Lecture
A typical representative is the Integrated Database Management System (IDMS) of Cullinet Software, Inc., designed for use on IBM main-class machines running most operating systems. The system architecture is based on the Data Base Task Group (DBTG) proposals of the Programming Languages Committee of the Conference on Data Systems Languages (CODASYL), the organization responsible for defining the Kobol programming language. The DBTG report was published in 1971, and in the 1970s several systems appeared, including IDMS.
The network approach to data organization is an expansion of the hierarchical one. In hierarchical structures, the child record must have exactly one ancestor; a descendant can have any number of ancestors in a network data structure.
A network database consists of a set of records and a set of links between these records, and more precisely, from a set of instances of each type from a set of record types specified in the database schema and a set of instances of each type from a given set of connection types.
The type of relationship is determined for two types of record: ancestor and descendant. A link type instance consists of one instance of the parent record type and an ordered set of child record type instances. For this type of connection L with the ancestor's record type P and the child record type C, the following two conditions must be met:
There are no special restrictions on the formation of communication types; the following situations are possible, for example:
A simple example of a network DB scheme:
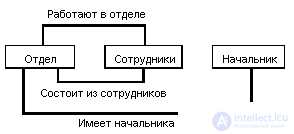
An approximate set of operations may be as follows:
In principle, their maintenance is not required, but sometimes they require integrity by reference (as in a hierarchical model).
Comments
To leave a comment
Databases IBM System R - relational DBMS
Terms: Databases IBM System R - relational DBMS