Lecture
The output power of the laser depends on the length of the active element, the losses in the resonator and on the transmission of the output mirror.
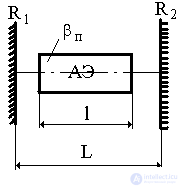
Fig.1 Block diagram of the resonator.
Fig.2 Multilayer mirror.
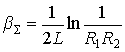 ,
,
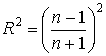 ,
,
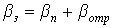 ,
,
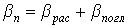 ,
,
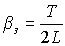 ,
,
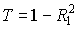 ,
,
Where 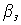 - specific mirror losses;
- specific mirror losses;
T is the transmission of the mirror;
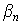 - total loss;
- total loss;
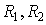 - the size of the mirrors.
- the size of the mirrors.
Full power:
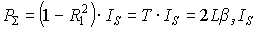 ,
,
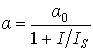 ,
,
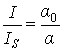 ,
,
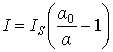 .
.
Threshold condition of self-excitation.
In this case, the laser resonator is completely filled.
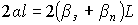 ,
,
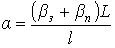 ,
,
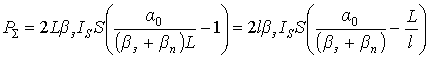 ,
,
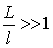 .
.
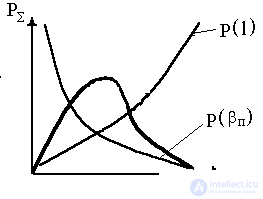
Fig.3. Dependence of power on various parameters of the resonator.
There is an optimal transparency of the mirror. Install analytically 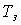 optimal.
optimal.
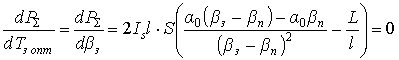 ;
;
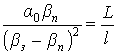 ;
;
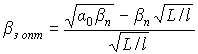 ;
;
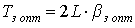 .
.
Radiation loss: 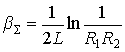 .
.
With increasing L and decreasing a, we can increase the diffraction loss 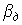 where a is the internal size of the diaphragm. By changing the diffraction loss, we can excite either one main or several modes.
where a is the internal size of the diaphragm. By changing the diffraction loss, we can excite either one main or several modes.
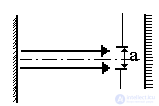
In the far zone, the radiation will be bound by the following formula
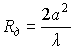 .
.
Comments
To leave a comment
Quantum electronics
Terms: Quantum electronics