Lecture
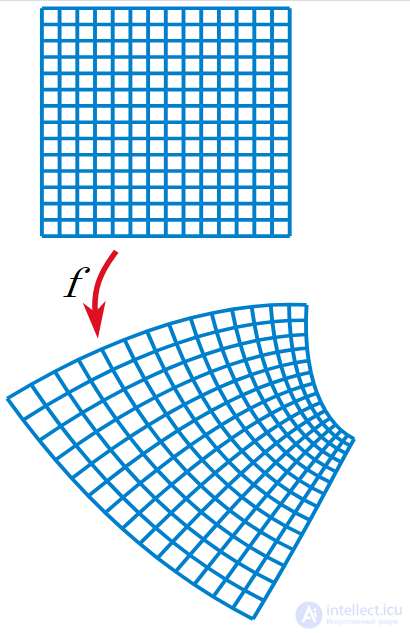
The holomorphic function realizes a conformal mapping, transforming an orthogonal grid into an orthogonal grid (where the complex derivative does not vanish).
A holomorphic function , sometimes called a regular function, is a function of a complex variable, defined on an open subset of the complex plane. 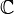 and complexly differentiable at every point.
and complexly differentiable at every point.
In contrast to the real case, this condition means that the function is infinitely differentiable and can be represented by a Taylor series converging to it.
Holomorphic functions are also sometimes called analytic , although the second concept is much broader, since the analytic function need not be defined on a set of complex numbers. The fact that for complex-valued functions of a complex variable of the set of holomorphic and analytic functions coincide is a nontrivial and very remarkable result of a complex analysis.
Let be 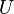 - open subset in
- open subset in  and
and 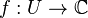 - complex-valued function on
- complex-valued function on 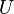 .
.
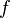 called complex differentiable at the point
called complex differentiable at the point 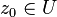 if there is a limit
if there is a limit
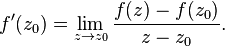
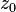 , for all such sequences, the expression must converge to the same number
, for all such sequences, the expression must converge to the same number 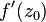 . Complex differentiation is in many respects similar to the real one: it is linear and satisfies the Leibniz identity.
. Complex differentiation is in many respects similar to the real one: it is linear and satisfies the Leibniz identity. called holomorphic in
called holomorphic in 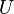 if it is complexly differentiable at each point
if it is complexly differentiable at each point 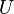 .
.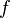 called holomorphic in
called holomorphic in 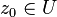 if it is holomorphic in some neighborhood
if it is holomorphic in some neighborhood 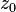 .
.The definition of a holomorphic function can be given a slightly different form, if you use the operators 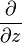 and
and 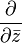 determined by rule
determined by rule
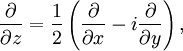
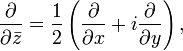
Where 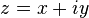 . Then the function
. Then the function 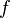 called holomorphic if
called holomorphic if
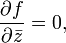
which is equivalent to the Cauchy – Riemann conditions.
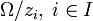 and having in all its particular points
and having in all its particular points 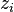 pole.
pole.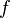 called holomorphic on a compact
called holomorphic on a compact 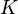 if there is an open set
if there is an open set 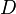 containing
containing 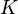 such that
such that 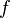 holomorphic in
holomorphic in 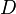 .
.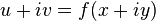 is holomorphic if and only if the Cauchy – Riemann conditions are satisfied
is holomorphic if and only if the Cauchy – Riemann conditions are satisfied
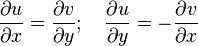
and partial derivatives 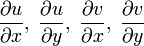 are continuous.
are continuous.
 . That is, if
. That is, if 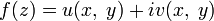 Is a holomorphic function, then
Is a holomorphic function, then 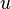 and
and 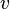 - harmonic functions.
- harmonic functions.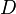 converges uniformly on any compact in
converges uniformly on any compact in 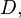 then its sum is also holomorphic, and its derivative is the limit of the partial sum of derivatives of the series [1] .
then its sum is also holomorphic, and its derivative is the limit of the partial sum of derivatives of the series [1] .The term “holomorphic function” was introduced by two students of Cauchy, Brio (1817–1882) and Bouquet (1819–1895), and is derived from the Greek words őλος ( holos ), which means “whole”, and μoφφ ( morphe ) - a form, image . [2]
Today, many mathematicians prefer the term “holomorphic function” instead of “analytical function”, since the second concept is more general. In addition, one of the important results of the complex analysis is that any holomorphic function is analytic, which is not obvious from the definition. The term “analytical” is usually used for more general functions that are not necessarily defined on the complex plane.
There is also a definition of the holomorphy of functions of several complex variables.
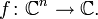
For the definition used concepts 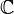 -differentiability and
-differentiability and 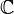 -linearity of such functions
-linearity of such functions
C-linearity [edit]
Function 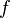 called
called 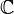 -linear if conditions are satisfied:
-linear if conditions are satisfied:
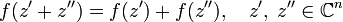 .
.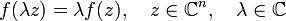
(for 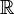 -linear functions
-linear functions 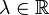 ).
).
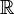 -linear function
-linear function 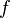 there are sequences
there are sequences 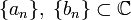 such that
such that 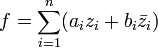 .
.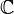 -linear function
-linear function  there is a sequence
there is a sequence 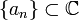 such that
such that 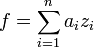 .
.C-differentiability [edit]
Function  called
called  -differentiable at a point
-differentiable at a point 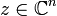 if functions exist
if functions exist 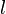 and
and 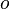 such that in the neighborhood of a point
such that in the neighborhood of a point 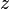
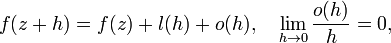
Where 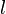 -
- 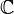 -linear (for
-linear (for 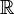 -differentiability -
-differentiability - 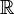 -linear function.
-linear function.
Holomorphy [edit]
Function 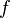 called holomorphic in the domain
called holomorphic in the domain 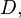 If she
If she 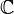 -differentiable in a neighborhood of every point of this area.
-differentiable in a neighborhood of every point of this area.
Comments
To leave a comment
Comprehensive analysis and operational calculus
Terms: Comprehensive analysis and operational calculus