Lecture
Let a double integral be given 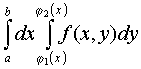 . If the integration domain is D (Fig. 15), given by the inequalities
. If the integration domain is D (Fig. 15), given by the inequalities 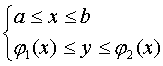 is also correct with respect to the OS axis, i.e. the boundary of the domain D is intersected by the straight line y = c ( c constant) at no more than two points, then the domain D can be given by other inequalities:
is also correct with respect to the OS axis, i.e. the boundary of the domain D is intersected by the straight line y = c ( c constant) at no more than two points, then the domain D can be given by other inequalities:
.
Here α and β are the largest and smallest values of y in the domain D , respectively;
x = 1 ( y ) is the left side of the boundary;
x = ψ 2 ( y ) is the right side of the boundary of the domain D.
Then in the double integral you can change the order of integration:
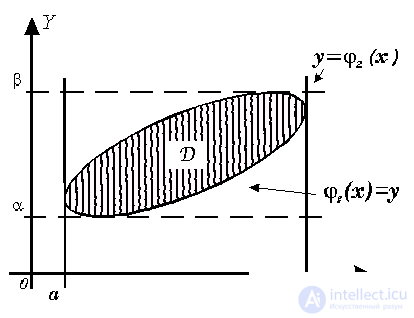
Fig. 15
Comments
To leave a comment
Mathematical analysis. Integral calculus
Terms: Mathematical analysis. Integral calculus