Lecture
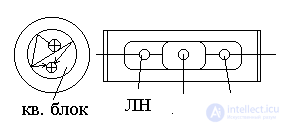
The pumping system in the solid-state laser.
Determine the minimum LF power required to excite a ruby laser.
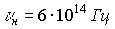 ,
, 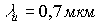 ,
, 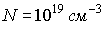 ,
, 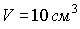 ,
, 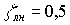 ,
, 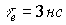 .
.
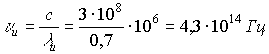 ,
, 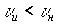 .
.
As is known, for a ruby laser to be emitted, it is necessary that the number of active particles 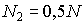 .
.
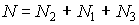 ,
, 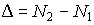 .
.
one). 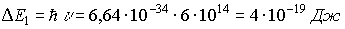 - this is for 1 photon.
- this is for 1 photon.
2). 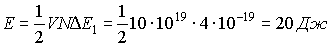 .
.
3). 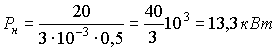 .
.
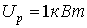 ,
, 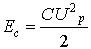 ,
, 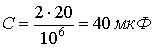 .
.
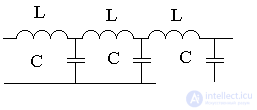
Laser efficiency
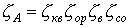 .
.
1 factor shows how many coherent quanta are in the excitation of light. The approximate value is 0.9-0.001.
2 - efficiency of an open resonator. 0.3-0.7.
3 - Excitation efficiency - how much energy is spent on pumping. 0.1-0.7.
4 - Service system Efficiency - the proportion of energy expended in cooling the Quanton. 0.5-0.9.
Turns out 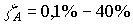 .
.
Working with laser devices requires strict adherence to safety rules, since laser radiation can cause serious harm to the eyes, skin and other organs. Below are the basic precautions.
1. Classification of lasers by hazard
Lasers are divided into several classes according to the international standard:
Class 1 - safe lasers (for example, in CD / DVD drives).
Class 2 - low-power visible lasers (up to 1 mW, for example, laser pointers).
Class 3R - moderately dangerous lasers (up to 5 mW, a short-term glance usually does not cause damage).
Class 3B - dangerous to the eyes and skin (up to 500 mW).
Class 4 - powerful lasers (over 500 mW), which can cause burns and fires.
2. General safety rules
Use of protective glasses – mandatory for lasers of classes 3B and 4. The glasses must match the wavelength of the laser used.
Access restrictions – work with powerful lasers must be carried out in specially equipped rooms with warning signs.
Beam direction control – it is prohibited to direct the laser beam at people, animals, mirror and shiny surfaces.
Radiation blocking – if necessary, switch off the laser using protective curtains, covers and locks.
Ventilation – when working with lasers that cause evaporation of materials (e.g. CO₂ lasers), an exhaust system must be used.
Use of laser protective screens – if the work requires protection from scattered or direct radiation.
3. Eye protection
Laser radiation can irreversibly damage the retina!
Never look into the laser beam, even if it seems weak.
Use special protective glasses that match the wavelength and power of the laser.
4. Skin protection
Avoid exposing exposed skin to the beam, especially when working with high-power lasers.
Wear protective gloves and clothing when working with ultraviolet lasers.
5. Fire safety
High-power lasers (Class 4) can ignite paper, fabric, and other flammable materials.
Keep flammable materials away from the work area.
Have a fire extinguisher available in the lab or room.
6. Electrical safety
Laser systems operate with high voltages - do not touch internal components during operation.
Use grounding and insulated tools when setting up laser equipment.
7. Administrative measures
Conduct safety training before starting work.
Mark laser radiation areas with warning signs.
Check equipment regularly for proper operation.
Following these rules will help prevent accidents and ensure safe work with lasers.
а как делают насадки на лазер и лазерные указки?
Нужно делать из осевые фазовые сфокусированные голограмм.
Их можно изготовить и на фотопластинках, но дешевые насадки делают на пластике, типа тисненых голограмм (дотматрикс)
Правда на счет осевых не уверен, но для внеосевых - если обычную просветную голограмму осветить неразведенным пучком, то действительное изображение будет плоским (т.е. практически не будет дефокусироваться на любом расстоянии пробовал сам на 3х мерных диффузных объектах). Изображение конечно рваное, но не хуже чем на китайских указках.Как делать: Берем диффузный объект - черный фон / белая надпись и пишем просветную голограмму лейта, потом отбеливаем. Светить под углом записи. Самое любопытное что из 1 пластинки 30 40 см можно нарезать около 5000 мелких голограмм (это наверное единственный практический случай когда кусок голограммы восстанавливает всё изображение )
Comments
To leave a comment
Quantum electronics
Terms: Quantum electronics