Lecture
The step-by-step planning approach recommended in the framework of this book, as it has already been mentioned, involves the development of detailed plans for each stage just before its occurrence. As a method to ensure such an approach, we can consider a hierarchical schedule.
Hierarchical schedule is a method for developing detailed schedule plans. This is a multi-level schedule with a variable degree of detail at each level [18]. At the planning stage, the hierarchical schedule is based on the SRI.
High-level operations are broken down into several smaller ones. Control events of the project, as a rule, provide communication of various levels. In fig. 14.1 presents an example of a hierarchical schedule.
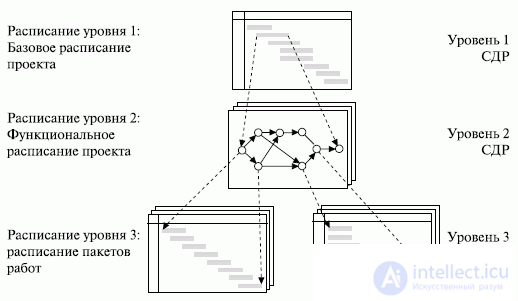
Fig. 14.1. Example of a hierarchical schedule (adapted from [18])
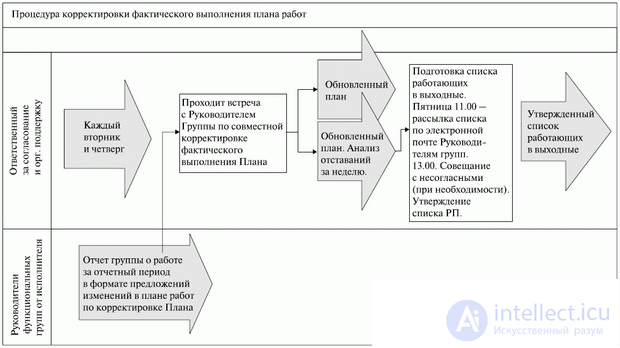
Fig. 14.2. Outline of the procedure for adjusting the actual implementation of the work plan
The main advantage of this method is that it can be successfully used on projects with a high degree of uncertainty, where information appears as the project progresses. In the process of detailed scheduling, members of the team who are responsible for the work package being detailed should be involved.
An important note is that the method of hierarchical timetable with a reasonable adaptation can be applied to the detailing and phased compilation of all basic project plans: by content, by cost, by quality, etc.
At the “Design” stage of the life cycle IT, it may be necessary to implement an adjustment of the project management plan - this is quite an expected situation, taking into account the recommendation on the implementation of the incident wave planning. Therefore, it is relevant to use the procedure for adjusting the actual implementation of the project plan, coupled with the already considered procedure for integrated change management.
Below is an example of a text description and a diagram of the procedure for adjusting the actual implementation of the project plan.
An example of the procedure for adjusting the actual implementation of the work plan
In case of the need to adjust the actual work plan:
The process of guiding and managing project execution requires that the project manager and team take a series of steps to implement the actions documented in the project management plan and the activities identified in the project description.
The project manager, along with the project management team, manages the progress of the planned project operations and the various technical and organizational relationships that exist within the project. The most typical actions include:
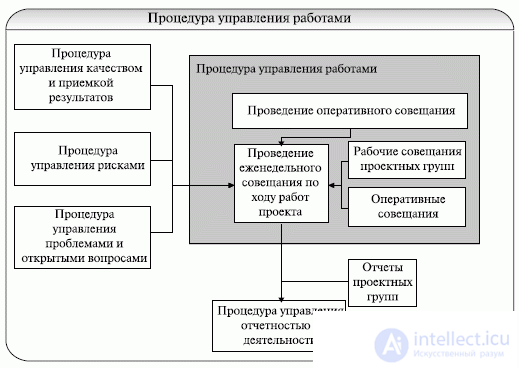
Fig. 14.3. Scheme of the project work management procedure
In the framework of the project, information on the performance of work is collected, including information on the state of readiness of delivery results and on work performed; this information is then sent to the performance reporting process.
This process is closely coordinated with the process of implementing an integrated change management project, as well as with the processes and tools for monitoring content, timing, quality and cost.
The key procedure supporting the implementation of the process “Managing and Managing the Project Execution” is the work management procedure, the scheme of which is shown in Fig. 14.3.
Below are charts of the operational and weekly meeting on the progress of the project (see fig. 14.4 and 14.5).
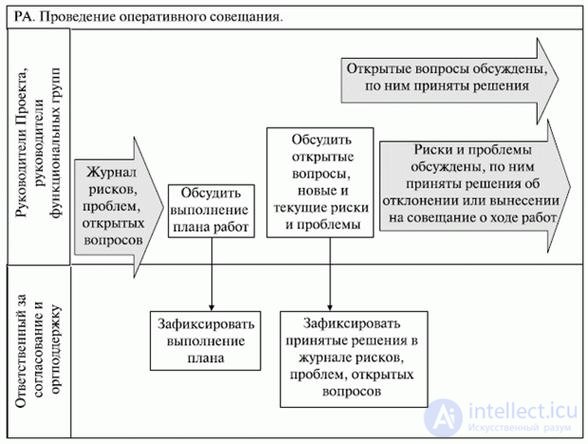
Fig. 14.4. Outline of the operational meeting procedure
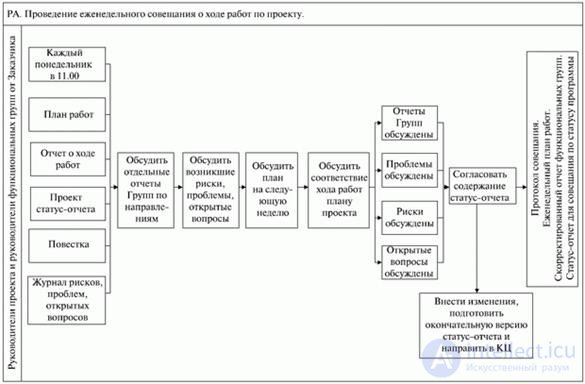
Fig. 14.5. Scheme of the weekly project progress meeting
At this stage, the key objectives of project quality management are:
The main objective of the stage is to clarify the strategies, standards and procedures so that they correspond to the objectives of the upcoming stage.
Another task of the stage is to ensure the preparation of an audit plan and a review of the quality of work at the stage. Planning begins with identifying key results and milestones at this stage. For each key result, a quality review is planned. Additional quality reviews are carried out before the checkpoints related to the acceptance by the customer of the project results, which will allow identifying problems in advance of the acceptance procedure by the customer and deciding on their elimination. The project schedule is adjusted to the quality audit. The set of procedures necessary to ensure quality management at this stage should be checked [22].
The above tasks are relevant for all stages of the life cycle of IP.
At the planning stage, the project manager, together with the quality manager, performs the adjustment of the project quality assurance program .
For this, a pre-quality manager is carried out:
o setting up the working environment;
o configuration setting (for system testing );
o infrastructure setup, system testing;
o perform system and user test;
o installation of the working environment;
o test run;
o preparation and conduct of training for end users;
Comments
To leave a comment
software project management
Terms: software project management