Lecture
The Internet every day more and more resembles a self-organized universe that is evolving with great speed. And although this system does not yet have full-fledged artificial intelligence, the beginnings of its creation are already beginning to appear (for example, a virtual interlocutor of information or Akinator, who reads thoughts, machine vision and voice interface of search engines). On the day when the Turing test will be passed and the Internet on a functional tool will become an indispensable assistant, and for someone else.
Who is behind all this? Of course, these are communities of people. Communities, united by common ideas, goals and interests, who are willing to spend their time and resources on the implementation of these ideas. Therefore, every day more and more reasonable programs appear on the Internet, their functionality is becoming wider, and visitors are turning from consumers into active content creators.
A virtual interviewer (bot consultant) is a technical support specialist who is available around the clock and instantly answers user questions. He communicates in a natural language. He can not only help find something on the site, but also offer useful information or product for the user. The bot keeps the questions asked to it. Thanks to this, the site owner can find out what they are looking for on the site, what is missing, what can be improved, what audience customers.
Bot is a built-in module. To view the bot module, you need to insert a short special code on the necessary pages of the site. The consultant may have a standard design. But it can also be designed as an individual character for a particular site.
Bot must be taught to answer questions from visitors. Initial training is based on the initial vocabulary. In the future, analyzing the customer and bot dialogs, the site owner can continue learning on their own.
All the steps for setting up the bot, placing its knowledge base, collecting dialogs, etc., are developed by the developer themselves. In case of any questions or necessary improvements, the company-developer supports the work of Bot-consultant.
 http://www.nanosemantics.ru/
http://www.nanosemantics.ru/
“Nanosemantika” is the leader of the Russian market of artificial intelligence technologies aimed at solving business problems. Since 2005, the company has been developing Infiv - virtual interlocutors controlled by artificial intelligence. "Nanosemantics" develops technologies and online services, which are based on a direct dialogue between the machine and the user.
 http://chatbot.tw1.ru/business.htm
http://chatbot.tw1.ru/business.htm
A consultant who is able to work 24 hours a day, 7 days a week without rest and lunch breaks is a dream for service companies with a large number of customers who ask the same questions.




The pioneer was a small Canadian company Tineye, the second - Google, and the third - the Chinese search engine Baidoo. Yandex has become the fourth player and hopes that Microsoft will follow up with them. However, Tineye has a very small database of images (3500000000), and in Baidoo there is a strong bias in the Chinese market. For a Ukrainian user, the use of a search in Yandex and Google will be appropriate: their database of images is tens of billions of images.
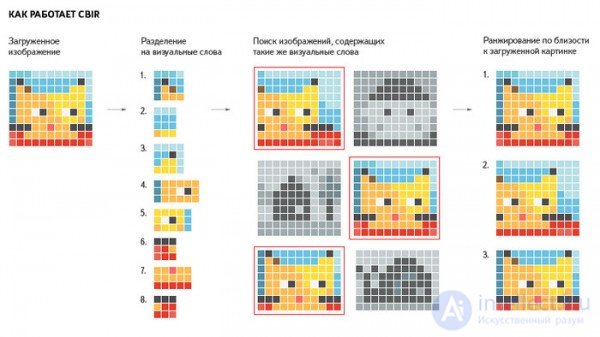
The image search service uses data analysis and classification algorithms, and computer vision technologies and image content descriptions are used to search for images by visual content. This technology turns the loaded picture into a set of "visual words". After that, the system among the billions of pictures that are contained in its database selects an image that have similar “visual words” and gives them to the user. In this case, the search will take less than a minute.
Alexander Krainov, Computer Vision Project Manager
The developers of Yandex have developed their own algorithm, which is very different from analogues. Computer technology used by Yandex is called Content Based Image Retrieval (CBIR) and is called Siberia within the company.
Based on the generalized limits of objects, contrasting areas and other key elements of the picture, the robot creates its image library, just like a regular search engine downloads simplified text versions of web pages when indexing, and is already searching for it. The ability to generalize already shows the search: sometimes there is not just the same picture, but another image containing the same object.
This algorithm works best with the URL of the image, rather than downloaded from the computer. That is, when the original image is placed on the Internet, and not on the user's computer. Since the search base outlines of objects is formed by images that are already indexed by the system, therefore, if the image is not in the search database, there will be no good result.
Unlike Google, which distinguishes colors, the new Yandex algorithm does not distinguish colors, but is able to analyze the outlines of objects. After the analysis, a search query is formed for the standard (verbal) image search. The exceptions are trademarks and fonts - popular logos, as a rule, the program recognizes. The same applies to monuments and architectural images. Therefore, the search for an architectural monument by the loaded picture (photo) will be more successful than the search for a photo of a home holiday.
It is worth noting that the search for images from Google also often does not work correctly - the results often show different images with similar colors. However, it is clear that this direction is just beginning to develop. Yandex went its own way, while not lagging behind other competitors. Further development of Yandex is moving in the same direction as Google, has introduced technology Goggles in mobile search. Google Goggles allow you to search in real time for an image that is taken from the camera of a smartphone.
Thanks to the Voice Interface, you can dictate requests in the client program on the device, and not enter them. To transcribe dictated words into written text, Google directs expressions to servers using pattern recognition technology.
In order to teach the system to better recognize the correct search queries, Google stores statements to improve the services, in particular: data about the language, country, expression and assumptions of the system about what was said. Audio data saved does not contain a Google account ID, if the user does not specify this.

For each language, Google Voice Interface collects voice clips that allow you to create language models that ensure the correct operation of services. Google has a database of audio images, pronounced by native speakers, distinguished by accents, age and individual characteristics, to pronounce frequently used phrases in various acoustic conditions, for example, in a restaurant, on the street or in a car. For each language, Google creates a dictionary containing over a million recognized words.
The service works on the basis of the Speech Input API system, due to which the voice control of the Internet browser is implemented. The service is now embodied in Google Search, Google Translator, Cmail, Google Docs.
 Voice Search is an extension for Google Chrome that allows you to search or otherwise act on the Internet using your voice. On the Google page in the search bar shows the microphone icon. The user must click on it and say a phrase or word loudly and clearly. To get voiced answers you need to use the language in accordance with the voice interface of Google Chrome.
Voice Search is an extension for Google Chrome that allows you to search or otherwise act on the Internet using your voice. On the Google page in the search bar shows the microphone icon. The user must click on it and say a phrase or word loudly and clearly. To get voiced answers you need to use the language in accordance with the voice interface of Google Chrome.
In the case of a request for noticeable or generally recognized objects, information will be announced that is taken from the “Knowledge Graph” of Google, a database containing information about various objects, events and their connection with each other. Information from the “knowledge graph” is usually displayed to the right of the search results and provides information on the query that the user entered.
This may be, for example, information about the actor, including films, in which he starred, and date of birth. For example, the answer to simple questions “How many dollars will be in 100 hryvnia”, “what is the name of the capital of France”, “who is Manuel Barroso” will be subject to voicing
The Google search engine offers a Google voice calculator that allows you to instantly get an answer to any, even the most complex, calculations using voice input devices.
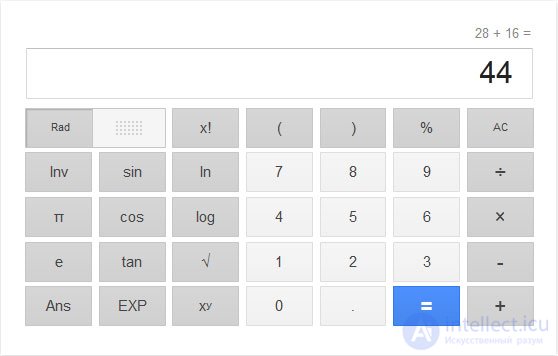
To run the calculator, you need to open Google Chrome and run google.com, better with an open account. Turn on the voice input device on your computer and clearly and clearly speak arithmetic in Chrome. A calculator will appear in the search line, showing the action and the result of the calculation.
You can interact with the calculator manually, by mouse or on the numeric keypad by typing numbers and variables. The Google voice calculator provides 15 algebraic operations, with parentheses, percentages, pi and e, and other variables.
Google has begun work on a universal translator of a fundamentally new type. The idea of the new project is to create a service that will allow users, communicate in different languages, to speak with each other in real time, and that is to “speak”, and not “correspond”. In other words, the translator must recognize the language, translate the resulting text and reproduce it in another language.
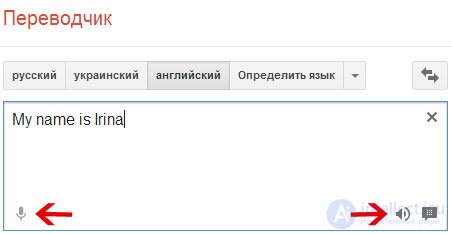
Google translate quite successfully translate texts into 52 different languages. Refinement of existing technologies to the required level will take several more years. To translate a specific phrase, just click on the microphone image in the program, say the right words into the microphone and the program will automatically send the recorded speech to Google servers, where the audio file will be analyzed and the phrase translated. After the text translation, you can listen to the pronunciation of the translation and the original text (synthesized female voice).
Google warns that while the function is experimental, and one should not expect 100% correct operation from it. Correct translation can be hampered by such factors as accent, clarity of pronunciation and background noise.
For Google cloud services, there are several text entry methods. The combination of IME editors or transliteration tool, virtual keyboards and handwriting allows you to support more than 90 languages.
 Google search
Google search  Gmail
Gmail  Google drive
Google drive  google translator
google translator  YouTube
YouTube Google has added handwriting recognition to popular services. For example, a special field appeared in Google Translate, supports handwritten data entry. For example, you can draw a hieroglyph and instantly know its exact notation. The new opportunity is useful to Europeans and Americans learning Asian languages (the project concentrates precisely on the languages of Asian groups) and do not know their clever writing. Today there is the possibility of recognition of texts in the Ukrainian language
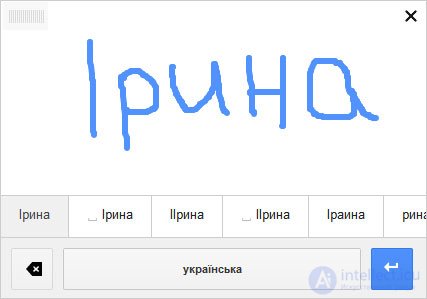
To enter text, you can use the mouse or touchpad, where there is normal support for handwriting. To get started with handwriting input, you’ll need to enable the corresponding feature in Gmail. In Google Docs it will be enough to use the Ctrl + Shift + K combination.
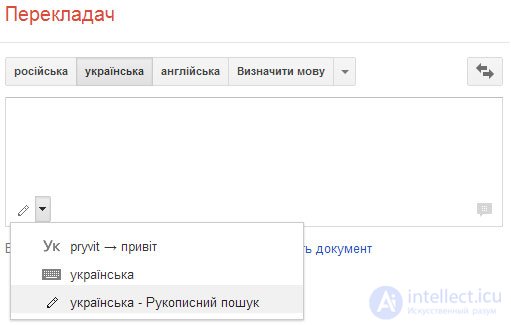
New Google will be gradually included for different regions, therefore, this feature may be absent from the user. For those who print faster than writing, this feature will not be needed. For users who type languages, characters in which more than the standard keyboard contains, innovation may be useful.
https://support.google.com/plus/answer/2370300?hl=uk
Google has come to grips with face recognition technology in the photo. In order to speed up this process, the corporation bought the company PittPatt, which is developing appropriate technologies. PittPatt is engaged not only in recognizing faces in photographs, but also in recognizing photographs in general, with subsequent marking (marking) of recognized objects.
The results of the development are being implemented in various programs and services of the company, both regular and mobile. The technology integrates into the photo and video applications of Picasa, Goggles, YouTube and Google+.
Comments
To leave a comment
Pattern recognition
Terms: Pattern recognition