Lecture
Methods for determining the value of quality indicators dependent
from the design and technological features of the products
or services.
The most common methods are:
- instrumental, using various measurements
ritelnyh and control devices;
- settlement and analytical - methods for calculating indicators and
establish relationships between them (for example, the definition
productivity of machine equipment in terms of supply);
- experienced, allowing by test to establish
and in some cases to check the value of the indicators
using other methods (for example, testing vehicles for
test site, accelerated engine tests, etc.);
- laboratory, used to determine indicators
through analysis and testing;
- organoleptic, consisting in determining the
through the senses (for example, control of color
skis, scratches, etc.);
- social, allowing to determine the quality by
questionnaire survey of consumers;
- points, allowing to evaluate individual indicators,
not having generally accepted dimensions, with the help of points;
- expert - methods that use experts in questionnaires
surveys in order to obtain more accurate values of
our indicator.
Usually several methods are applied simultaneously for
determine the same indicator. In fig. 7 are presented
main methods of qualimetric assessment of product quality
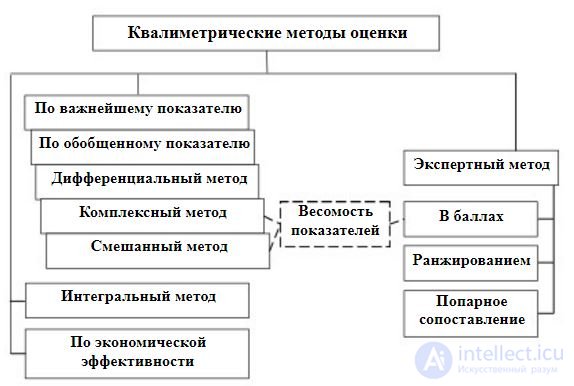
Fig. 7. Methods of qualimetric assessment of product quality
In the Russian legislation there is a clear
the concept of homogeneous and heterogeneous goods.
Homogeneous goods which, although not identical
in all respects, have similar characteristics and
are made of similar components, which allows them to perform the same
functions as the goods being valued, and being commercially interoperable
replaceable. In determining the homogeneity of the goods, the
The following signs are: quality, presence of a trademark and
reputation in the market, country of origin of goods, manufacturer
Products are not considered homogeneous with estimated, if
have not been produced in the same country and if their designs
development work on them, their art
design, designs, sketches, drawings, etc. were
performed in the Russian Federation. In other words,
native goods are not identical in quality, in recruitment
basic characteristics.
Recall that in marketing depending on the degree
product interchangeability is divided into four levels of competition.
Rencia:
1 level. General competition : with it, the firm sees
each manufacturer participating in the fight for the day
gi consumers. (All firms present on the market).
2nd level. Formal competition : the firm considers the
cents of all those who produce products that are designed to
create the same needs. (For example, the need for
The movement - a bicycle, car, motorcycle).
Level 3 Sectoral (species) competition : competitive
firms that produce the same product or
product group. (Cars - Ford, Nissan, Audi, Merce
Des, VAZ, GAZ).
4th level. Brand competition : takes place in
If the firm regards as its competitors
Rent firms offering similar product and / or theme services
same target buyers at reasonable prices (Coca-Cola, Pepsi).
Thus, under the category of homogeneous goods throughout
visibility are those products that are characters for the fourth
That and the third level.
However, in assessing the quality of industrial products
recommendations to rely on a specific document, regulations
rules and assessment procedure: “Methodological guidelines
assessment of the technical level and quality of industrial
products. RD 50-149-79 ". In accordance with this document
Uniform understand products of one type, one class.
and destination. In assessing the quality level of such products,
It is recommended to use differential, complex,
shanny and integral methods. To evaluate the technical
level (quality level) of dissimilar products apply the method
based on indexing qualities. Sometimes applied to one
native or heterogeneous products use the method of expert-
quality assessment
To assess product quality, it is necessary to take into account
opportunities, all its properties. Usually the product has some
There are many different and significant properties that
have a different impact on the final quality level indicator
estimated product.
Available data on various properties of the assessed and
base (reference) objects must be brought to match
common quantities, i.e. to such quantities, operating with which
You can get the desired value of the quality level of the investigated
object.
The procedure for bringing different essentially (physical, chemical)
technical, environmental, economic, etc.)
indicators of the properties of the objects in question are mathematics
chesky action
(conversion) and data presentation
properties of the analyzed objects to their comparability in the form
dimensionless relative values. This procedure is sometimes
called the formalization or normalization of a heterogeneous information
formations.
There are several methods for normalization. In general,
even normalized, comparable values of indicators of different
properties of a certain set of objects are found by the formula:
Where
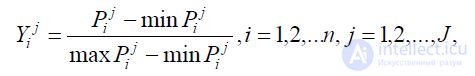
Yi j is the reduced value of the i -th property of the j -th object from the set J ;
Pij is the quantitative value of the i- th property of the j -th object;
min Pij is the minimum value of the i- th property of the j -th object from the entire initial set J of indicators of this property;
max Pi– maximum quantitative value of the i -th property
j-th object of the entire original set J;
n is the number of considered properties;
J - the number of analyzed objects.
Thus obtained normalized values match
set properties of objects are expressed in dimensionless form
share or relative level ( Y ) of i -th, properties relative to
to the highest value of this property
j object.
In qualimetry, the reported values of all
properties of the evaluated object to their comparable form are called
are formalized or comparable data system. For
calculating a particular formalized (reduced) element
system of comparable data use one or other
mathematical formulas.
Provided min Pi 0
use simplified formulas
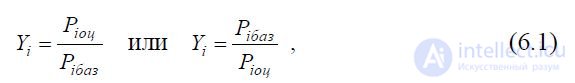
Where
Y
- the relative level of the i- th property, the level of mappable
i
indicators or the level of a specific property indicator in relation to
to the indicator of the corresponding property of the base (reference)
object (sample);
Piоts - and the indicator of the i- th property of the evaluated object;
Pibaz is an indicator of the i- th property of the base or reference sample;
i = 1, 2, 3 ... n, and n is the number of properties taken into account when assessing the levels of properties
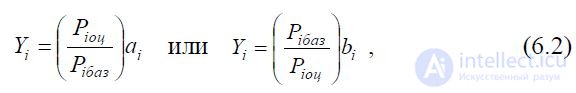
here ai and bi are the weighting factors (significance) of the corresponding
The i-th indicator of the property of both the evaluated and the base objects.
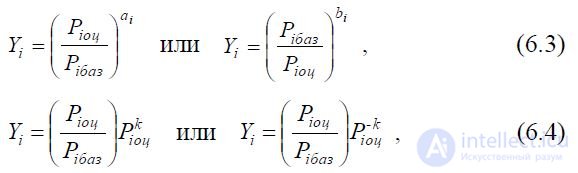
where k is the exponent, entered under the condition when the indicators
properties of the evaluated and base objects have almost identical
values.
The use of formulas 6.1, 6.2, 6.3 or 6.4 depends on
Ractera (patterns) changes in individual parameters. So,
For example, if the Pioc or PiBaz values differ by a minor
but, their relations are close to unity, which does not allow to give ad-
quatt estimate of levels of compared indicators. In such
case for comparative analysis is recommended formally
Call parameters by formulas 6.4.
An expert is a specialist competent in solving this
tasks
(from Latin glory
"Expertus"
- experienced). Com-
the tendency of the expert in relation to the object of study -
professional competence, and with respect to the methodology
Experiences of solving an investigated problem are expert
competence. The expert must be impartial and
tive when evaluating the object of study.
The expert method is a method for solving problems
based on the use of generalized experience and intuition
expert sheets. Expert method of assessing the level of quality
products used in cases where it is impossible or
It is very difficult to use the methods of objective determination.
division of values of single or complex indicators
properties by methods such as instrumental, empirical
sky or settlement.
Expert method
(or expert method, i.e. method
expert assessments) is a combination of several different
methods that are varieties that can
method of examination expertise.
Known varieties of expert method apply-
wherever the decision is based on a collective decision
competent people (experts).
The need and legitimacy of expert assessment of quality
properties:
1. A person is able to solve certain logical problems.
giving faster computer due to the inclusion of intuition, insight,
etc. methods.
2. For some objects (drugs, perfumes), with
the current level of development of technology, man is
is the only “instrument” that allows
lead organoleptic evaluation of the quality of the goods.
3. In cases involving uncertainty of the situation,
its probabilistic nature, it is impossible to get accurate
data available to date assessment methods
quality. Therefore, the heuristic solution given by the expert,
it often turns out to be more correct than the resulting
in an even way using mathematical formulas
Expert methods for evaluating product quality can
used in the formation of a general assessment immediately (without details
the level of product quality, as well as when solving many
these particular questions related to the definition of indicators
properties of something. Therefore, expert methods find
application at:
- general (generalized) assessment of product quality;
- classification of the product being evaluated;
- determining the nomenclature of indicators of the properties of
your product;
- determination of weight factors
product properties;
- evaluation of the quality index of organolep-
tic method;
- selection of base samples and dimensionless values of
Call quality indicators;
- determining the final complex indicator of quality
based on a combination of individual and complex (generalized
general and group indicators;
- product certification and certification.
Expert method of assessing the level of product quality is not
can be used if it is possible to assess the quality
other analytical or experimental methods
dami with greater accuracy or with less cost.
The results of the general expert assessment of such a complex
complex properties, which is the quality of products, have
elements of uncertainty and groundlessness. Therefore, ex-
The first assessment of the quality of products as a whole is a preliminary
informational, unsaturated and only in the first
near; roughly describes the quality of the assessed
products. Based on such an expert quality assessment, it is obvious
no opportunity to take any engineering and technical
solutions. This method can, for example, be used in com-
merchant transactions when there are no specific (numerically
information about the level of quality of the purchased products and
etc.
However, it should be noted that the expert method for assessing
Key indicators of many properties of technical and other products
is the only possible, sufficiently wide
It has been developed for this purpose.
Expert methods are appropriately applied in the following
cases:
1. When other methods can not solve the problem.
2. Other methods are more laborious or less accurate.
3. When it is necessary to determine the nomenclature of
quality assurance and structural or hierarchical construction
scheme.
4. Organoleptic evaluation - only by expert.
5. Determination of weight coefficients.
6. Determination of the values of a number of quality indicators for
which there are currently no methods tools
measurement.
Subject to all necessary procedures and rules
conducting an expert survey, its error is in
limits of 5-10%, which is comparable with the methods of technical
measure
Comments
To leave a comment
Qualimetry reliability and quality
Terms: Qualimetry reliability and quality