In practice, in order to obtain a small angular divergence, they strive to make a single-mode single-frequency mode. Single mode allows low angular divergence.
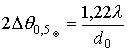 .
.
For example, 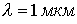 ,
, 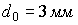 . Then
. Then 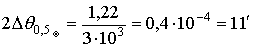 .
.
For multimode modes, the divergence will be less, which follows from the following formula.
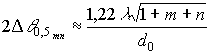 .
.
Increased angular ability is important to have in laser radar systems (LLS).
Single-frequency is important for high-precision measurements in the Doppler location.
Selection of cola *** laser types.
- Selection of longitudinal modes.
It consists in the suppression of all types of stake *** except one.
one).
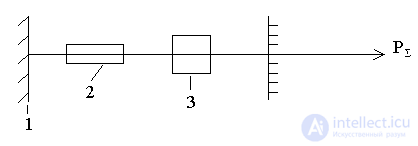
1 - deaf mirror  , 2 - active element, 3 - absorbing cell, 4 - output mirror
, 2 - active element, 3 - absorbing cell, 4 - output mirror 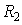 .
.
In a geleneone laser, ammonia is used as an absorbing cell.
2). Using Newton's dispersing prism.
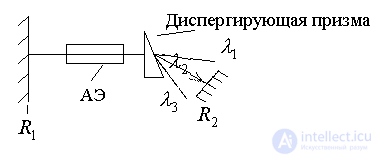
3). Fabry-Perot interferometer method.


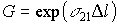 .
.
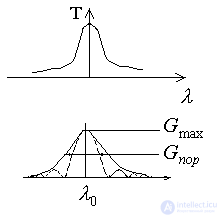
four). With an absorbing film.
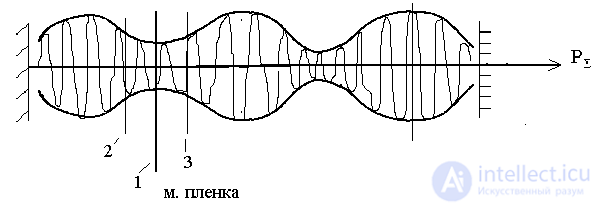
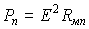
In the node, the losses are minimal, and in the antinodes are maximum. At points 2 and 3, the losses increase, G decreases. Since G <G then , the laser is therefore not excited. As the frequency changes, the field distribution changes and losses increase, which leads to a decrease in the gain. This design is very sensitive to changes in ambient temperature.
five). Using a two-resonator system (Fox-Smith resonator).

P - dividing cube. The result is two coupled resonators.
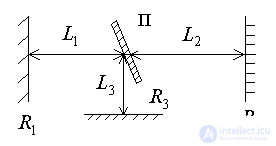
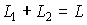 ,
, 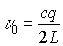 ,
,
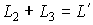 ,
, 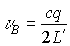 .
.
Since the auxiliary resonator is shorter than the main resonator, the frequency response will be more rarefied. The resulting characteristic is equal to the product.
6). Active method of selection using APPF.
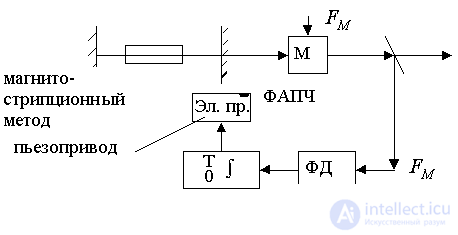
The selected signal from the optical signal is detected and compared with the reference. From PD to drive the laser mirror, which shifts it to a maximum radiation.
In practice, precision systems use dual-circuit systems with a FAN and FAP.


Comments
To leave a comment
Quantum electronics
Terms: Quantum electronics