Lecture
If the boundary of the region D is intersected by any straight line x = c ( c - const ) at no more than two points, then the domain D is called regular in the direction of the axis OX . The bounded domain D , correct in the direction of the OX axis, is given by the inequalities:
a ≤ x ≤ b , φ 1 ( x ) ≤ y ≤ φ 2 ( x ) ,
where φ 1 ( x ) , φ 2 ( x ) are functions that are continuous on the interval [ a, b ] .
In this case, the double integral reduces to a double integral 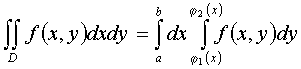 .
.
First, assuming that the integration variable x is constant, we find a definite integral 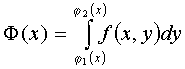 as a function of f ( x ) variable x .
as a function of f ( x ) variable x .
Then we find a definite integral 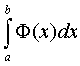 .
.
Comments
To leave a comment
Mathematical analysis. Integral calculus
Terms: Mathematical analysis. Integral calculus