Lecture
Caesar's cipher is one of the oldest ciphers. When encrypting, each character is replaced by another, separated from it in the alphabet by a fixed number of positions. The Caesar cipher can be classified as a substitution cipher; for a narrower classification, a simple replacement cipher.
The cipher is named after the Roman emperor Guy Julius Caesar, who used it for secret correspondence. The natural development of the Caesar cipher was the Vigenere cipher. From the point of view of modern cryptanalysis, Caesar’s cipher does not have acceptable resilience.
Mathematical model
If we compare each character of the alphabet with its sequence number (numbering from 0), then encryption and decryption can be expressed by the formulas:
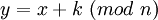
where x is the plaintext character
y is a ciphertext character
n - the power of the alphabet (number of characters)
k is the key.
You can see that the superposition of two encryption on the keys k1 and k2 - there is just encryption on the key k1 + k2. More generally, the multitude of Caesar cipher cryptographic transformations form the Z group.
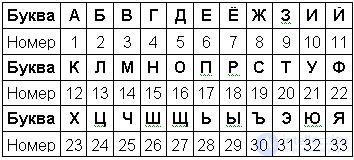
Alphabet:
Example:
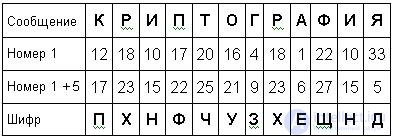
Answer: “Phnfchuzheschnd”
Comments
To leave a comment
Information security, Cryptographic ciphers
Terms: Information security, Cryptographic ciphers