Lecture
Content
When we have decided on the main roles in the project team, we should proceed to the development of a very useful document called the responsibility matrix. We, dear reader, it is important to realize that during the development of the matrix table, PM fixes a complex not only of the responsibility of the members of the group, but also of their powers. I suggest you understand this topic in more detail.
In the PMBOK manual (fifth edition), the responsibility matrix also has other designations: “matrix diagrams”, “RASI matrix”. In domestic practice, this tool often sounds like a matrix of responsibility distribution. Under the MO in the PMI-manual refers to some table that shows the resources assigned to each work package. It displays the connections between team members and work stages.
To fill the MO traditionally used technique RACI. This is an abbreviated name, formed by the first letters of the words: "Performer" (Responsible), "Responsible" (Accountable), "Consultant" (Consult before doing), "Observer" (Inform after doing).
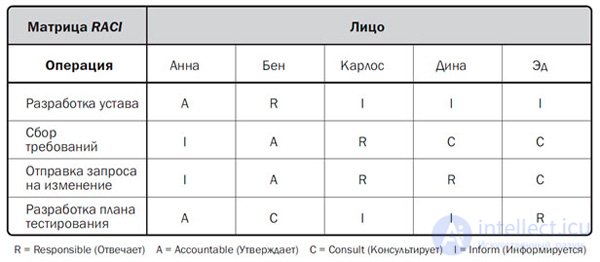
Depending on the scale of the project, PMBOK allows the use of MO at various levels with varying degrees of elaboration of the responsibility of the members of the working group. If we consider high-level MOs, then groups and subdivisions of the team are involved on the one hand, and large components of the SRI, on the other, to build the matrix. On the contrary, low level MOs “descend” to the detailing of the distribution of responsibility of specific team members down to the level of operations.
Russian design practice is often distinguished by the expansion of responsibility options, including the inclusion of competences in the MO. This brings imbalance into the matrix. An illustration of this approach can be seen below.
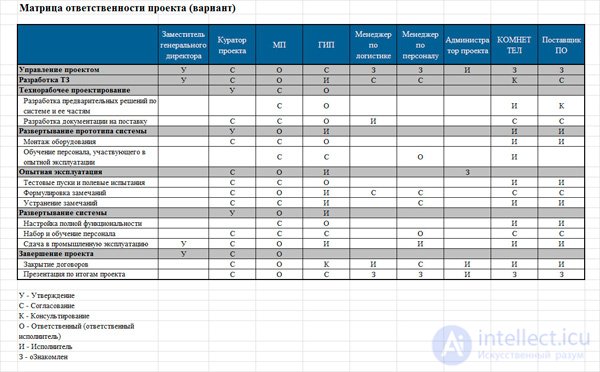
The previous example clearly demonstrates the blur situation focuses on responsibility. How to avoid a similar situation? Recall, colleagues, a subsection devoted to the tasks of management. In it, we sorted out an important category of management - “responsibility”. Then we established that the responsibility of a resource implies its right to accept and the duty to perform the task without referring to any obstacles. Let me remind you an example of a Krasnoyarsk hunter who took on the task of delivering squirrels to the skin of a skin broken in the eye, but under the condition that their number is no more than 45 instead of 100. That was his rule: to take only what he is capable of doing.
A responsible resource for a unique project task is the manager. At the time of planning a project, its manager is obliged to ensure the decomposition of the result into subtasks, the consistent implementation of which automatically leads to the solution of a key task. It is advisable to perform such decomposition collectively, involving the members of the project management team to work by brainstorming. Its results should be a hierarchical structure of work, a plan for milestones.
Typically, the composition of the wording of the elements of the table corresponds to the functional doctrine of management:
Much more effective is obtained if we apply the methods of control from tasks. I offer you an example of such a decomposition.
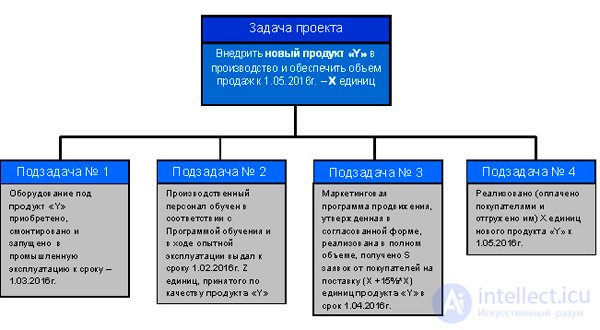
This example is indicative. Naturally, the manager is responsible for the top-level task. And it is obvious that project management establishes the division of responsibility for decomposed subtasks between team members. Thus, the logic of creating such a table as a liability matrix naturally ripens. Its construction begins with the formulation of tasks.
Personally, I am impressed by the laconic approach to the use of the matrix model, because obligation as a synonym for the subject of our research is also a human condition: either it exists or it does not exist. And most importantly, such a state cannot be distributed among several people. For management purposes, it can only have a single carrier. Otherwise, the responsibility in one degree or another is lost. Our decomposition example dictates the following matrix form.
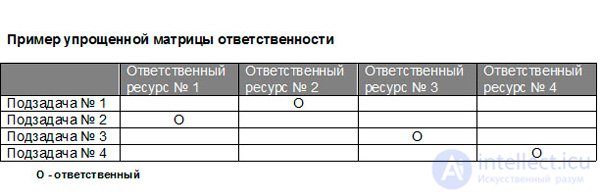
I believe that especially beginners in PM need to learn how to fill in a simplified matrix and ensure its operability and control, and then move on to more complex configurations, while avoiding typical errors that sometimes occur. Regardless of the number of liability options (the letters used in the table to fill it), you should be guided by certain filling rules. Building a project MO requires compliance with important rules:
If you do not take into account the special rules outlined above, it is easy to make mistakes, which then worsen the possibilities of control, and reduce the effectiveness of project management. To avoid such a situation, it is better to immediately control the possibility of making a mistake while working on the MoD. The construction of MO may be accompanied by typical errors:
In this article, dear colleagues, we, together with you, addressed the issue of the concept, essence and content of the responsibility matrix as an essential element of project planning and implementation. Presents traditional methodology and examples of MO construction. Declared the author's position on the benefits of a more categorical approach to responsibility and its distribution. Clarified the rules for the development of MO and related errors.
I am convinced that the project manager, who is guided by the rule “Better less and better”, is more successful. This is also due to the fact that the construction of the MO is implemented in the uniqueness mode. Therefore, I advise each PM to start with simpler forms, gradually complicating the practice of application.
First of all, one person is responsible for everything that happens in the project - the project manager. But, since there are a lot of tasks in the project, and the manager is one, he has to delegate responsibility for certain tasks and groups of tasks to other team members.
The responsibility matrix determines the degree of responsibility of each team member for a particular task, if he has something to do with it.
There can be many degrees of responsibility. For example, RMVOC defines 4 types of liability:
1. Responsible (M) - is fully responsible for the task and has the right to make decisions on how to implement it
2. The contractor (I) - performs the task, but in the general case, is not responsible for the method of its solution.
3. Consultant (C) - oversees the progress of the task and provides its views on the way and quality of implementation. Responsible, if you do not notice a clear blooper.
4. Observer (H) is the same as the consultant, but is not responsible.
The responsibility matrix looks like this:
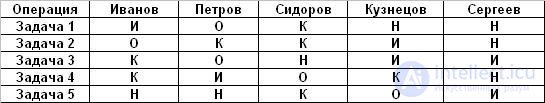
Please note that for each task the role of "Responsible" exists necessarily and in a single copy, in accordance with the saying "If more than one person is responsible for something, there is no one to blame." Other roles may not be (with the exception of the "Contractor", of course), or they can be duplicated.
The responsibility matrix explicitly establishes the degree of responsibility of each project participant for certain types of work, so it is very useful to compile it and familiarize all project participants with it before the execution stage. If someone disagrees with the role assigned to him at the beginning of the execution of works, this is, of course, not very good, but to find out at the time of the start is much better than before the finish.
Another good feature of the responsibility matrix is that it allows you to balance the responsibility for the project between its participants. If all responsibility in the project is concentrated in the hands of one or two people, then in the event of their absence, the work on the project will stall - the rest, after all, have no right to make decisions.
Comments
To leave a comment
software project management
Terms: software project management