Lecture
The goal of quality planning is to make project management processes predictable. Quality planning needs to start in the early stages of project planning, since it is important to determine the quality requirements at the very beginning and take them into account when developing the plan. At the planning stage, a system of measures to ensure the quality of the project is formed and documented.
Planning the quality of a project begins with the identification of objects whose quality is necessary to ensure. In tab. 8.1 a description of the processes affecting the project quality assurance process, the impact of which should be considered when developing a project quality management plan.
The quality assurance plan describes how the project management team will implement the implementing organization’s quality policy. Depending on the needs of the project, this plan can be very detailed or generalized. The plan contains a list of work that must be performed in the field of project quality management, as well as the time (schedule) of work. Quality assurance activities should be developed at the very beginning of the project and should be carried out on the basis of independent expert assessments [11]. The plan allows you to highlight exactly the work and the time of their implementation, which are necessary for quality project management.
To develop a quality management policy for information system implementation projects, it is necessary to define a list of procedure procedures.
One of the main components of project management is to prevent the loss of value of products or services by reducing their quality. Accordingly, companies providing information systems implementation services accumulate knowledge about emerging problems and losses on implementation projects and then try to prevent these losses.
Table 8.1. Analysis of quality management processes
Title | Description | Consequences of not doing | Consequences when doing | Process evaluation | Owner | Comments |
Quality management planning | Quality management planning is based on standards and is intended to be a guide through which the quality of the project being carried out will be assessed. This process ensures that the customer receives a project that meets their requirements. Quality management planning should be considered in conjunction with the capacity management process, as quality planning is part of this process. | If you do not make a project management plan, it will be difficult to track the quality of the tasks performed by the project and the deviation of results from customer requirements. | The results will meet customer requirements. | Critical | Customer Manager and Project Manager | It is proposed to consider without breaking into subprocesses. |
Analysis of factors external and internal environment of the enterprise | Identify the conditions that may affect the progress of the project, taking into account the quality policy adopted at the enterprise, procedures, regulations and accumulated knowledge from previous projects | The emergence of a contradiction with the legislation or with the policy in the field of quality, existing in the enterprise | Execution of the project in accordance with the conditions and obtaining the desired results | Is important | Project Manager | Recommended for execution |
Quality management plan | Drawing up a document on the basis of which the quality of the project and the results obtained will be assessed | Getting results that do not meet customer requirements | Execution of the project in accordance with the conditions and obtaining the desired results | Critical | Project Manager | Required for execution |
Quality assurance | Adoption of planned systematic measures (external and internal) that ensure the implementation of all envisaged processes necessary to meet the quality requirements | Getting results that do not meet customer requirements | Execution of the project in accordance with the conditions and obtaining the desired results | Is important | Project manager or project team | Recommended for execution |
Execution of the project plan | Carrying out measures to ensure the implementation of the quality management plan | Deviation of project results from customer expectations | Getting the expected results on time | Is important | Project Manager / Project Team | Recommended for execution |
Time, content and cost management | Approval of measures to ensure the implementation of the quality management plan, cost accounting and sufficient resources for their implementation | Unjustified increase in the cost of the project and the timing of its implementation | Cost optimization for project quality assurance | Critical | Project Manager | Required for performance |
Quality control | Monitoring project results to establish compliance with quality standards. Identification and elimination of causes causing deviations | Deviation from expected results, the cause of which cannot be established and corrected | Timely elimination of deviations from expected results | Is important | Project Team / Project Manager | Recommended for execution |
Table 8.2. Project Quality Assurance Plan
Project Quality Assurance Events | Execution Schedule (weeks) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
one | 2 | 3 | four | five | 6 | 7 | eight | 9 | ten | eleven | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | sixteen | 17 | 18 | nineteen | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | |
1. Analysis of the requirements of the project results | x | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2. Selection and approval of project implementation standards | x | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3. Development and approval of a project risk management plan | x | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
4. Quality Assurance Tasks | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
4.1. Development and approval of the procedure for managing problems (deviations) in the project | x | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
4.2. Monitoring the status of risks and problems of the project | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | |||
4.3. Project working group meetings (weekly) | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
4.4. Review and approval of project documents submitted to the Customer | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | |||||||||||
4.4.1. Review and approval of technical specifications | x | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
4.4.2. Review and approval of technical design | x | x | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
4.4.3. Review and approval of other documents | x | x | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
4.5. Meeting on the analysis of the results of the project phase | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
5. Tasks of the organization and testing of tests | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | |||||||||||||||||||
5.1. Development and approval of test methods and testing of IP | x | x | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
5.2. Development and approval of test plan | x | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
5.3. Development and approval of the report on the results of testing and testing | x | x | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
5.4. Preparation and approval of the certificate of acceptance of IP | x | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
b. Internal and external project audits | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||
6.1. Internal audits | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||
6.1.1. Audit of the project initiation phase (in accordance with the project management company standard) | x | x | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
6.1.2. Audit of the project implementation phase (in accordance with the project management company standard) | x | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
6.1.3. Audit of the project completion phase (in accordance with the project management company standard) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
6.2. External audits | x | x | x | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
6.2.1. Audit by an IP supplier on the implementation of an IP implementation methodology | x | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
6.2.2. Audit of the project implementation by the Customer’s representatives | x | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
7. Preparation and approval of a report on a completed project or project phase | x | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The causes of loss of quality are very diverse: violations of technology, inadequate quality of resources, human factor, imperfect management system. Essential is the fact that all these quality losses occur when performing individual processes and operations. In this regard, modern quality management has come to understand that it is not the quality of products or services that should be managed, but the quality of process execution. In particular, this circumstance is reflected in international standards ISO 9000, which have already been mentioned. Based on this theory, we define the necessary procedures for quality management on the implementation project. So, first we define the processes at which losses are possible, and the quality losses themselves (Table 8.2).
Examples of quality planning procedures
1. Documentation Procedure
This procedure is intended to control the documentation in the project.
Functional team leaders and employees submit current versions of project documents, reports on work for the current period, and other project documents to the person responsible for coordination and organizational support. Responsible for coordination and organizational support the employee places the received documents in the project library
2. Procedure for approving project documents
Preparation of documents is carried out by the working groups of the project. In the course of the discussion, the participants of the working groups may consult on the issues under discussion with other members of the ETS project team.
The document, which is ready for approval, is transmitted to the team leader, who conducts the incoming quality control of the document.
For the approval procedure, employees are assigned responsible for the approval.
The staff responsible for coordination, in accordance with the approval scheme and the approval list of each document, determine the list of officials with whom documents are to be agreed, and within one day after notification of the readiness of the documents send them for approval.
The coordinating official analyzes the document and within 3 days sends its comments to the coordinator.
The person responsible for coordination on the same day sends his comments to the group leaders and to the working groups for processing.
Table 8.3. Defining a list of procedures for quality management
Stages | Project Works | Possible loss of quality | Procedures |
Project planning | Project planning | Errors in determining the complexity of development, resource allocation, budget development | Procedure for creating a quality plan, creating a quality assurance program |
Definition and description of discrepancy solutions | When analyzing and documenting the key business requirements and criteria for their success, a misunderstanding of customer requirements is possible. | Customer Requirements Management Procedure | |
High-level business process analysis | |||
High-level interface description | |||
Detailed analysis of individual business processes | |||
Documenting Individual Interfaces | |||
Assessment of the project framework | With inadequate documentation of the project scope | Project Document Control Procedure | |
Detailed analysis of business processes | When describing business processes, misunderstanding of requirements, in assessing the coverage of customer requirements with system functionality, important tasks may be missed. | Customer Requirements Management Procedure | |
Development and harmonization of functional requirements | When approving and approving documents, problems are possible due to the absence of the person responsible for this work, or the procedure for conducting this work. | Procedure for approval and approval of documents | |
The developed document may not meet the requirements for it. | Project Document Control Procedure | ||
Approval of infrastructure analysis results | When approving and approving documents, problems are possible due to the absence of the person responsible for this work, or the procedure for conducting this work. | Procedure for approval and approval of documents | |
Creating a learning environment | |||
Develop training for key users | |||
Key user training | |||
Design | Creation of design specifications | When making changes at the design stage, problems and inconsistencies with the originally designed system are possible. | Problem and Change Management Procedure |
Creation of technical specifications | When describing system improvements, some important features of the processes and functions may not be provided. | Quality assurance procedure as per plan | |
Definition of integration methods and modifications | |||
Definition of testing criteria | |||
Identify additional training requirements | |||
Configuration setting | |||
Setting up the development environment | |||
Test environment setup | |||
Development of functional characteristics | When making changes at the development stage | Problem and change management procedure. Quality assurance procedure as per plan | |
Testing parameters / functions | Errors during testing, inadequate test cases | The quality control procedure of the project results. Test Case Development Procedure | |
Process testing | Errors during testing, inadequate test cases | Project quality control procedure | |
General testing | Errors during testing, inadequate test cases | Project quality control procedure | |
Creation of technical and user documentation | Creating Inappropriate Instructions | Project Document Control Procedure | |
Setup and implementation | Setting up the working environment | ||
Configuration Setup (for system testing ) | |||
Infrastructure setup, system testing | |||
Perform a system and user test | Errors during testing, inadequate test cases | Project quality control procedure | |
Installation of the working environment | |||
Run a run test | |||
Preparation and conduct of training for end users | |||
Operation and support | Formation of documentation | Creation of inappropriate documents, problems in the approval and approval of the system of reception and transmission system | Documentation procedure. The procedure for approval of the act of reception and transmission system |
Extra education |
The working groups analyze the comments and prepare a revised version of the document within 3 days. The corrected document and the report is sent to the coordinating person to express their assessment of the correctness of the corrections made within 3 days. For each of the comments, it is necessary to impose a resolution “accept” or “reject” (with explanation of the reasons). If necessary, group leaders discuss comments and possible solutions with the authors of the comments. If it is impossible to adopt a resolution at the group level, the team leader escalates decision making on the comment to the level of the project managers. Project leaders make decisions on comments not agreed at the group level.
Approval Procedure
After the final preparation of the document, an e-mail notification is sent about the time the document was submitted for approval and its location in the project library.
A package of documents is formed, consisting of two electronic copies of documents on a CD and sheets that are signed (cover and approval sheet for each document to be approved). Two identical packages of documents are intended for the customer and the performer.
The next day, at the agreed time, a package of documents is delivered to the office of the approver. Documents approved by the Criminal Code are printed in full (not just subscription lists).
Approvers after receiving the notice, get acquainted with the package of documents in detail. After review and approval, the approver signs the document.
After that, the document is approved. Signed sheets and the corresponding electronic versions of the documents are approved versions of the project.
Quality assurance is the process of carrying out planned systematic quality operations that ensure the fulfillment of all the stipulated processes necessary for the project to meet the established quality requirements [23]. The quality assurance function can be performed by the project team , the executive organization’s management, the customer or the sponsor, other project participants. To control the quality of the project, audits are carried out, the purpose of which is to determine whether the quality of the project complies with the standards established in the quality plan.
The quality assurance process includes methods for continually improving the quality of future projects. The knowledge and experience in quality assurance accumulated in the current project should be used in the preparation of quality plans for subsequent projects.
To ensure the quality assessment process of a project, at the planning stage, quality checklists are developed - tables with instructions for the reviewer. Checklist items should be significant enough, because if the checklist is overloaded, it will not be used (see Table 8.4). Quality checklists are quality metrics that are defined for each project phase based on customer expectations; these metrics are assigned their status: critical, serious, important. The inclusion of unimportant metrics in the quality checklists is undesirable, since otherwise this list will not be used. The advantage of its use is simplicity; even in small projects, this tool does not require large expenditures of resources and time, while using the quality checklist you can track down at the work execution stage, which was not fulfilled according to customer requirements [11].
Table 8.4. Sample quality checklists
Project stage | Expected Result | Type of | Yes | Not |
Adjustment Settings | The percentage of settings that correspond to the description in the documentation (permissible error of 3%) | Critical | ||
Determining environmental requirements | List of requirements | Critical | ||
Infrastructure setup | Settings List | Critical | ||
Development of functional characteristics | Number of errors encountered during operation. Percentage of errors during operation | Critical | ||
Определение параметров разработки и плана тестирования | Список параметров разработ-ки.План тестирования.Про- цент исходов, не учтенных в плане тестирования | Критичный | ||
Анализ проекта | Наличие протоколов по анализу результатов каждой фазы проекта | Серьезный | ||
Управление изменениями | Документирование всех запро-сов на изменение в соответствии с принятой формой и их сохранение в единой базе | Критичный |
Пояснения к заполнению формы контрольных списков
Данные о результатах контроля передаются исполняющей организации для использования в процессе обеспечения качества, для повторной оценки и анализа стандартов качества на последующих фазах ЖЦ ИС. Пример формы представления результатов контроля качества приведен в табл. 8.5.
Table 8.5. Форма представления результатов контроля качества
№ п.п. | Объект контроля качества | Дата замечания | Замечание | Автор замечания |
На рис.8.1 приведено графическое изображение процедуры разработки контрольных списков качества.
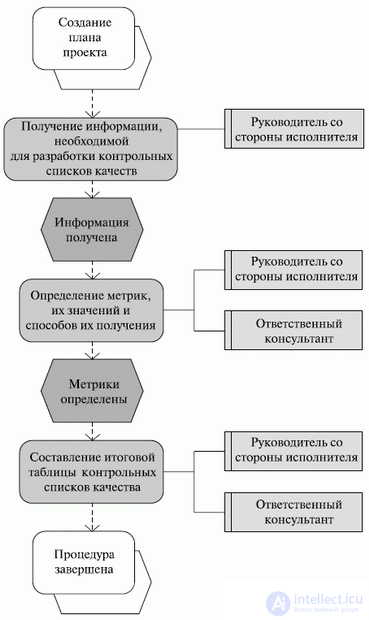
Fig. 8.1. Процедура разработки контрольных списков (графическое изображение)
Для выполнения операций по обеспечению (оценке) качества используют аудит . Аудит качества - независимая экспертная оценка, определяющая, насколько операции проекта соответствуют установленным в рамках проекта или организации правилам, процессам и процедурам. Целью аудита качества является выявление неэффективных и экономически не оправданных правил, процессов и процедур, используемых в проекте. Количество и сроки плановых проектных аудитов могут определяться основными этапами проекта или ключевыми событиями. Внеплановые аудиты проводятся по запросам заказчика, руководителей департаментов и отделов. Аудиты качества проводятся на основе критериев, каждый из которых является следствием требований нормативной документации системы менеджмента качества (требование ISO 9000 ) и системы управления проектами (PMBOK). Схема проведения внутреннего аудита качества проекта может выглядеть следующим образом:
Ниже приведен шаблон для регистрации списка отклонений и описание процедуры обеспечения качества (табл. 8.6).
Table 8.6. Шаблон регистрации отклонений
№отклонения | Дата выявления | Название работы | Описаниеотклонения | Статус отклонения | Предпринятые действия |
[номер по порядку в таблице] | [дата совещания, на котором выявлено отклонение] | [название работы, в которой выявлено отклонение результатов от требований заказчика] | [описание возникшего отклонения] | [незначит .- работа будет принята несмотря на выявленное отклонение | [отложено - работа будет принята несмотря на выявленное отклонение, поэтому нет необходимости предпринимать какие-либо действия |
серьезное - отклонение необходимо устранить, чтобы качество проекта соответствовало заданному уровню | в работе - отклонение передано в рассмотрение в процедуре управления проблемами, ответ ожидается | ||||
критическое - работа полностью не соответствует требованиям заказчика] | исправлено - отклонение исправлено и работы завершены] |
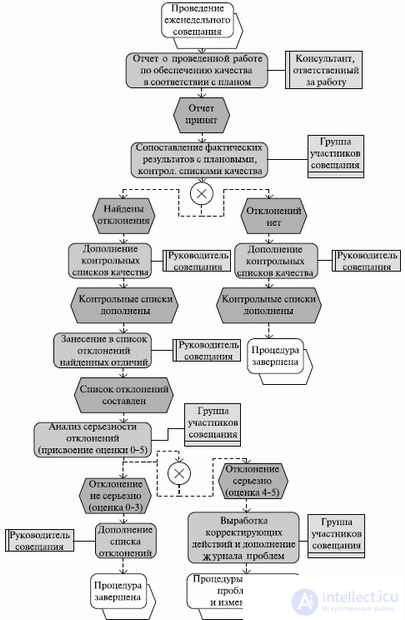
Fig. 8.2. Графическое описание процедуры управления качеством
Comments
To leave a comment
software project management
Terms: software project management