Lecture
Let be 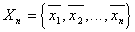 - the set of objects of the training sequence, that is, the belonging of each of them to one or another pattern is reliably known. Let also
- the set of objects of the training sequence, that is, the belonging of each of them to one or another pattern is reliably known. Let also 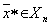 is the object closest to the recognizable
is the object closest to the recognizable 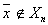 . Recall that in this case the nearest neighbor rule for classification
. Recall that in this case the nearest neighbor rule for classification 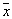 is that
is that 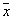 attributed to the class (image), which belongs
attributed to the class (image), which belongs 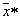 . Naturally, this assignment is random. Probability that
. Naturally, this assignment is random. Probability that 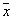 will be referred to
will be referred to 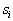 there is a posteriori probability
there is a posteriori probability 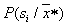 . If a
. If a 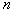 very large, it is entirely possible to assume that
very large, it is entirely possible to assume that 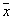 located close enough to
located close enough to 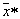 so close that
so close that 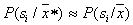 . And this is nothing but a randomized decision rule:
. And this is nothing but a randomized decision rule: 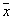 attributed to
attributed to 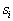 with probability
with probability 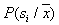 . The Bayesian decision rule is based on the choice of the maximum a posteriori probability, that is,
. The Bayesian decision rule is based on the choice of the maximum a posteriori probability, that is, 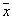 attributed to
attributed to 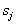 in case if
in case if
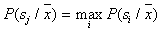 .
.
This shows that if 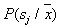 close to unity, the nearest neighbor rule gives a solution, which in most cases coincides with Bayesian. Recall that these arguments have sufficient grounds only for very large
close to unity, the nearest neighbor rule gives a solution, which in most cases coincides with Bayesian. Recall that these arguments have sufficient grounds only for very large 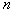 (the volume of the training sample). Such conditions in practice are not common, but they allow one to understand the statistical meaning of the nearest-neighbor rule.
(the volume of the training sample). Such conditions in practice are not common, but they allow one to understand the statistical meaning of the nearest-neighbor rule.
Comments
To leave a comment
Pattern recognition
Terms: Pattern recognition