Lecture
In order for project communications to most effectively accomplish the tasks facing the project, it is necessary to clearly formulate a communication strategy in the planning phase of the project. As was shown earlier, the most important element of communication planning is the identification of recipients of information, then you should take care of planning the content of informational messages, which can vary considerably depending on the addressee. Then there is the choice of the communication channel and the definition of the sender. For the actual implementation of communications, you must always implement feedback , allowing us to adjust our actions in the future.
Regarding the content, any message on the project should include the following information.
1. Satisfying the needs of project participants to understand. Project participants should be able to obtain objective, complete and consistent information on the goals and objectives of the project and be able to form their own rational opinion about the project.
2. Satisfying the needs of project participants to feel. Stakeholders should clearly understand what procedures are provided for organizing their participation in project decisions, whether there are feedback channels, how they can be involved in the implementation of the most significant part of the project.
3. Satisfying the needs of project participants to act. Employees should be informed what means,
methods, tools are provided for their quick adaptation in the new organizational and functional environment of the organization's business.
The typical structure of a communication strategy includes the following sections.
1. Goals and objectives of informing project participants. For example:
Within the framework of the implemented strategy, information is not limited solely to providing employees with the necessary information about the project. The objectives of informing are aimed at increasing the loyalty of the company's personnel to the project, which serves to achieve the ultimate goal of change management - ensuring a smooth transition to a new business standard. The process of informing has three main objectives:
1. providing the target audience with information about the goals, objectives and results of the project:
§ inform the company employees about the project, its importance and benefits;
§ to ensure the availability, correctness and timeliness of receiving information about the project;
§ to maintain interest in the project at all phases of its implementation;
2. providing the target audience with information about the awareness of the project team about the upcoming changes in the functional environment and organizational structure of the company, and about the problems associated with them:
§ to ensure timely receipt of information about upcoming changes by target audiences;
§ to form the image of the project as an open, transparent and accessible initiative;
§ to collect information on the expectations / concerns of business experts about the upcoming changes;
3. providing the target audience with information on plans for the transition to new processes, responsibilities, methods of work:
§ to form an image of the project as an initiative, ready to support feedback , answer questions and help solve future problems;
§ to ensure that end users are informed in advance of upcoming change management activities;
2. Roles and responsibilities
Identification of specific persons responsible for project communications and their place in the organizational structure of the project.
3. Target audience
Based on the informational objectives described above, it is advisable to identify three target groups to which the actions described in the communication plan will be directed. Differences between the selected groups, characterized by the degree of responsibility / participation in the project, the hierarchy of positions within the company, and consequently, loyalty to the results of the project, determine the use of several channels and information measures for each of them.
1. Business experts
As a rule, they are heads or leading experts of line units, have full information about existing business processes in a specific area, and participate in the coordination of a list of process changes.
2. Responsible for the transformations (1st and 2nd level) The first level is represented by employees from among the leaders
directorates and departments that are the main point of contact between the change management team and the network responsible for implementation. The level of their awareness and active participation in the change management process is critical for project implementation.
The second level is represented by staff at the level of department heads who are responsible for implementing change management measures at the local level, as they are the link between the network responsible for transformation and the end users
Business experts may be among those responsible for the transformation.
3. End users
Employees of the company who subsequently will deal with new processes and system in their daily work. The objectives of informing are primarily aimed at increasing the level of acceptance of the system by this particular target audience.
4. Channels of communication
It is recommended to list the channels of project communications in the context of the categories reflected in the template (see Table 12.1).
Table 12.1. Project communication plan template
Title | Description | Frequency | The target audience | Responsible and regulations |
. | ||||
. |
Communication channels can include both standard means of communication (telephone, e-mail) and more specific ones (group meetings, field seminars, question and answer sessions); in addition, one should not lose sight of the communication channels that operate on the principle of pull, such as Internet portals, knowledge bases, etc. (see fig. 12.1).
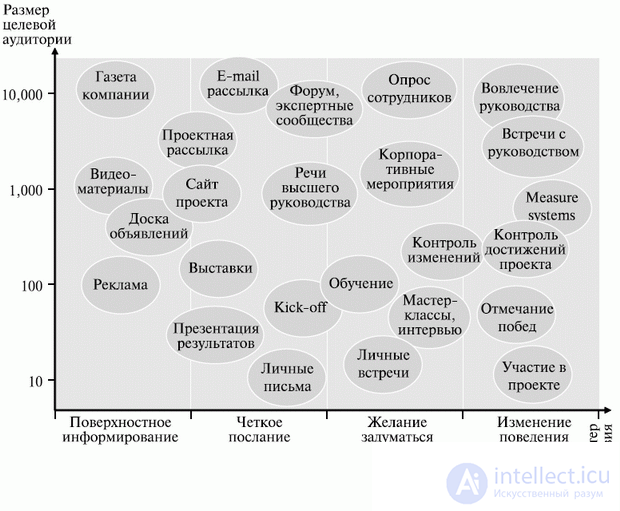
Fig. 12.1. Communication channels and their impact
To identify the effectiveness of existing formal communication channels, below is a list of recommended questions [5].
1. How quickly and how often are official company management decisions broadcast through these communication channels?
2. Which stakeholders can be informed through this channel?
3. How applicable and effective is this communication channel : is there a person in charge, is it possible to use it for internal and external communication?
4. How is this communication channel evaluated?
5. How does this channel meet modern information needs, does it have an interface for interacting with new information and communication technologies?
To identify the most effective informal communication channels it is proposed to use the following list of questions.
Thus, the communication channels form 3 groups: formal, project-specific and informal.
The communication matrix (see Table 12.2) horizontally lists all communication channels grouped into 3 categories, which are mentioned above, and all project participants are vertically listed. At the intersection of the corresponding rows and columns, it is necessary to reflect what kind of status a particular communication channel has: the main, additional or specific. Thus, looking through the lines, one can estimate the degree of duplication of information - interaction with the participants through several communication channels. Each group of participants must be informed at least once through a formal channel, at least once through a specific and once through an informal communication channel of the project. The degree of duplication should be correlated with the impact analysis (see relevant section) of the project participants: if the project participant is an “agent”, the degree of duplication should be as high as possible.
Table 12.2. Example of communication matrix
Legend | Formal | Specific | Informal | |||||||||||
0 The main communication channel? Additional communication channel | Meetings | the Internet | Newsgroups | Bulletins | Info Sessions | Project Newsletter | Training | Booths issues | Coaching | Communication in the lobby | Telephone conversations | elevatorpitch | ||
Project participants | Sales department | |||||||||||||
Manual | ||||||||||||||
middle managers | ||||||||||||||
Production | ||||||||||||||
ny departments | ||||||||||||||
Suppliers | ||||||||||||||
Customers | ||||||||||||||
Unions | ||||||||||||||
Analyzing the communication matrix vertically, one can determine the strategic importance of a certain communication channel: if it turns out to be the main communication channel for a large number of groups of participants, then it should be considered as a significant project asset.
1. Organization of project feedback
The need to implement a control loop, including in communications, can be justified as follows.
Effective informing is possible only if the project communications are bidirectional - there is a direct and reverse communication channel. The last one provides control of the first.
Monitoring the effectiveness of information channels involves the following aspects:
The process of monitoring the effectiveness of information will be carried out by distributing questionnaires (questionnaire) with a fixed frequency and using the telephone hotline of questions and answers.
The 5 points considered are not an exhaustive list of sections of the communication strategy , but they are the most significant and, as a rule, mandatory for the proper preparation of a communication plan .
Comments
To leave a comment
software project management
Terms: software project management