Lecture
1. Organization of multiprocessor systems (common bus)
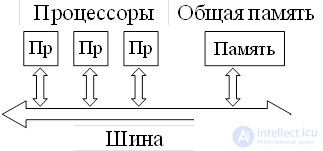
Multiprocessor system with a common bus To prevent simultaneous access of several processors to memory, arbitration schemes are used to ensure that the bus has monopoly ownership of the device that captures it.
The disadvantage is that even a small increase in the number of devices on the bus (4-5) very quickly makes it a bottleneck, causing significant delays in exchanges with memory and a catastrophic drop in system performance in general
Dignity : simplicity and low cost design
2. Organization of multiprocessor systems (matrix switch)
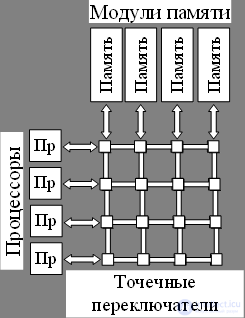
The matrix switch allows you to divide the memory into independent modules and ensure that different processors can access different modules at the same time. At the intersection of the lines are located elementary point switches that allow or prohibit the transfer of information between processors and memory modules.
Disadvantage : a large amount of necessary equipment, since nxn elementary switches are required for communication between n processors with n memory modules Multiprocessor system with a matrix switch
Advantages : the possibility of simultaneous operation of processors with different memory modules
3. Organization of multiprocessor systems Multiprocessor system with omega network 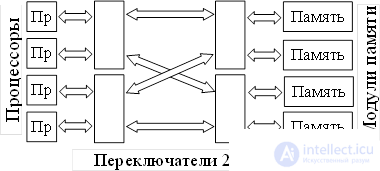
Multiprocessor system with omega network Using cascade switches
Each switch used can connect either of its two inputs to any of its two outputs.
This property and the used switching circuit allow any processor of the computing system to access any memory module. In general, to connect n processors with n memory modules you need log 2 n casc
Disadvantages - delays
Comments
To leave a comment
Highly loaded projects. Theory of parallel computing. Supercomputers. Distributed systems
Terms: Highly loaded projects. Theory of parallel computing. Supercomputers. Distributed systems