Lecture
A data center (from the English data center ), or a data processing center ( data processing center ), is a specialized building for hosting (hosting) server and network equipment and connecting subscribers to Internet channels.
The data center performs the functions of processing, storing and distributing information, as a rule, in the interests of corporate clients - it is focused on solving business problems by providing information services. Consolidation of computational resources and data storage in the data center reduces the total cost of ownership of the IT infrastructure due to the possibility of efficient use of technical means, for example, the redistribution of workloads, as well as by reducing administrative costs.
Data centers are usually located within or in close proximity to a communication center or point of presence of one or more communication operators. The quality and bandwidth of channels affect the level of services provided, since the main criterion for assessing the quality of any data center is server availability time (uptime).
8 designing cxd
The history of the development of data centers begins with a huge computer rooms since the birth of the computer industry. Then the computer systems were more difficult to manage and required to provide special conditions for work. Since they occupied a lot of space and required a lot of wires to connect various components, standard server racks, raised floors and cable channels (laid on the ceiling or under the raised floor) were used in computer rooms. In addition, such systems consumed a lot of energy and needed constant cooling so that the equipment would not overheat. Security was equally important - the equipment was very expensive and was often used for military needs. Therefore, the basic design principles for access control in the server were developed.
In the period of rapid development of the computer industry, and especially in the 1980s, computers are beginning to be used everywhere, without worrying about the operational requirements. But with the development of the IT industry, companies are beginning to pay more attention to the control of IT resources. With the invention of client-server architecture in the 1990s, microcomputers, now called servers, began to occupy places in the old server ones. The availability of low-cost network equipment along with new standards for network cables made it possible to use hierarchical design, so the servers moved to separate rooms. The term "data center", in those days applicable to specially designed server, began to gain popularity and became more recognizable.
The boom of data centers occurs in the period 1995-2000. Companies needed a stable and high-speed Internet connection and uninterrupted equipment to deploy systems and establish their presence on the network. To place equipment capable of coping with these tasks was a matter of overwhelmingly for most small companies. Then began the construction of separate large premises that can provide the business with all the necessary set of solutions for the placement of computer systems and their operation. New technologies began to develop to address the scale and operational requirements of such large systems.
Nowadays, the design and construction of data centers is a well-studied area. Formed standards that establish requirements for the design of data centers. For example, experts Telecommunications Industry Association have made a great contribution to the formation of standards for data centers. But still there are still many unsolved problems in the methods of work, as well as the construction of data centers that do not harm the environment, etc.
Data centers are costly both during the construction phase and during the maintenance process in order to maintain work at the proper level. For example, the Amazon.com data center in Oregon, with an area of 10,800 m², is estimated at $ 100 million. [one]
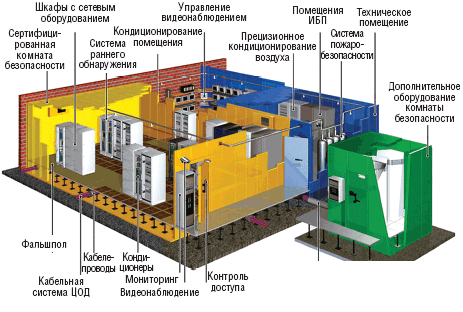
A typical data center consists of:
Engineering infrastructure includes: air conditioning to maintain the temperature and humidity level in the given parameters; uninterrupted power supply for autonomous operation of the data center in cases of disconnection of central sources of electricity; security and fire alarms and gas fire extinguishing system; Remote IP control, power management and access control systems.
Some data centers offer customers additional services for the use of equipment for automatically avoiding various types of attacks. Teams of qualified specialists around the clock monitor all servers. It should be noted that data center services are very different in price and quantity of services. To ensure the safety of data backup systems are used. To prevent data theft, data centers use various systems to restrict physical access, video surveillance systems. In corporate (departmental) data centers are usually concentrated most of the servers of the organization. The equipment is mounted in specialized racks and cabinets. As a rule, only rack-mounted equipment, that is, standard-sized enclosures adapted for rack-mounting, is accepted into a data center. Computers in desktop cases are inconvenient for data centers and are rarely located in them.
In a number of countries, there are standards for equipping data center premises that allow an objective assessment of the ability of a data center to provide a particular level of service. For example, in the United States adopted the American (ANSI) standard TIA-942, which carries recommendations for the creation of data centers, and dividing data centers into types according to the degree of reliability. Although there is no such standard in Russia yet, data centers are equipped according to the requirements for communication facilities, and also are oriented to the requirements of TIA-942 and use additional documentation from the Uptime Institute and the State Standards 34 series.
In fact, the TIA-942 is perceived throughout the world as a single standard for data centers, however, it should be noted that it has not been updated for a long time and it is rather difficult to apply in the Russian context. At the same time, the BICSI 002 2010 Data Center Design and Implementation Best Practices standard, which was introduced in 2010 and updated in 2011, is actively developing. According to the creators of the standard, the BICSI 002 2010 standard, which was created by more than 150 experts, complements the existing TIA standards, CENELEC and ISO / IEC for data centers. "
Each of the standards, as a rule, has its own internal classification of data centers by a combination of their parameters.
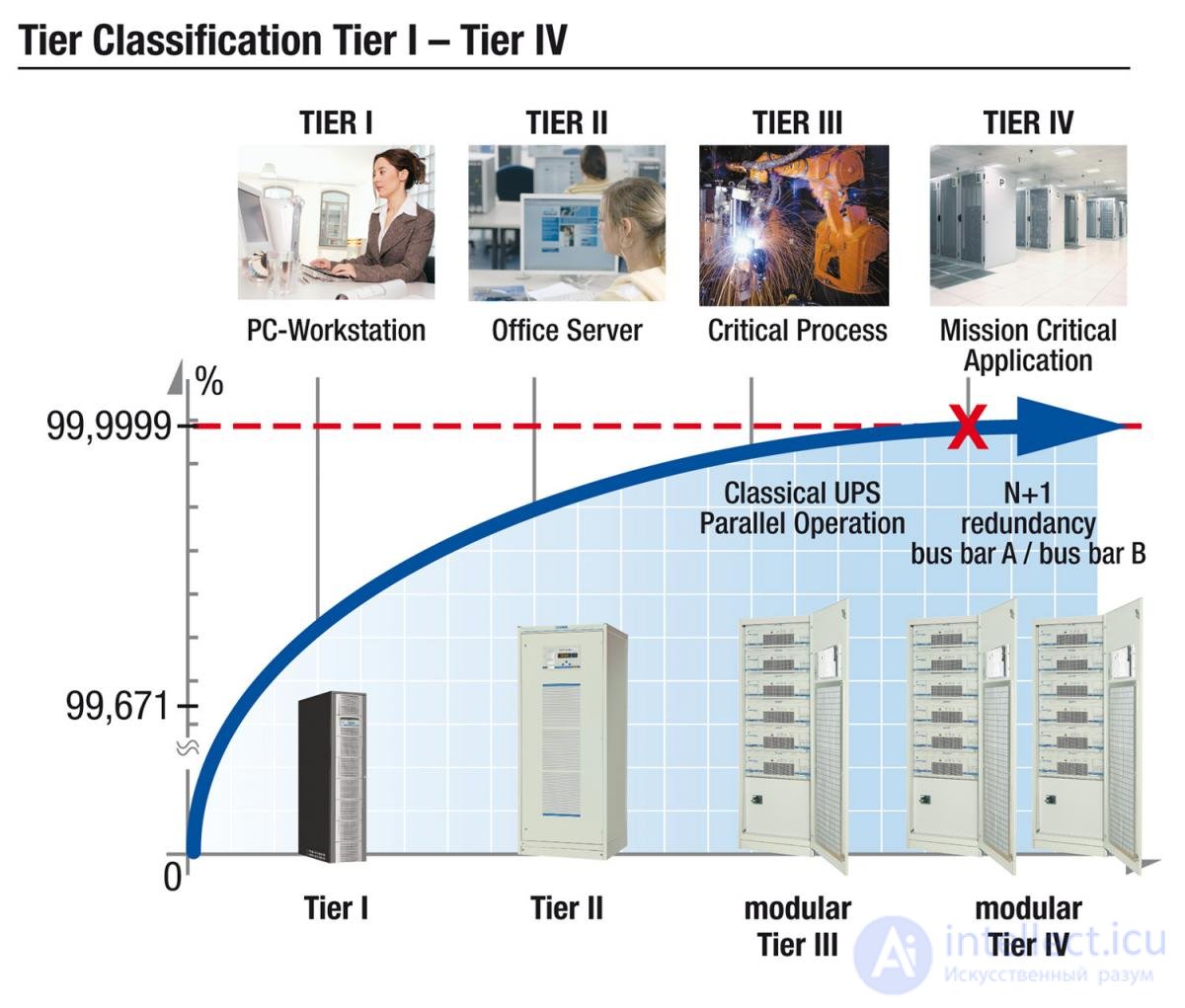
The main indicator of data center operation is fault tolerance; Also important is the cost of operation, energy consumption and temperature control.
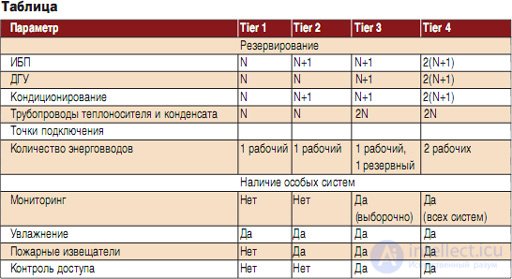
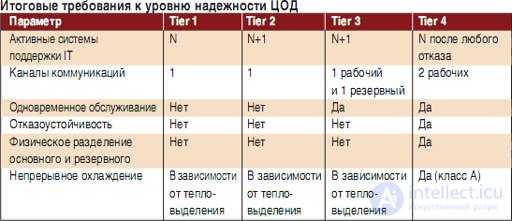
For example, the TIA-942 standard assumes four levels of reliability of data centers:
Data centers by type of use are divided into corporate, designed to serve a particular company, and commercial (outsourcing), providing services to everyone. Also share provider-independent and provider-independent data centers. The former serve to support the activities of telecommunications operators, the latter can be used by different companies in accordance with their needs.
Data center communications are most often based on networks using the IP protocol. The data center contains several routers and switches that control traffic between servers and the “outside world”. For reliability, the data center is sometimes connected to the Internet using a variety of external channels from different providers.
Some servers in the data center are used for basic Internet and Intranet services that are used internally: mail servers, proxy servers, DNS servers, etc.
Network security level is supported by firewalls, VPN gateways, IDS systems, etc. Also, traffic monitoring systems and some applications are used.
In recent years, against the backdrop of the global crisis, projects of maximally budgetary “thrash data centers” have developed (eng. Trash - garbage). As a rule, it is a large warehouse or hangar, minimally adapted to accommodate the racks, which according to the TIA-942 classification does not always correspond to even the Tier 1 level. The client is provided with unguaranteed power supply, Internet connection and a place for the rack. If the customer wants to have a guaranteed power supply, he must put his own UPS in the rack. Equipment cooling occurs due to natural air exchange in the room [2] .
The advantage of this service for the client is an extremely low price, amounting to 20-30% of the cost of hosting the server in Tier 2 and Tier 3 data centers. However, it is worth noting that the lack of centralized uninterruptible power supply, air conditioning and fire suppression systems allows using these data centers only as a temporary solution and an extreme measure [2] .
Regardless of what size will be the server or data center, you need to choose a place for it, which will allow to increase it in the future. Usually guided by the following recommendations:
It is not recommended to place a data center near the internal structures of the building, which limit the possible expansion in the future: flight of stairs, lift shafts, etc. It is recommended to use a room without windows under the data center. If windows are provided in the data center, then in accordance with clause 3.4 of the CH 512-78, the data center is recommended to be located on the north or north-east side of the building.
According to paragraph 17.6 of RD 45.120-2000, it is prohibited to place a data processing center under the premises related to water consumption (toilets, showers, etc.).
It is not allowed to have a data center near storage rooms for flammable or aggressive chemical materials (paragraph 4.2 of PPB 01-93).
It is not recommended to place the data center on the upper floors of the building, since They are most susceptible to damage in the event of a fire and can be flooded with roof leaks. Through the data center should not be laid in transit pipelines of building engineering systems.
According to the instructions СН 512-78, it is prohibited to place the data processing center or server in the basement of the building.
It is necessary to avoid close placement of powerful sources of electric and magnetic fields, as well as equipment with increased vibration.
Before proceeding with the design, you need to decide on the concept of the data center, as it should reflect the main IT and business goals of the company. At this stage, you can see the possible risks, non-productive costs and determine plans for the development of the data center.
After creating the concept, you can proceed to the design. Design begins with a pre-project study and ends with budget documentation. The finished data center project includes the following sections:
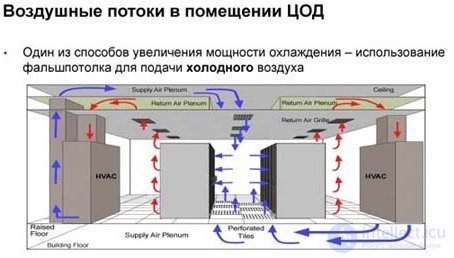
Все эти задачи может решить Группа компаний ТЕРРА СБ обладающая большим опытом в проектировании и строительстве. Мы всегда понимаем потребности наших клиентов и ищем для них самые верные решения, сочетающие в себе баланс цены, качества и высокой производительности. Но основная задача – это увеличение вычислительной плотности наших клиентов с помощью самых современных решений. Заметим, что при проектировании серверных помещений решаются схожие задачи, но в меньшем объёме.
Comments
To leave a comment
Highly loaded projects. Theory of parallel computing. Supercomputers. Distributed systems
Terms: Highly loaded projects. Theory of parallel computing. Supercomputers. Distributed systems