Lecture
Logical disk organization. The operating system represents any hard disk, regardless of volume, as a storage location consisting of two areas - system and data area. The system area performs a supporting role and serves to organize data storage (forms the disk file system), under normal conditions this area is not available to the user.
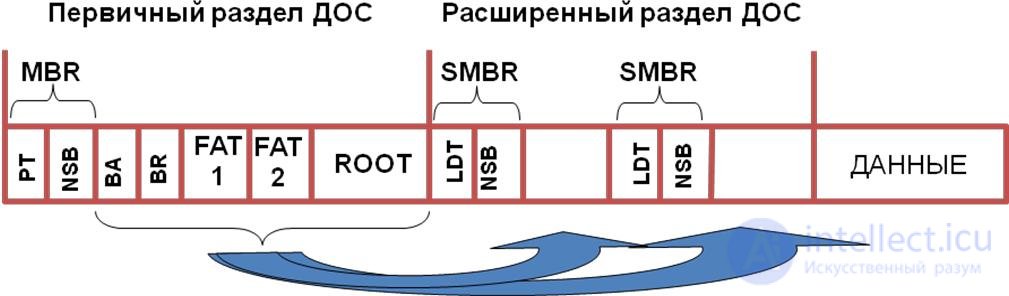
The block diagram of the system area device is presented in the figure. Figure 42 - Layout of data on the disk (logical disk organization) MBR- (Master Boot Record) - master boot record. PT- (Partition Table) - a partition table. NSB- (Non-System Bootstrap) off-system loader BA (Boot Area) - boot area of the operating system BR (Boot Record) - boot record OC. ROOT - The root directory of the SMBR- disk (Secondary Master Boot Record) –– the secondary MBR LDT - (Logical Disk Table) partition table of the logical disk. Any violations in the system area are displayed as file system errors. Diagnostics of file system violations Causes file system violations can be diagnosed by paying attention to the appearing messages: If the entire message is in upper case (i.e. capital letters), then this BIOS does not find the MBR on the specified device in the Setup device, which indicates an error reading or the absence of a sign of the system sector in the first sector of the disk (ie, the disk is not marked) To make sure that everything is fine with the disk, you need to go into the BIOS Setup and run Autodetect. The messages "Invalid partition table" and "Error loading operating system" belong to the bootloader from the MBR; the boot sector of the active partition is either unreadable or not (yet). The messages "Invalid system disk" and "Disk I / O error" give the bootloader from the boot sector, indicating that there are no operating system files or a disk error. Causes: If the problem is not related to the disk itself, you need to seriously consider where the system sectors are. In the second case, there is either a violation of the PT table, or destruction of the boot sector. In the third case, the system files could be deleted or corrupted, you can try to correct the situation by booting from a floppy disk and entering the command "sys c: \". Signs of the destruction of the partition table. The partition disappeared from Explorer. When you run the utility "Disk Management" displays an empty space. Or ghost partitions may appear, and the summation of the volumes of all logical drives exceeds the size of the hard drive itself. This means that some sections overlap with each other. The system cannot boot, but issues messages like "Bad or missing partition table" or "Error loading operating system". Windows shows a blue screen with the words "STOP: INACCESSIBLE_B00T DEVICE". Reasons for the destruction of the partition table. Erroneous deletion of the wrong partition. This option is the least dangerous because all data remains in place, but there is no access to it. Destruction of the chain of sections. This happens in case of damage to EPP (Indexes of Extended Sections). Simultaneous destruction of MBR and EPP. Manual recovery of partitions and information: To recover lost (damaged) data, you need information about: Probable partitioning of the disk into partitions and the number of logical disks. The size and history of the creation of logical drives. The history of creation implies possible artificial resizing of disk partitions. Features of the file system FAT or NTFS. The type and version of the Operating System (DOS, Win) used on the disk. The unique names of directories and files that were in the root directory of drive C, the name of the directory with the data to be prioritized and the unique names of files and subdirectories located in this directory. For manual data recovery you can use the following utilities: DiskEdit from the Norton Utilities Tiramisu kit (http://www.recovery.de) or Hard Drive Mechanic. UnFormat (from the same set of Norton Utilities). NDD - Norton DiskDoctor (from the Norton Utilities kit). Disadvantages: It is necessary to know the initial logical disk organization and features of the organization of FAT, NTFS and Linux systems. Can be used only by trained users. it takes a lot of time. When using any of the above programs for manual recovery, the following sequence of actions should be followed: 1. DIAGNOSTICS OF DAMAGES. 1.1) Start DiskEditor and, by transferring it to the viewing mode of a damaged disk at the physical level, successively check the integrity of the RT, MBR, FATs, ROOT and DA. At this stage, try to find out (if it is not known for certain) the file system type of the first partition of the disk (FAT16 or FAT32). 1.2) In the case of the integrity of any elements of the disk structure, save them as files on the backup disk. For example: MBR.HEX, BR1.HEX, FAT01.HEX, FAT02.HEX, ROOT0.HEX. 1.3) Further recovery of the disk depends on the extent and nature of the damage. If any copy of FAT remains intact (or at least partially)
Comments
To leave a comment
Diagnostics, maintenance and repair of electronic and radio equipment
Terms: Diagnostics, maintenance and repair of electronic and radio equipment