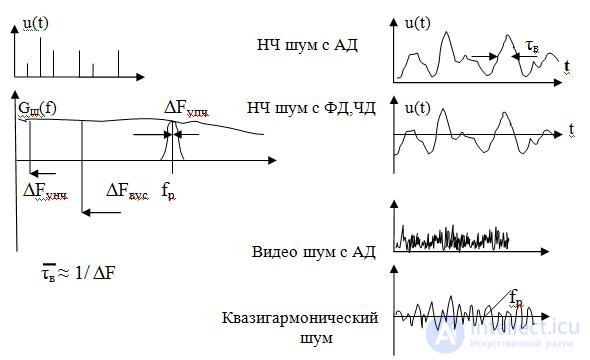
Radio devices have both passive and active functional units. So, the radio receiver consists of a large number of transistors, which operate on the principle of charge transfer with different conductivity, having shot quantity. At the output there are signal detectors and information amplifiers in the form of low-frequency amplifiers, a television signal or a digital code, etc. Amplifiers have filters tuned to different frequencies with their own bandwidth. Therefore, the type of noise, if viewed on an oscilloscope, will be different. In this regard, different types of noise are called differently: quasi-harmonic, video noise and low-frequency. In fig. 2.2 illustrates the kind of noises of these types and their features.
rice 2.1. Noise classification
If broadband noise arrives at the device input, a process is formed at the output in accordance with the frequency bandwidth. For low frequency amplifiers ? F unch is 10-30 kHz. Naturally, at the output we will see relatively slow bursts of noise. Average release duration ? at will be about 0.03-0.1 ms.
At the output of the HRO, if f p >> F , the uneven and fluctuating central frequency sine wave will be traced. f p .


Comments
To leave a comment
Radio Engineering Systems
Terms: Radio Engineering Systems