which determined the nature of the peace treaty with Germany. The treaty was signed on June 28, 1919, Soviet Russia, which concluded a separate peace with Germany in March 1918, did not participate in the development of the Versailles system.
The outcome of the war.
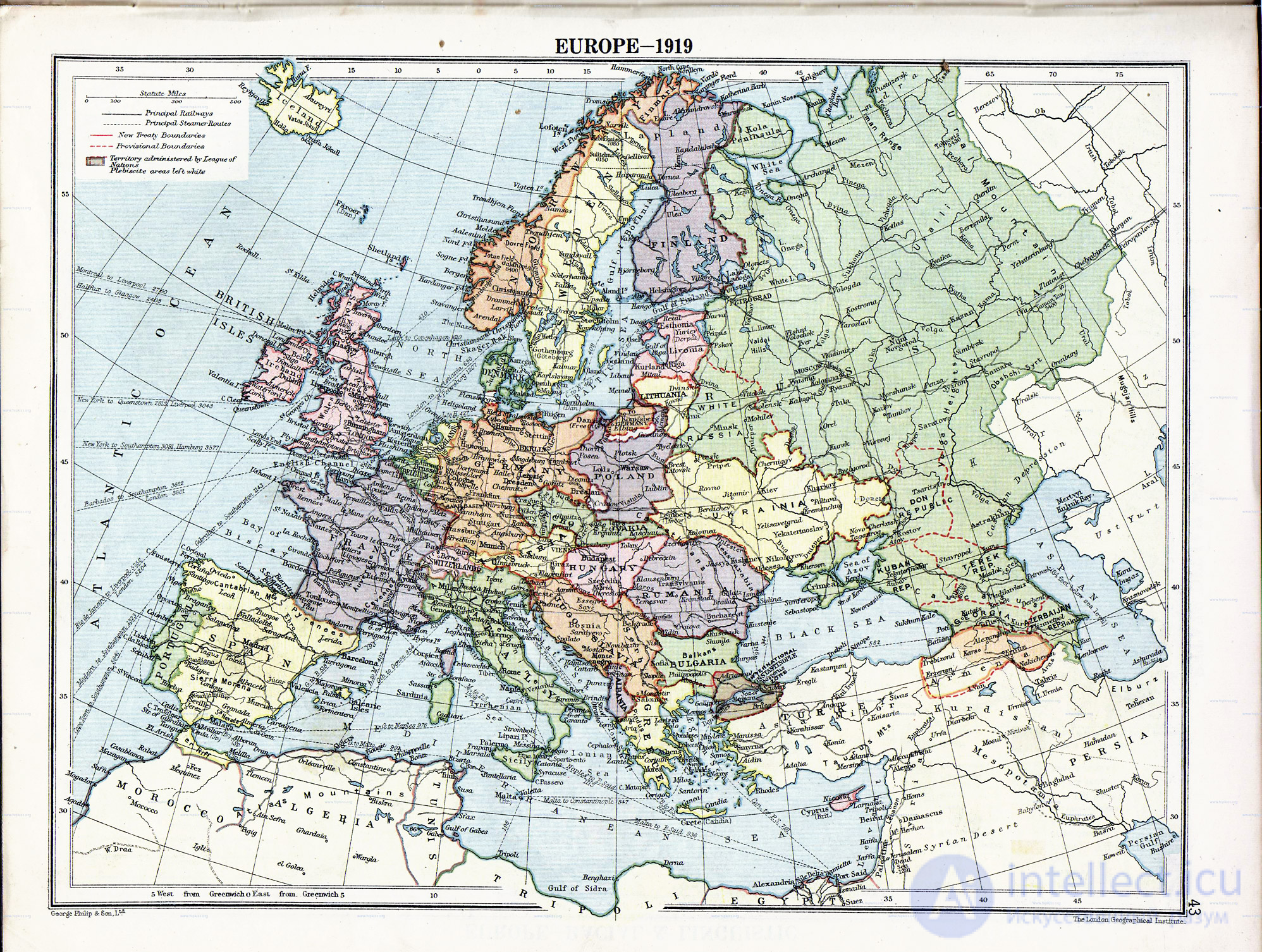
The outcome of the war. According to the Versailles Treaty, the territory of Germany decreased by 70 thousand square meters. km, she lost all the few colonies; military articles obliged Germany not to impose military service, to dissolve all military organizations, not to have modern types of weapons, to pay reparations. The map of Europe was thoroughly redrawn. With the collapse of the Austro-Hungarian dual monarchy, the statehood of Austria, Hungary, Czechoslovakia, Yugoslavia was formalized, the independence and borders of Albania, Bulgaria, and Romania were confirmed. Belgium, Denmark, Poland, France and Czechoslovakia regained the lands occupied by Germany, having received under their control a part of the original German territories. Syria, Lebanon, Iraq, Palestine were separated from Turkey and transferred as mandated territories of England and France. The new western border of Soviet Russia was also defined at the Paris Peace Conference (the Curzon Line), while consolidating the statehood of parts of the former empire: Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Finland and Estonia.
The consequences of the First World War. World War I demonstrated the crisis state of civilization. Indeed, in all the belligerent countries, democracy collapsed, the sphere of market relations narrowed, giving way to strict state regulation of the sphere of production and distribution in its extreme statist form. These trends contradicted the economic foundations of Western civilization.
No less striking evidence of a deep crisis were fundamental political changes in a number of countries. So, after the October Revolution, socialist revolutions in Finland, Germany, and Hungary swept through Russia; in other countries, there was an unprecedented upsurge in the revolutionary movement, and in the colonies - anti-colonial. This seemed to confirm the prediction of the founders of the communist theory of the inevitable destruction of capitalism, as also evidenced by the emergence of the Communist 3rd International, 2 1/2 Socialist International, the coming to power in many countries of the socialist parties and, finally, the lasting conquest of power in Russia the Bolshevik Party.
World War I was a catalyst for industrial development. During the war years, 28 million rifles were produced, about 1 million machine guns, 150 thousand guns, 9200 tanks, thousands of aircraft, and an underwater fleet (only in Germany over 450 submarines were built over the years). The military focus of industrial progress became apparent, the next step was the creation of equipment and technologies for the mass destruction of people. However, in the years of the First World War, monstrous experiments were carried out, for example, the first use of chemical weapons by the Germans in 1915 in Belgium near the town of Ypres.
The consequences of the war were disastrous for the national economy of most countries. They resulted in widespread long-term economic crises, which were based on huge economic disparities that arose during the war years. Only the direct military expenditures of the warring countries amounted to $ 208 billion. Against the background of the widespread decline in civilian production and the living standards of the population, there was a strengthening and enrichment of monopolies associated with military production. Thus, by the beginning of 1918, the German monopolists accumulated 10 billion gold marks as profits, American monopoly - 35 billion gold dollars, etc. Having strengthened during the war years, the monopolies began to determine the ways of further development leading to the catastrophe of Western civilization. . Confirmation of this thesis are the emergence and spread of fascism.
Comments
To leave a comment
The World History
Terms: The World History