It consists in receiving single-mode mode.
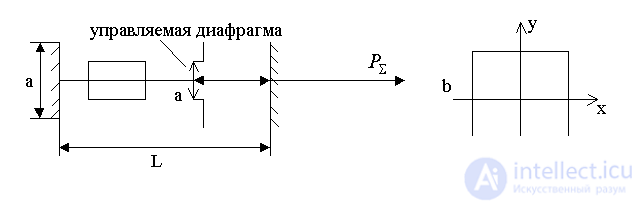
one). Selection method of controlling the Fresnel number.
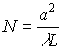 .
.
It is known that the Fresnel number controls the diffraction loss.
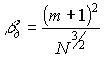 .
.
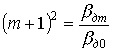 .
.
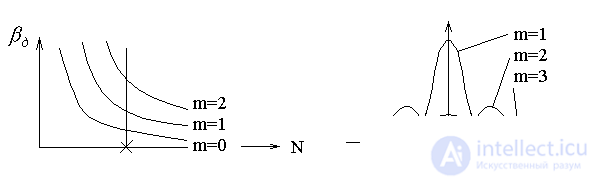
With a change in the size a of the aperture, as follows from the figure, the diffraction losses of the fundamental mode decrease, but naturally the radiation energy decreases.
2). Selection using the reflection coefficient of the mirror, the reflection coefficient of which repeats the shape of the mode to be selected.
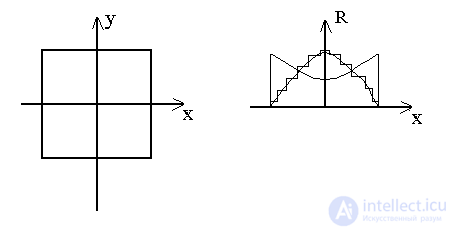
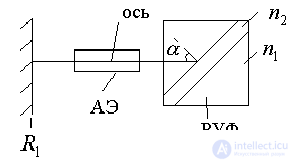
3). Selection using RUF.
In the far zone, the radiation is the FS in the coordinate. Consequently, limiting the angular spectrum, we can select the transverse modes, since each transverse mode has its own spectrum.
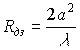 .
.
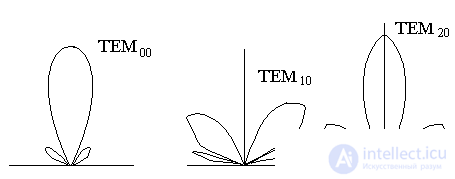
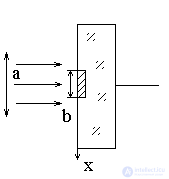
PV angles (PV spatial frequencies).
b << a 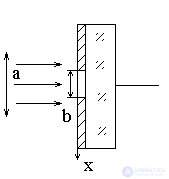
FNU (FNPCH).
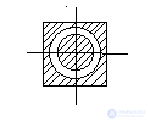
PPPF (PPUF).
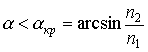 .
.
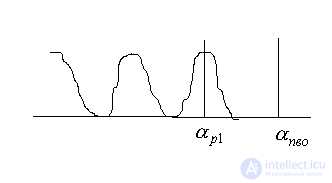
Disadvantage: multi-wave system (multilobe pattern).
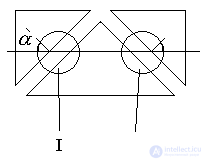
Another type of angular resonant filter is presented in the following figure.
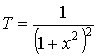 .
.
The crossed filter allows you to get rid of side lobes.
four). Open resonator as a filter in a reflective device.
Due to the imposing devices, it is possible to obtain a single-mode regime in a wave-like resonator, which corresponds to the dielectric waveguide mode.
five). Telescopic resonator.
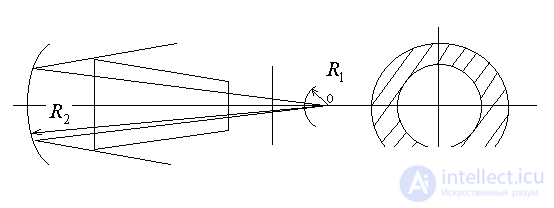
6). Gaussian filter.
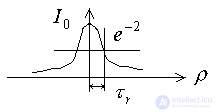
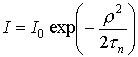 .
.
Gaussian filter is widely used in cellular communication (the impulse is obtained of a bell shape).


Comments
To leave a comment
Quantum electronics
Terms: Quantum electronics