Lecture
Administrative communication is fundamentally conflicting, approximately 70-80% of the work of a manager is under the weight of hidden and obvious contradictions and confrontations, ignoring of which leads to conflicts.
Conflict is a collision of oppositely directed goals, interests, positions, opinions of individuals and social groups.
The conflict has many faces and is sometimes extremely complex, “multi-storey” in its origin, rooted in the depths of the human psyche, social problems, ethnic characteristics, etc. Explain the nature of the conflict, diagnose its development, predict the phases of its development, i.e. All analytical work on the study of the components of the conflict is the key to conflict management. For even the ancient sages said that evil can be eradicated only by knowing its causes.
Leaving conflict without attention is the same as leaving embers in an empty house: a fire may not happen, but if it happens ... In general, the analogy between conflict and fire is very deep: both are easier to prevent than to extinguish; in both In some cases, the time factor can be decisive, since both conflict and fire are terrible in their growth.
The proliferation, "escalation" of conflicts occurs according to the following scheme:

This is explained by the fact that the participants in the conflict are looking for support from others, "recruiting" their supporters. Especially trying to attract to their side leader. The original conflict is overgrown with new clashes reflecting the interests of all participants. At the same time, the tension of relations grows, the emotional intensity of the passions in the team begins to "go off scale". All of this convinces us that, having received information about the differences that have arisen, the leader must act and take measures without waiting for the conflict to grow. Moreover, inaction, the position of non-interference in the team is regarded as indifference, and even as cowardice.
To be able to choose an adequate impact method and manage conflicts, it is necessary to freely navigate in their classification, types. One of the possible variants (far from the only one!) Of the typology of conflicts is presented in fig.
|
|
|||||||||||

In terms of conflicts are divided into intrapersonal , interpersonal , intergroup .
By the duration of the flow of conflicts are divided into short-term and protracted . The former are most often the result of mutual misunderstanding or mistakes that are quickly realized. The latter are associated with deep moral and psychological trauma or with objective difficulties. Long-term conflicts are very dangerous, because in them the conflicting personalities reinforce their negative state. The frequency of conflicts can cause deep and long-term tensions.
The criterion for grouping conflicts can be considered the degree of their influence on the life of the team. In this case, they speak of febrile conflicts and destructive contradictions for the collective. There are conflicts that give complications in the subsequent life of the team (after the conflict) and do not have any negative consequences. Post-conflict manifests itself in negative behavior or dissatisfaction after the termination of the conflict. This means that the conflict was not resolved or was resolved unfairly, or by methods affecting the personal dignity of people. The emergence of post-conflict can be promoted by dissatisfaction of interests, reliance on one-sided benefits, insufficient opportunities to “save face”, a feeling of pressure and coercion, “spiotechnics” and other psychological and behavioral factors.
The focus of conflicts are divided into horizontal , vertical and mixed . Horizontal conflicts include those in which persons who are subordinate to each other are not engaged. Vertical conflicts are those whose members are subordinate to each other. In the mixed are presented both vertical and horizontal components.
Vertical conflicts are most undesirable for a manager, since in this case, it is usually “bound hand and foot”. Each of its actions is viewed by all employees (not to mention the parties to the conflict) through the prism of this conflict. And even in the case of complete objectivity of the head, at any step he will look for secret designs and machinations in relation to his opponents. Misunderstanding of subordinates is usually more than compensated by speculation, mainly of an aggressive nature. As a result, the conflict is aggravated, and working in such conditions is extremely difficult. Already from this preliminary consideration some of the necessary attitudes of managerial behavior are visible: the greatest caution should be exercised with respect to vertical conflicts and not letting oneself be involved in them, if not in that particular interest.
By the nature of the causes of conflict can be divided into objective and subjective .
At the same time, the objective causes of conflicts are usually divided into groups according to their underlying factors - information, structure, values, attitudes, and behavior.
Many conflicts are based on information that is acceptable for one side and unacceptable for the other. These may not be complete and inaccurate facts, rumors, doubts about the reliability and value of information sources, suspicions of deliberately hiding information, controversial conclusions and conclusions, etc.
Structural factors of conflict are usually associated with the existence in the social group, the organization of formal and informal structures and their interaction on issues of ownership, status, authority, various norms and standards, issues of encouragement and punishment, reporting, etc.
Value factors are those principles that we proclaim or reject. These are group or personal belief systems, beliefs and behaviors (preferences, aspirations, prejudices, fears), ethical, cultural, professional values and needs.
Relationship factors are associated with a sense of satisfaction (or lack thereof) of interpersonal interaction. At the same time, it is important to take into account the basis of relations (voluntary or coercive), their essence (independent, dependent, interdependent), balance of power, mutual expectations, duration of relations, contribution of the parties to relations (money, emotions, time, energy), etc.
Behavioral factors inevitably lead to conflicts, if interests are infringed, self-esteem is undermined, security risks arise, if selfishness, irresponsibility, injustice, etc. appear.
Such a grouping of the causes of conflicts contributes to their understanding and analysis, but it should be remembered that real life is richer than any scheme and many other causes of contradictions can be identified, as well as to identify the close intertwining of various factors in a given conflict.
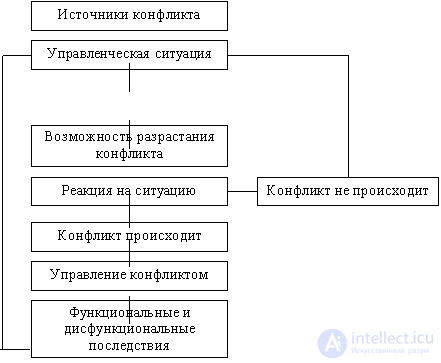
The presented conflict model gives a clear idea that even if a conflict situation exists, its further aggravation is not inevitable if the reaction to the conflict is correct. A manager can convince others to make a proposed decision with the help of such means as coercion, bribery, appeal to traditions and mediators, expert assessments, charisma, etc.
But it is always preceded by a qualified analysis of the conflict (causes, participants, type, dynamics, etc.).
To determine the formula of a conflict, one should skillfully operate with the categories which are basic for a conflictologist:
“ Conflict agent ” (Cg) is words, actions (or inaction) that can lead to conflict.
“ Incident ” (I) is a confluence of circumstances, a cause for conflict.
A “ conflict situation ” (CC) is an accumulated contradiction containing the true cause of the conflict.
“ Conflict ” (K) is an open confrontation as a result of mutually exclusive interests and positions.
The degree of inevitability of conflict clearly emerges from the analysis of the following conflict pattern:
Formula conflict.
Conflict type |
Conflict formula |
The degree of inevitability of conflict |
|
BUT B AT |
Kg 1 + Kg 2 + ... K KS + and K КС 1 + КС 2 + ... К |
Case Is natural Inevitable |
There is a conflict in Model A, since the escalation of conflicts is most often the result of either a person’s bad manners or a bad mood. It is enough to interrupt the conflict conflict chain in order to prevent a conflict or extinguish it at the very beginning.
Therefore, the rules of conflict-free communication are so simple in this case:
one. Do not use conflict users (the most powerful of them are manifestations of selfishness, superiority or aggression)
2 Do not respond to the conflict agent with the conflict agent.
3 Show attention and sympathy to the interlocutor.
four. Show active goodwill.
It is much more difficult to choose the tactics of the leader’s behavior in model B and B conflicts.
Necessary is a thorough diagnosis of the conflict.
The scheme of diagnosis of the conflict.
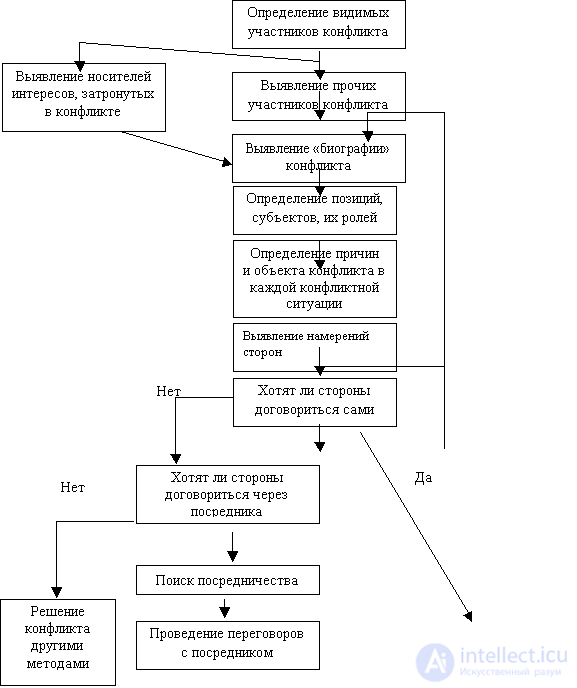
Perhaps the greatest difficulty is the formulation of the essence of a conflict situation. Therefore, the head needs to learn the basic rules for formulating a conflict situation . Here they are:
RULE 1.
Remember that a conflict situation is something that needs to be fixed.
Consequently, the following wording is not suitable: “a conflict situation is in this person” (or “... in the socio-economic situation”, or “... in shortage of vehicles on the line”), etc., because we have no right to eliminate a person at all; None of us will change the socio-economic situation alone and the number of buses on the line will not increase !!!
RULE 2.
A conflict situation always occurs before a conflict.
The conflict also occurs simultaneously with the incident. Thus, the conflict situation precedes the conflict and the incident.
It is not by chance that in the conflict formula the conflict situation comes first, then the incident and then the conflict !!!
RULE 3.
The wording should tell you what to do.
For example, conflict situations have shown that it is necessary to continue to behave more patiently, to prevent the fall of its image, authority !!!
RULE 4.
Ask yourself “why?” Questions until you get to the root cause, from which others flow.
If we use the analogy with a weed, then this means: do not pull out only a part of the root, the rest will reproduce the weed anyway !!!
RULE 5.
Formulate a conflict situation in your own words, if possible without repeating words from the conflict description.
The bottom line is that when considering a conflict it is usually said a lot about its visible sides, that is, about the external manifestation of the conflict or about the incident. To understand the conflict situation, we approach after some conclusions and generalizations (combinations) of heterogeneous constituents. This is how words appear in its wording, which were not in the original description.
RULE 6.
In the formulation manage with a minimum of words.
When there are too many words, the thought is not concrete, side nuances appear, etc. Here, as the aphorism “brevity is the sister of talent” is appropriate anywhere !!!
Conflicts are open and hidden. The first lie on the surface, and the second are hidden behind the screen of favorable relations. Hidden conflicts can only be recognized by indirect manifestations . The manager needs to have an idea about the signs of conflict situations in production.
The most characteristic signs of conflict situations in labor collectives are:
a) the facts of humiliation of the dignity of the individual in a formal or informal setting;
b) a dramatic change in attitude to work (functional responsibilities);
c) the facts of evasion from the fulfillment of instructions, orders of immediate superiors;
d) isolation, solitude, depression of individuals;
e) the formal formulation of work on personnel management;
e) negative judgments about the life and activities of colleagues, etc.
The study of conflicts in organizations shows that the main condition for their occurrence is a violation of the moral forms of relationships between employees and the organization of the production process itself. Observations indicate that the more people in a team are satisfied with their work, the more favorable the moral and psychological climate is, the more developed a partnership and mutual assistance and, conversely, the more dissatisfied with work, the worse the atmosphere in the team, the more often various conflicts erupt . In some organizations, managers are forced to spend 50% or more of their working time studying and settling various conflicting relationships.
All workers on the commitment to conflict can be divided into three groups: stable, withholding and conflict. The number of the third group is about 6 - 7% of the total number of organizations. These are difficult people who create various excesses in the control system, and the tactics of relationships with them require from the manager sufficient knowledge and psychological subtlety.
Consider the main types of "difficult" people and acceptable ways to communicate with them.
"The mad bulldozer".
Rude, unceremonious type, everywhere bursting through. In dealing with him, the main thing is equanimity. Let the "bulldozer" go crazy. Do not try to object or argue, and his rage will gradually fade away. When this happens, you can express your point of view, pretending, however, that you do not doubt that he is right, otherwise he will throw himself at you again and try to crush.
"Secret dirty dog".
A vile type, weaving intrigue and building intrigues behind your back. His weapon is betrayal and treachery. It does not matter who he is - your subordinate or your business partner, the main thing is that he does not shun anything and always digs a hole for you. It is possible to neutralize the “secret dirty dog” if this hole is shown to him and hinting that he himself can go there. Finding that his machinations are revealed, the dirty dog will calm down, he does not act on the light.
"Aggressive child."
A person is kindly kindly, but explosive (often for the reason that he is not sure of himself). If you let him scream, he will soon calm down, like a child, which returned the toy. In this state, it is possible to twist the rope, but ... until a new explosion.
"Whiner."
Forever whining and complaining, feeling like a victim of fatal circumstances. In any event he looks out for a threat, always blames others for his troubles. He looks very gloomily at life in general and at his work, and therefore has a lot of problems. If the whiner finds that the cause of all his troubles - you do not try to object, common sense does not pass here. Tell (with a slight hint of arrogance) that you took his words into account, and keep your distance, otherwise you will earn rheumatism of the shoulder joint. The whiner loves to cry in the waistcoat. Especially those who, it seems to him, "do not justify his best hopes."
"Mumbler".
Very insecure person, more than anything else in the world is afraid of change. He rubs, presses, does not look into the eyes and never makes decisions, expecting that the problem will be solved by itself.
" Adventurer ."
Unscrupulous type, capable of shameless lies and forgery for their own purposes. Building his career, strides over the heads, not disdaining the dirtiest methods. Those who trust him, take advantage of themselves, breaking people's fates.
"Dynamo".
He does not refuse anything to anyone, promises everything to everyone, but (perhaps for this very reason) never does anything. The main advantage is harmlessness. The main disadvantage is absolute insecurity.
"Maximalist".
He sees only black and white in life: for him there are no half tones. Very categorical in judgments. He defends his point of view with an assertive stubbornness, even if it goes against his personal interests. Sharp and subjective in the estimates. The one who behaves “correctly” is a friend. The one who does the wrong thing is the enemy.
" Silence ."
It accumulates in itself insults and irritations, in no way showing its true feelings, until they reach a critical point. Then, like a bulldog, he rushes at the offender, but he does not understand where it has come from. You can never guess what he thinks, it is difficult to call for frankness. Such people are unpredictable, they should not be hurt again. Noticing that the silence is "pouting" on you, try to delicately find out what is the matter. The situation, which was allowed to take its course, can be discharged by a far-reaching conflict.
Such a classification of conflict types can help a manager to develop his own behavioral stereotypes, however, for a successful exit from conflict situations, it is necessary to master the general tactical principles of behavior in an explosive atmosphere:
- determine the psychological characteristics of the person, his strengths and weaknesses;
- do not fall under its influence, keep calm;
- Listen carefully and try to find a way to meet his interests;
- Use a collaborative approach to conflict resolution.
Conflict management is a conscious activity towards it, carried out at all stages of the emergence, development and termination of a conflict. It is customary to single out four main options for managing the conflict: prevention, suppression, delay, and resolution. Each of them has its own specifics and a certain position in the force field of the conflict.
Of course, conflict forecasting and prevention deserves special attention, since it is much easier to prevent it than to resolve it constructively.
Conflict prevention should go along the following main lines:
a) the creation of objective conditions that prevent the occurrence of conflict situations (working and rest conditions, housing, salary, development of the necessary regulatory procedures, etc.).
b) optimization of organizational and management activities (functionality of the interconnections of departments, quality of management decisions, observance of the principle of equity, etc.).
c) blocking personal and socio-psychological causes of conflicts.
In this regard, this kind of management as criticism, which, for all its undesirability, is inevitable at the same time, and therefore requires adherence to certain rules and approaches, deserves serious attention. To give the criticism positivity and improve its efficiency, the manager should be well-intentioned, instead of a general assessment, always offer a clear structural analysis of the situation and carefully choose the form of criticism.
Critical ratings may be:
one. Encouraging criticism: “You’ll do better next time. And now - did not work.
2 Criticism-reproach: “Well, what are you? I was counting on you so much! ”Or“ Oh, you! I had a higher opinion of you! "
3 Criticism hope: "I hope that next time you will make this task better."
four. Criticism-analogy: "Before, when I was like a young specialist, you also made the exact same mistake. Well, I got it from my boss!"
five. Criticism, praise: "The work is done well, but not for this purpose? Tea."
6 Criticism-concern: "I am very concerned about the current state of affairs, because the whole team is responsible for not completing this task on time."
7 Impersonal criticism: "There are still workers in our team who do not cope with their duties. We will not give their last names. I think that they themselves will draw proper conclusions for themselves."
eight. Criticism-empathy: "I understand you well, I come into your position, but you also understand me. After all, the matter is not done."
9. Criticism is regret: "I am very sorry, but I must note that your work was done poorly."
ten. Criticism-surprise: "How ?! Really you haven't done it yet? I didn't expect ..."
eleven. Criticism-irony: "They did, did, and ... did. Work is necessary. But how are we going to look into the eyes of the authorities ?! "
12. Criticism hint: "I knew one person who did exactly the same thing as you. Then he had a bad time ..."
13. Criticism-mitigation: "Probably not only you are guilty of what happened ..."
14. Criticism-reproach: "What did you do so carelessly? Yes, and not at the right time!"
15. Criticism remark: "They did not do that. Next time, consult if you do not know how to do the task!"
sixteen. Criticism warning: "If you once again allow a marriage, blame yourself!"
17 Criticism-requirement: "You will have to redo the job!"
18. Criticism challenge: "If you have made so many mistakes, decide for yourself how to get out of the situation."
nineteen. Criticism advice: "I advise you not to get excited, wait, cool off and tomorrow with new forces, analyze what and how to fix it."
20. Constructive criticism: "The work was done incorrectly. What exactly are you going to do?" Or: "The job is not done. Consider using this option."
21. Criticism-fear: "I very much fear that the next time the work will be performed at the same level."
22 Criticism is a cry: "Stop! What are you doing? How can you do this work?"
23. Criticism-insult: "Oh, you! I did not expect this from you! Where is your conscience ?!"
24 Criticism patronage: "Yes! It did not work! Well, nothing, I will help you."
25 Criticism of the threat: "I am forced to apply the most stringent disciplinary measures to you."
When choosing a specific form of critical utterance, one should proceed from the fact that criticism becomes useful only when a person perceives it positively.
Conflict suppression is applied in the destructive phase and in the case of its irrelevance.
To this end, the head purposefully and consistently reduces the number of conflicting ones, determines the system of norms and rules of relations between conflicting parties, creates conditions that impede or eliminate the interaction of potentially conflicting employees.
In the event of a postponement of the conflict (this measure is temporary, only temporarily removing the severity of the conflict situation), the manager should concentrate his efforts on reassessing the prevailing views of the conflict on the situation in general and about each other in particular. It is important to change the significance of the object of conflict in the imagination of the participants (reduce or increase the value) and thereby make it correspondingly unnecessary or practically unattainable.
However, not all conflicts can be prevented, suppressed or delayed. Therefore, it is very important to be able to constructively resolve conflicts.
In general, it is possible to distinguish interaction strategies based on the characteristics of motivation that determines the choice of strategy.
Assessing the emotional state of the conflicting parties in each of the main strategies can be graphically represented as follows:
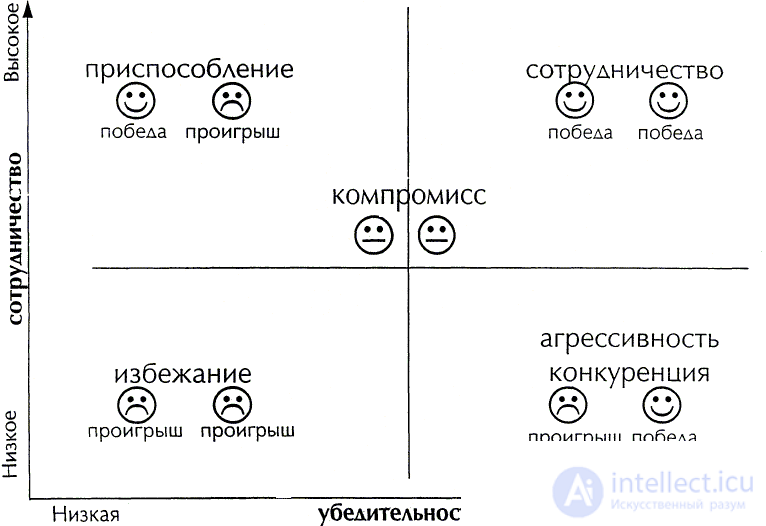
Fig. 1.5.6. Conduct in conflict.
Each of the strategies has its pros and cons and is situational in use. Schematically it looks like this:
| Conflict resolution strategy | Terms of Use | Possible adverse effects |
| Counteraction (competition) | Possession of power and authority. No alternative. Extremity, hopelessness. Lack of time. Danger (aggressor, criminal, etc.). Great benefits for the whole group. | Alienation. The deterioration of the relationship. Loss of existing savings (money, credibility, career). |
| Avoiding (care) | The need to ease the psychological tension of the relationship. Indifference to the result. Lack of power. Late action (no time and effort). | Reduction or loss of credibility. Losses (failed transaction). |
| Cession (fixture) | Indifference to the situation. Saving relationships. Realized advantage of the opponent. Lack of power. Heavy addiction. Insignificance problems. The threat of loss. | Damage to collaboration results. |
| Compromise | Equality of opportunity and authority. Mutually exclusive interests. Lack of time. Mutual losses. Inefficiency of other solutions. Saving relationships. | Concessions may be more expensive than acquisitions. The subsequent aggravation of relations after short-term satisfaction with the results. |
| Cooperation | Close interdependent relationship. Perspectives of collaboration plans. The possibility of constructive dialogue. Equal power and the ability to seek equal solutions. Direction at each other (lack of "enemy image"). Prejudice and unfaithfulness. |
Strategies in conflict are implemented through various tactics. Tactics - (from the Greek. Tasso - I line up troops) - this is a set of methods of influencing an opponent, a means of implementing a strategy. The same tactic can be used in different strategies. So, the threat or pressure, considered as destructive actions, can be used in case of unavailability or inability of one of the parties to surpass further certain limits.
There are the following types of tactics impact on the opponent:
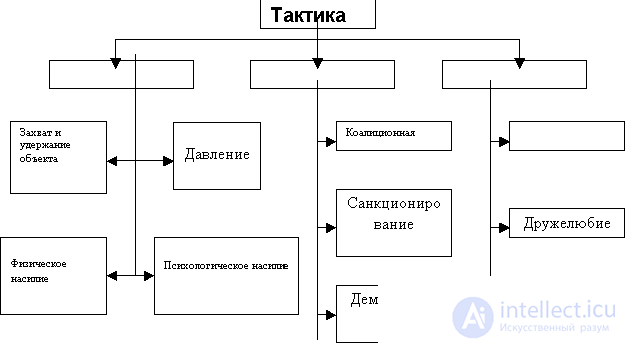
- The tactic of seizing and holding an object of conflict is used in conflicts where the object is material (for example, unauthorized settling into an apartment, forcibly taking a computer with the latest modification, and so on).
- The tactics of physical violence (damage) uses such methods as the destruction of wealth, physical impact (up to murder), blocking someone else's activities, and so on.
- The tactic of psychological violence (damage) causes an offense to the opponent, hurts pride, dignity and honor. Its manifestations are: insults, rudeness, negative personal evaluation, slander, misinformation, deception, dictation and tight control over behavior and activities.
- The pressure tactic in conflicts vertically is used in two cases out of three and includes the presentation of demands and instructions, orders, threats, the use of compromising materials and blackmail.
- Tactic demonstrative action is used to attract attention to his person. These can be public statements and complaints, absenteeism, deliberately unsuccessful suicide, etc.
- Validation implies an impact on the opponent through penalties, increased workload, veto, blockade, open refusal to perform work.
- Coalition tactics are used to strengthen one’s rank in a conflict. Expressed in the formation of unions, the creation of support groups, contacting the media, etc. Used in more than one third of conflicts.
- The tactics of fixing one's position is used most often (in 75–80% of conflicts). Based on the use of facts, logic to confirm their position (criticism, requests, beliefs, etc.)
- The friendliness tactic includes correct appeals, a demonstration of readiness to solve a problem, offers of help, provision of services, apology, encouragement.
- The tactics of transactions involves the mutual exchange of benefits, promises, concessions, apologies.
Tactics are hard, neutral and soft. In addition, they distinguish rational (fixing their position, friendliness, sanctioning) and irrational (pressure, psychological violence) tactics.
The correct choice of not only the overall strategy in the conflict, but also the appropriate tactical means is due to the manager's ability to provide a thoughtful and objective analysis of the conflict situation with the subsequent settlement of the confrontation of the parties. The general scheme of the necessary management actions is as follows:
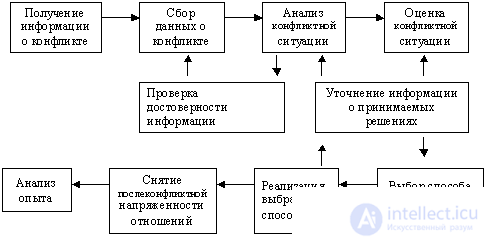
Analysis of the experience allows the manager to reflect on their actions to regulate interpersonal relationships.
Cybernetics claim that any system (including a social group) is controlled by the part that has the greatest flexibility and variability, i.e. has the most degrees of freedom. Effective managerial communication therefore involves, above all, creativity and greater sensitivity to extremely changing circumstances and relationships. If the manager always does only what he is used to doing, then he will receive only what he always received, and this boring routine will surely give rise to conflict.
In order to prevent managerial conflicts, it is important for the leader of any rank to establish feedback with all levels of management, as well as with all objects of management. This is the first necessary condition for the prevention of conflicts in management. The second condition is the constant adjustment of style, forms, means and methods of management to the specific conditions. In particular, the head should possess various forms of influence on subordinates:
- direct effects (orders, directives, instructions, tasks, etc.);
- impact through motives (stimulating needs and interests for the purposes of desired behavior and activities);
- impact through the value system (education, education, mass media);
- impact through the social environment (changes in working conditions, status in the organization, interaction systems, etc.).
Developed by practical psychologists "Commandments of behavior in a conflict situation" is very easy to remember using the keyword CONFLICT . In this word, the number of letters corresponds to the number of commandments:
K - criticism whenever possible to eliminate!
It is undesirable because it acts as a psychological ax or a mirror in which a person looks like a freak. In case of inevitability, the criticism must be constructive, correct and gentle and be submitted in the appropriate circumstances.
O - take 100% responsibility!
As I. Goethe said, "The one who is smarter is to blame for the dispute."
H - misunderstanding of the subject of disputes, interests of the parties and their positions to eliminate!
If we compare conflict with a weed, then the incident is the tops, and the root is the conflict situation, and attention should be focused on it.
F - the background of the conflict does not expand!
A step to the left, a step to the right (past transgressions, a transition to "personalities", etc.) is the execution of oneself!
L - “Lady / Gentleman” (do not leave this image!).
In the words of B. Russell, "a gentleman is a person in contact with whom you feel like a gentleman." Only the performance of this role helps to extinguish the conflict.
And - look for common interests!
It is necessary to ask not only “What do you want?”, But also “Why do you want this?” The answer to the first question will reveal the position of the opponent, the second - the interests. As a result, there will be a real opportunity to “get out of the trenches of war to a common springboard” and begin a joint search for a solution acceptable to both sides.
To - a constructive solution to look for together!
All objections and attacks should be translated into a constructive form, asking the question: "What do you propose to do?".
T - Tolerance to maintain in all situations!
It is psychologically wise and beneficial. A glass half filled with water can be viewed as either half empty or half full. Lack of wisdom is not a crime, but a loss of many possibilities.
The killing power of the conflict is akin to the Kalashnikov assault rifle. Conflicts cause irreparable harm to production, people, society in the event that they become destructive and uncontrollable. Is it possible to avoid conflicts or to leave them without success? Of course, yes. But this should be learned. For there is the arithmetic of life, but there is also higher mathematics. All people learn arithmetic by experience and error. Higher mathematics through the "method of trial and error" (or rather, the "spear method") can not learn. It must be mastered purposefully and consistently. Such a higher mathematics for a leader is conflictology - a serious science and essential for organizing effective managerial communication.
One of her laws was formulated by the wise Seneca: “The strongest who has the power to rule himself.”
Test questions.
1. What is a “conflict” and what are its main reasons?
2 What is the difference between destructive and constructive conflict?
3 What are the main strategies of behavior in a conflict?
four. What is the main content of the conflict management model?
five. What is an “internal conflict”?
6 What kinds of conflicts do you know?
7 What are the main features of the compromise?
eight. How can conflict be prevented?
9. Highlight the main types of conflicting personalities.
Literature.
Antsupov A.Ya., Shipilov A.I. Conflictology. M., 1999.
Vishnyakova N.F. Conflictology. Minsk, 2004.
Grishina N.P. The psychology of conflict. SPb., 2002.
Gromova O.N. Conflictology. M., 2000.
Siegert, Lang L. Lead without conflict. M., 1990.
Kozyrev T.I. Introduction to conflictology. M., 1999.
Samygin S.I., Stolyarenko LD Psychology of management. Rostov-on-Don 1997.
Comments
To leave a comment
Psychology of management
Terms: Psychology of management