Lecture
The line L is called the asymptote of the curve. 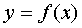 , if the distance from a certain point of the curve M (x, y) to the straight line L tends to zero with an unlimited distance of this point along the curve from the origin (that is, if at least one of the coordinates of the point M tends to infinity).
, if the distance from a certain point of the curve M (x, y) to the straight line L tends to zero with an unlimited distance of this point along the curve from the origin (that is, if at least one of the coordinates of the point M tends to infinity).
Asymptotes are divided into vertical and oblique.
Straight 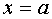 called the vertical asymptote curve
called the vertical asymptote curve 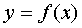 , if a
, if a 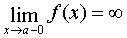 and (or)
and (or) 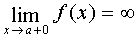 .
.
Straight 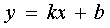 called the sloped asymptote curve
called the sloped asymptote curve 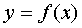 if there are finite limits:
if there are finite limits:
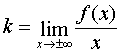 ;
; 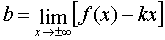 . If it turns out that k = 0, then the asymptote is called horizontal.
. If it turns out that k = 0, then the asymptote is called horizontal.
Comments
To leave a comment
Mathematical analysis. Differential calculus
Terms: Mathematical analysis. Differential calculus