Lecture
To describe them, I use a case from an IT project (you need the same case from real life), but you can use the described approaches absolutely in any project.
The project team of a software product development receives a technical task for the product, which contains a description of automated processes in IDEF0 notation, a description of software usage scenarios and requirements for it. The task of the team is to calculate the timing of the project and the budget for it. I am the leader of the future project. My actions?
The first thing I will do is develop a list of works on the project. If I do not have enough competences, then I will find the most competent expert in the subject area and ask him to do it with me.
In a real case, I gave a technical task to study the future architect of the product. He sketched the product architecture on a draft, breaking the product into elements, and we identified a list of works. Then I asked him to give two estimates of labor costs for each element of the architecture. The first assessment is the answer to the question: what will be the labor costs in man-hours for the implementation of the work, if there are no problems and a highly qualified programmer will implement this part? The second assessment presupposes the answer to the question: now imagine that the weakest programmer from our team will implement the task, moreover, he will face all possible problems in the appendage to everything? So I received an optimistic and pessimistic assessment of labor costs for each job.
To use the method I am writing about, I need another third type of assessment, with which most of the complexity arises. This estimate is called the most likely estimate of labor costs. Based on what you can get this assessment? Of course, based on statistics of similar tasks. Yeah, and where in the CIS you can find statistics on the labor costs of projects? I can start to accumulate it in my projects, and this will be a great investment in the future, but I need the statistics today.
In fact, there is a solution. And it is called the Delphi method . Its essence is to use a group of experts and with the help of a series of successive iterations to achieve maximum consensus in determining the group decision. In practice, I liked to use a modification of the Delphi method - poker planning. In the Delphi method (and its modifications) it is very important to obtain independent expert evaluations, i.e. Experts should not be aware of each other’s assessments until each of them makes their choice. Why is it important? The fact is that the so-called “binding” has a magical effect on people. D. Kaneman writes very well about the binding effect: “The binding effect is manifested when the subjects encounter an arbitrary number before evaluating an unknown value. This experiment gives one of the most reliable and stable results in experimental psychology: the estimates do not move away from the considered number, hence the image of binding to a certain point ”. For example, three friends estimate the labor costs of the task “to dig a shovel with a trench 5 meters long, 25 cm wide and 1 m deep”. One of them says the number 20 ... And this value has already had the effect of brainstorming and has become a guideline, starting from which two other experts will make their assessments. Of course, they will make adjustments in one direction or another, but will these adjustments be bold enough to give an assessment that is many times different from what has already been made? Cognitive psychologists say no.
In order to get a group independent assessment, none of the experts should give their assessment until everyone makes a choice, and only after that the results are announced.
How is poker planning going? Oh, that's fun enough.
Several experts and a moderator gather in the same room (you can also remotely via the Internet, they say there is already special software). Each expert has a deck of cards on hand. You can use a special deck of cards for poker planning , in which the values of the numbers are selected for the Fibonacci series, or adapt the classic deck of poker cards.

In a special deck, as you have already noticed, not all the values of the cards correspond to the Fibonacci series: starting with “20” the numbers do not follow the Fibonacci law (the sum of the two previous numbers should give the next number). This is done intentionally, because if the work takes, according to the expert, a lot of time, then it will be 21 hours or 20 is not very important. Moreover, it does not matter for values of 40 or 100 hours - labor costs are too high, and the step after “20” is deliberately chosen to be very large. There are several interesting cards in the deck: for example, “?” Means that the expert does not understand the essence of the task and is not ready to make an assessment, and “coffee cup” means that the expert really wants to break and drink some coffee (or tea).
Poker planning is a game of evaluation, but a game with a useful result for a project manager. People love to play games, and my experience has shown that experts play poker planning with pleasure. More importantly, it gives very good accuracy of assessments, especially if they are made by people who have a good understanding of the subject area and have approximately the same qualifications.
On one of the projects where we used poker planning, we achieved that the team doing the evaluation of the iteration work, for a large number of iterations, fulfilled its obligations by 100%, and the actual labor costs for the iteration tasks were almost equal to the planned ones.
So, the moderator announces the essence of the task and answers the experts' questions about the essence of the task, after which he asks to evaluate the labor costs for the task if the expert himself implements it. Having made an assessment, the expert must draw out a card with a number corresponding to this assessment, but at the same time put it face down so that no one can see the number. For example, I estimate the task to be completed in 10 man-hours. In this case, I draw a card with the number 10 from the deck.
After all the experts have drawn the cards and put them face down, the cards are opened and the moderator announces the results. The purpose of the procedure is to bring together the opinion of experts, so the moderator asks the expert who has the lowest mark to speak out. The expert tells in details how he plans to accomplish the task in the estimated time. Sometimes it turns out that the expert misunderstood the requirements for work, sometimes he describes a very elegant approach that requires less effort than other approaches to solving the problem. After that, the moderator asks the expert who made the highest mark. After the statements of the two experts, as a rule, the requirements for the results of the task become more understandable, and the group often chooses the approach to the implementation of the task. The moderator asks the participants in the discussion to think again about labor costs and the second round of voting is being held. Most often, the spread of expert evaluations decreases after the second round. After the second round, you can stop, average the assessments of experts and thank them. But you can hold a second round of discussions and after it arrange a third round of evaluation. In practice, I was limited to two rounds. The average expert estimate obtained can be taken as the most likely one and used to calculate the labor costs using the three-point method.
So now I have three estimates for using the described method. I need to choose the type of probability distribution and the formulas for mathematical evaluation calculations.
What are the probability distributions? I hope you remember the theory of mathematical statistics and the type of normal distribution a little?
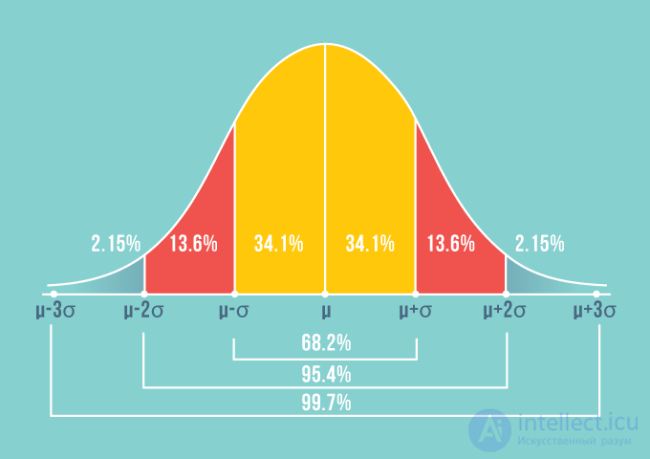
The figure shows the most frequently occurring value in a measurement for a phenomenon (µ is the expectation) and ranges that indicate deviations from it (sigma is the standard deviation from the expectation). The probability of hitting some value in the interval from the expectation plus one sigma is equal to 68.2%, and adding to the mathematical expectation of 2 sigma allows you to be sure that the event will happen with a probability of 95.4%.
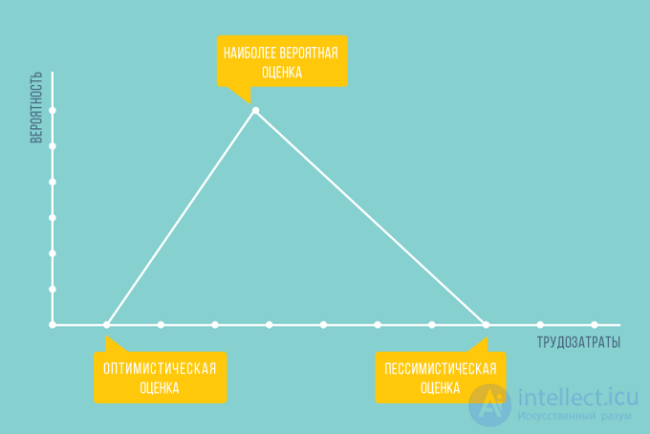
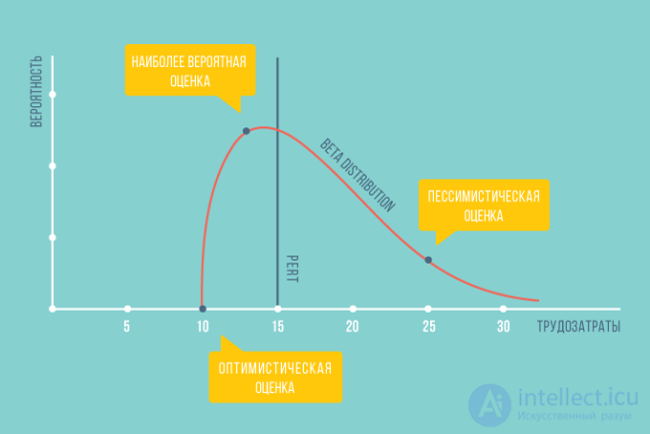
So, there are a large number of probability distribution curves, but the three-point estimation method uses two types of probability distribution: a triangular probability distribution and a beta distribution.
The formula that is used for the triangular distribution is:
E = (O + M + P) / 3,
Where O is an optimistic estimate,
M is the most likely estimate,
P - pessimistic assessment.
The shape of the triangular distribution may be something like this:
The formula that is used for beta distribution is:
E = (O + 4 * M + P) / 6
Why not take a normal distribution to calculate project estimates? The answer to this question is given by N. Taleb in his book “The Black Swan” . “The great fraud” of Gauss, according to Taleb, is able to predict only those events and values that belong to the dimension space, where no observation can have a significant impact on the results. Human height, weight, and other biological variables are a good example for using the normal distribution: the probability density is clustered around a narrow range of options, and the variation of options is not so large. You will not find a person 5 meters tall or weighing 100 grams. By adding to the statistics the growth of the highest or lowest person on the planet, you will only slightly affect the results of the sample - the average growth rate and sigma will barely change.
But such events as the sale of the best-selling book, the popularity of videos on Youtube, the movements of the stock market, the profitability of investments, the statistics of incidents related to the operation of the information system are not subject to the normal distribution of Gauss.
Design works clearly belong to the category of phenomena that are not described by the normal distribution. Therefore, mathematicians suggested that we use the beta distribution or the triangular probability distribution to predict labor costs, deadlines and budgets.
It should be noted that when using the formula for beta distribution, the coefficient of the four at the most probable estimate strongly shifts the final result of the calculations to the area of this assessment. No matter how wide the interval between the optimistic and pessimistic estimates - as a result of the calculations, the estimate is close to the most likely.
In the formula used for the triangular distribution, all the estimates have the same weight, and the result largely depends on the intervals at which the extreme values are located from the expected estimate (optimistic and pessimistic estimates).
So back to our case.
To estimate the scope of work at the start of the project, I used the knowledge of the strongest expert in the subject area of the project to get a high-level list of work on the project and pessimistic and optimistic estimates of labor costs for each work of the project. To score on three points, I needed the most likely estimate that I could take from statistics on similar problems, but it is not available to me. I have attracted several experts and evaluated the effort using poker planning. He took the obtained values as the most probable and used the evaluation formula for the beta distribution. In order to get the project laboriousness, it remains for me to sum up the estimates for all the project tasks obtained using the three-point method and add a reserve for risks. The risk reserve can be calculated using the standard deviation. The fact is that for a large number of project tasks with independent properties, the central limit theorem acts, the form of the probability distribution for the entire project will be close to normal.
To determine the complexity of the project with an accuracy of over 50%, I need to calculate the standard deviation for each project task, square it, and then extract the square root of the sum of the square deviations of all the problems. It is difficult to read, simple to do. Look at the formulas.
To calculate the complexity of a single task using the PERT method , the formula is used:

The complexity of the whole project with an accuracy of 95% is determined by the formula:

I want to say that what I wrote is not theoretical reflections, but descriptions of approaches tested in practice. The only exception is that we used the group assessment already at the project implementation stage when planning project iterations, and at the start of the project we used only the estimates of the strongest expert, which made it necessary to abandon the three-point method and use the arithmetic average for the two estimates.
What do you think about the above approach? What prevents you from using this approach in your projects?
I am waiting for comments and see you on the air!
Comments (2)
Denis, thanks for the positive feedback. I know about attempts to derive standards for types of work in construction and in some IT companies developing software.
Maxim, thanks for the article, informative! In his article on the differences between the American approach to project management and the Soviet one, Ivanov V. points out the advantages of the resource method (where there are strictly standard-hours, strict employee qualifications, etc.) within the limits of these very resources. Now the question. The method of estimating the duration of the work may also include a variant of calculations according to the standards of labor costs. Tell me, are there such norms nowadays in general, if they exist, in which branches? The reason for the question is often faced with the incorrectness of “expert assessment” of the duration of operations, for example, in design. But if there were such standards, then you can simply load them into the project (here the common name) and that's it. Thank.
Comments
To leave a comment
software project management
Terms: software project management